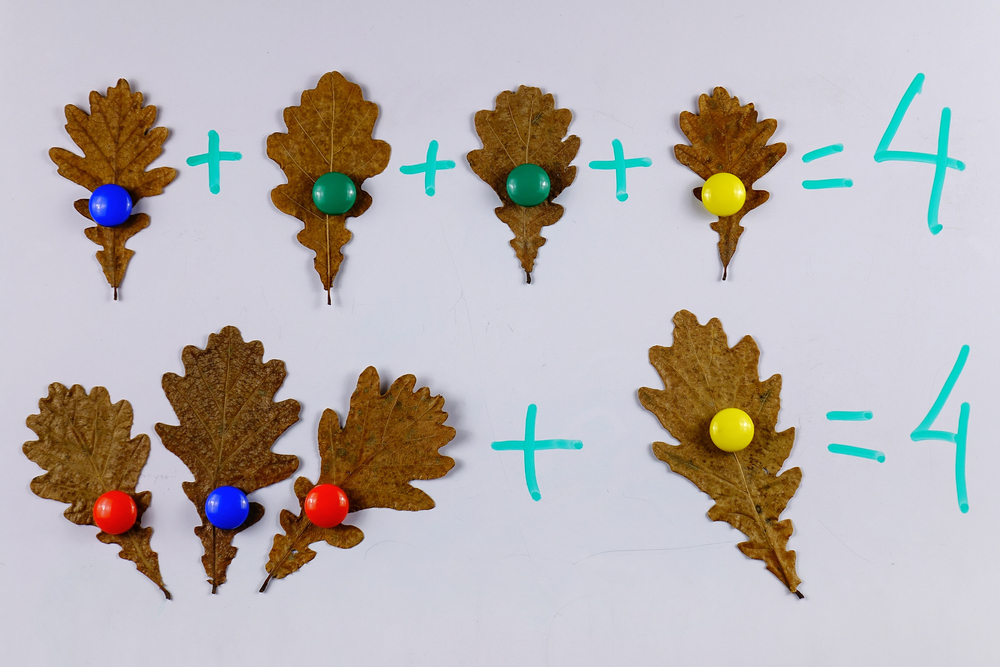
Basic arithmetic is fundamental for young children (ages 3-9), as it establishes a strong foundation for future academic success and everyday life. For parents and teachers, fostering an early interest in math is crucial. Learning arithmetic fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills – vital competencies for all areas of learning, and life in general. It also develops cognitive abilities such as memory, pattern recognition, and logical reasoning.
Introducing basic arithmetic to young children supports their readiness for school and helps to bridge any gaps in learning that may appear later. Math proficiency at an early age can boost a child's confidence, making them more eager to explore advanced concepts as they grow older. A strong base in arithmetic also correlates with success in other subjects like science and engineering, where quantitative skills are equally essential.
Additionally, early math skills are crucial for developing financial literacy from a young age. Understanding basic arithmetic helps children perform everyday tasks such as counting money, telling time, and measuring quantities, all of which are essential life skills.
In sum, parents and teachers should prioritize early arithmetic education to empower children with the quantitative literacy they need for future learning stages and life challenges, fostering a lifelong appreciation and competence in math.