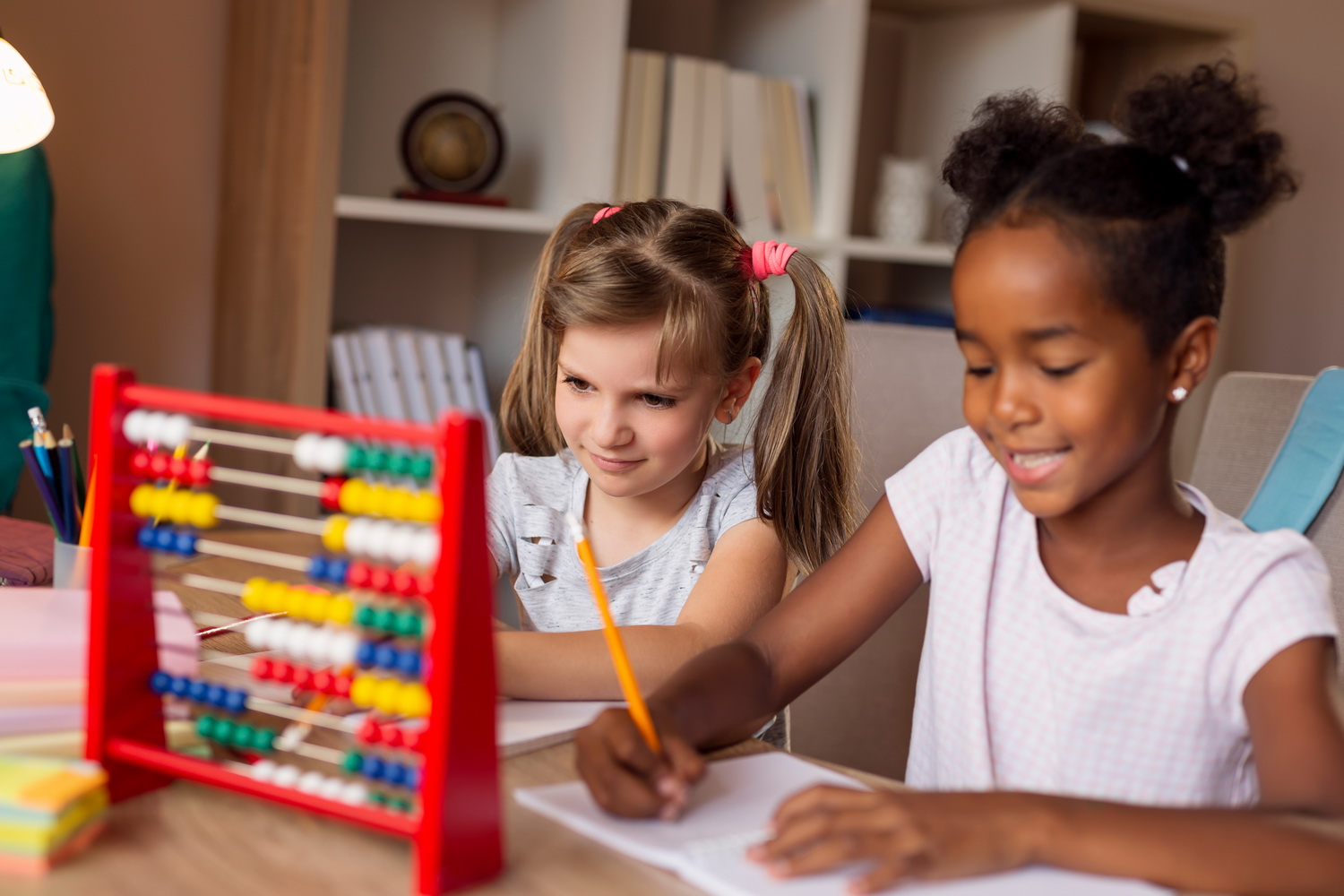
Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-9 - Page 7
149 filtered results
-
From - To
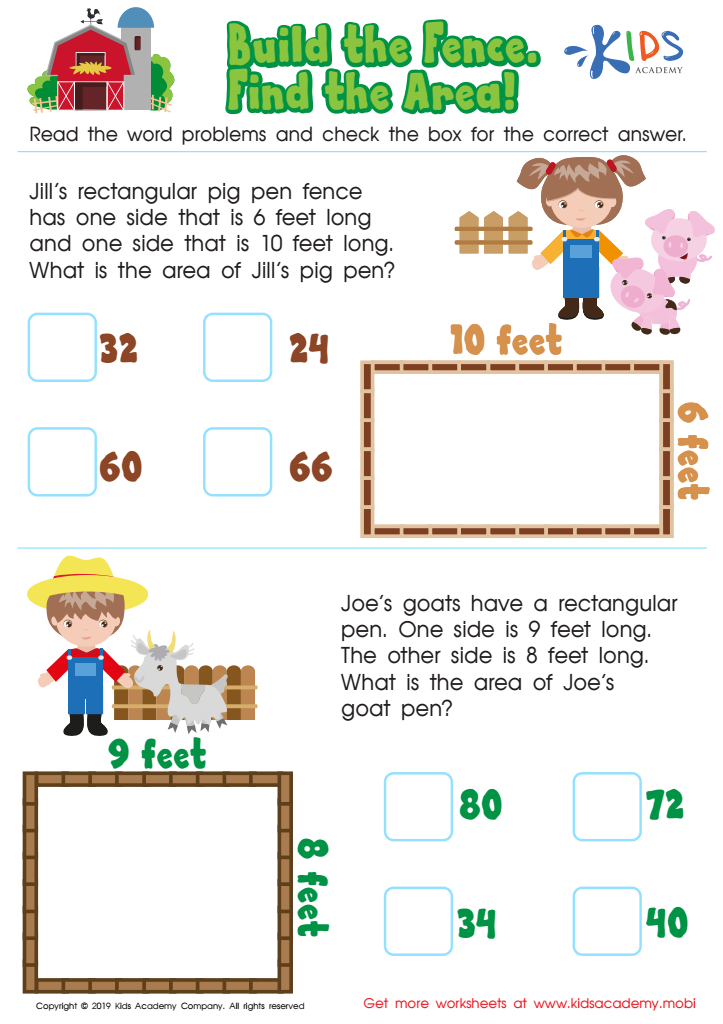

Build the Fence, Find the Area Worksheet
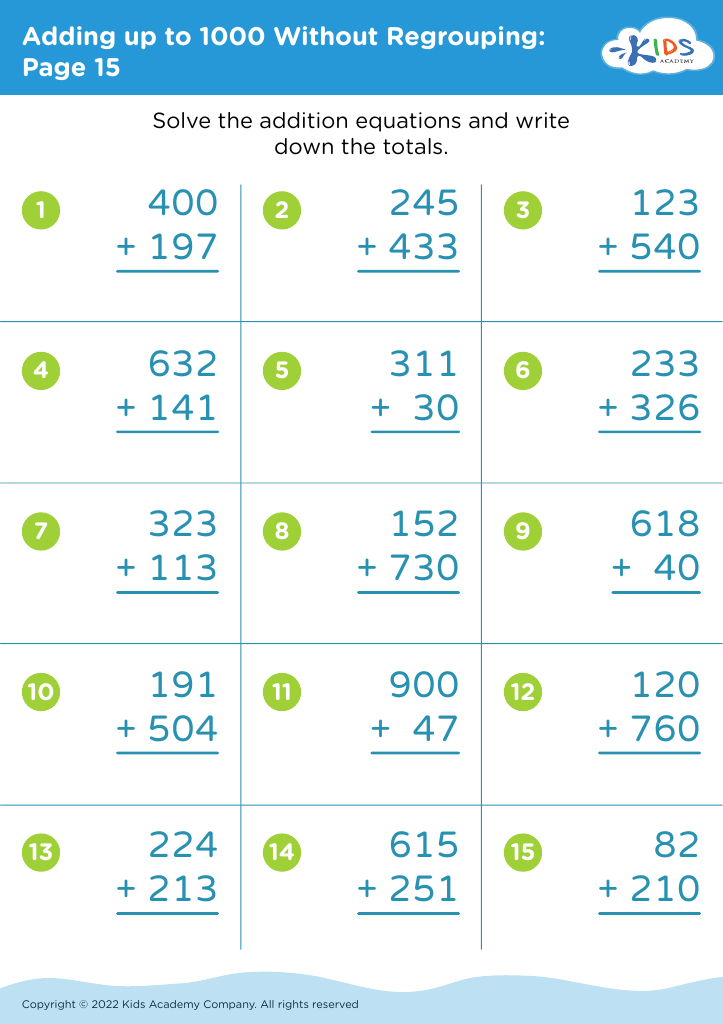
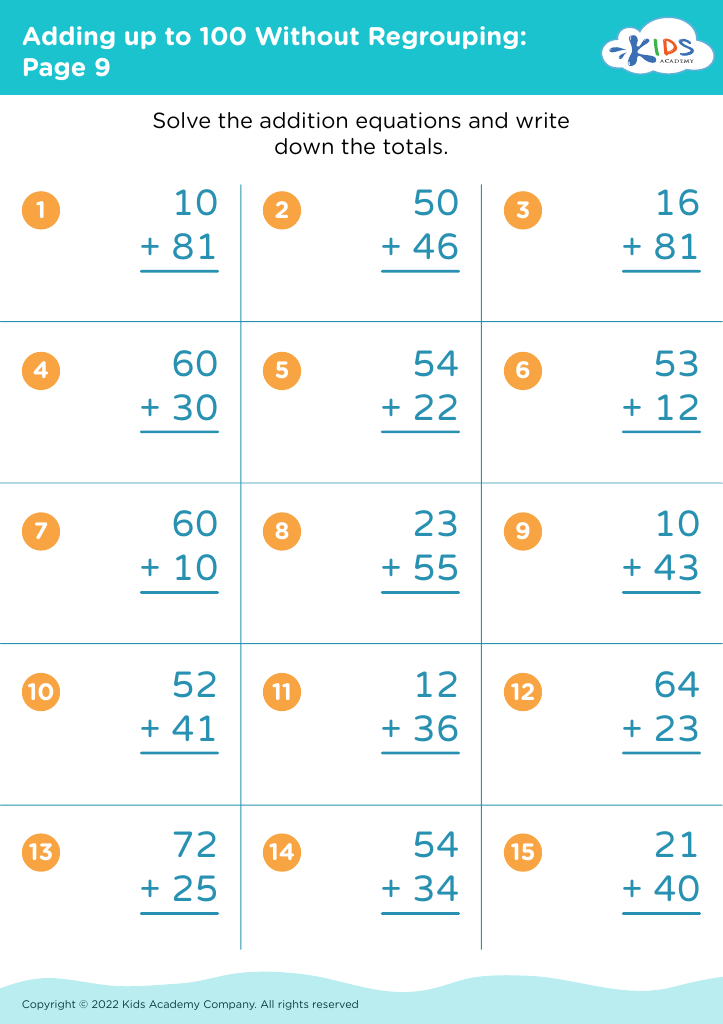
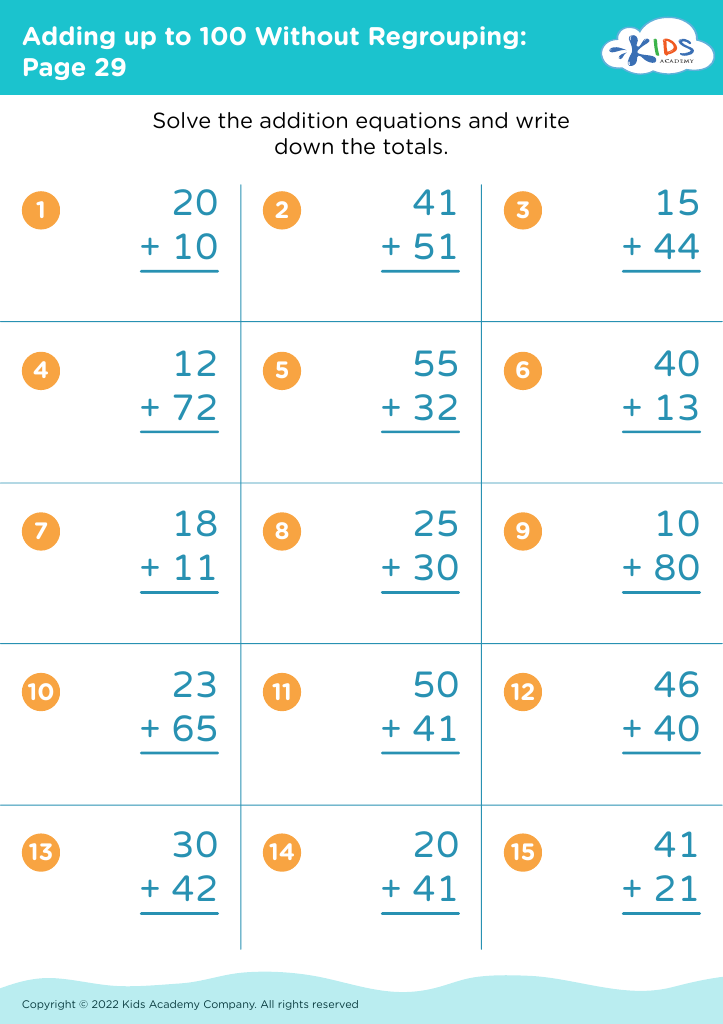
Problem-solving skills are essential for children aged 3-9 as they lay the foundation for critical thinking, adaptability, and resilience in navigating life’s challenges. For parents and teachers, fostering these skills during this formative period is vital for several reasons.
Firstly, problem-solving encourages creativity. Children learn to think outside the box, enabling them to approach tasks and conflicts with innovative solutions. Moreover, effective problem-solving promotes perseverance; when faced with obstacles, children develop resilience by working through difficulties rather than giving up.
Additionally, these skills enhance academic performance. Early exposure to problem-solving in mathematics, science, and everyday situations boosts cognitive abilities, leading to improved reasoning and comprehension in all subjects. This early foundation supports more complex learning later on.
Socially and emotionally, problem-solving skills aid in conflict resolution and decision-making. Children learn to communicate their ideas and listen to others, fostering cooperation and empathy.
In essence, when parents and teachers emphasize the importance of problem-solving for young children, they equip them with crucial tools that foster independence, academic success, and positive social interactions—essential skills for lifelong learning and personal development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students