Understanding prepositions Geometry Worksheets for Ages 4-6
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Understanding Prepositions Geometry Worksheets for Ages 4-6" are designed to develop early geometry and spatial awareness skills in young learners. Engaging activities teach children the concepts of "above," "below," "next to," and more, using vibrant and kid-friendly illustrations. Ideal for preschool and kindergarten, these worksheets enhance critical thinking, vocabulary, and comprehension in a fun, interactive way. Teachers and parents can easily integrate these resources into lesson plans or at-home learning routines to support cognitive development and readiness for more advanced math concepts. Empower your child to explore and succeed with our thoughtfully crafted preposition activities!
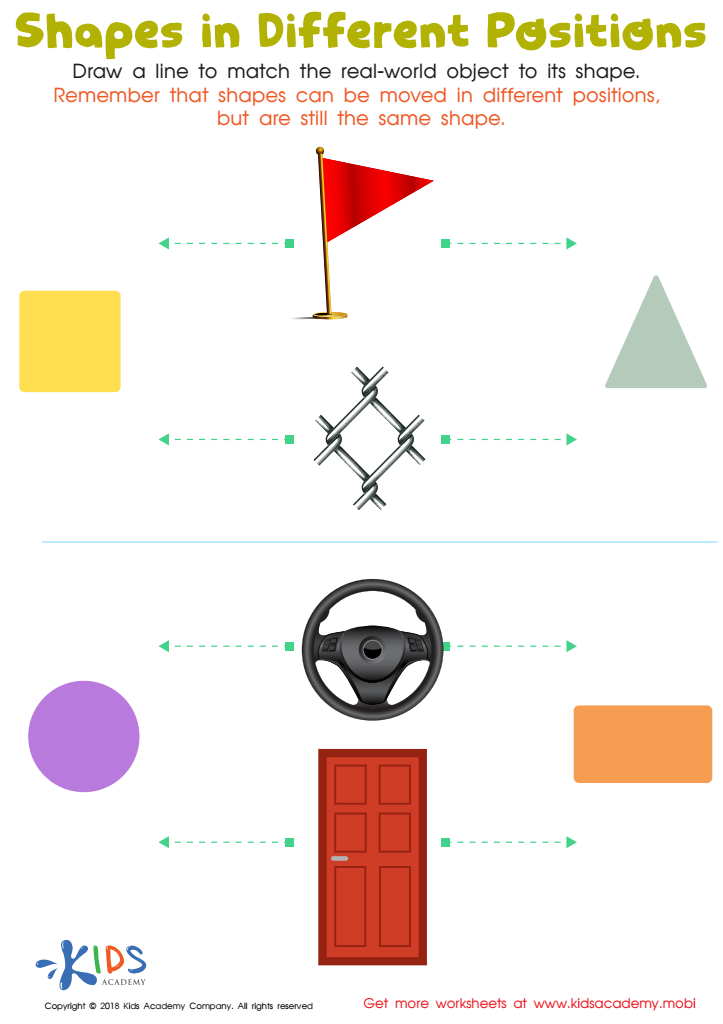

Shapes in Different Positions Worksheet
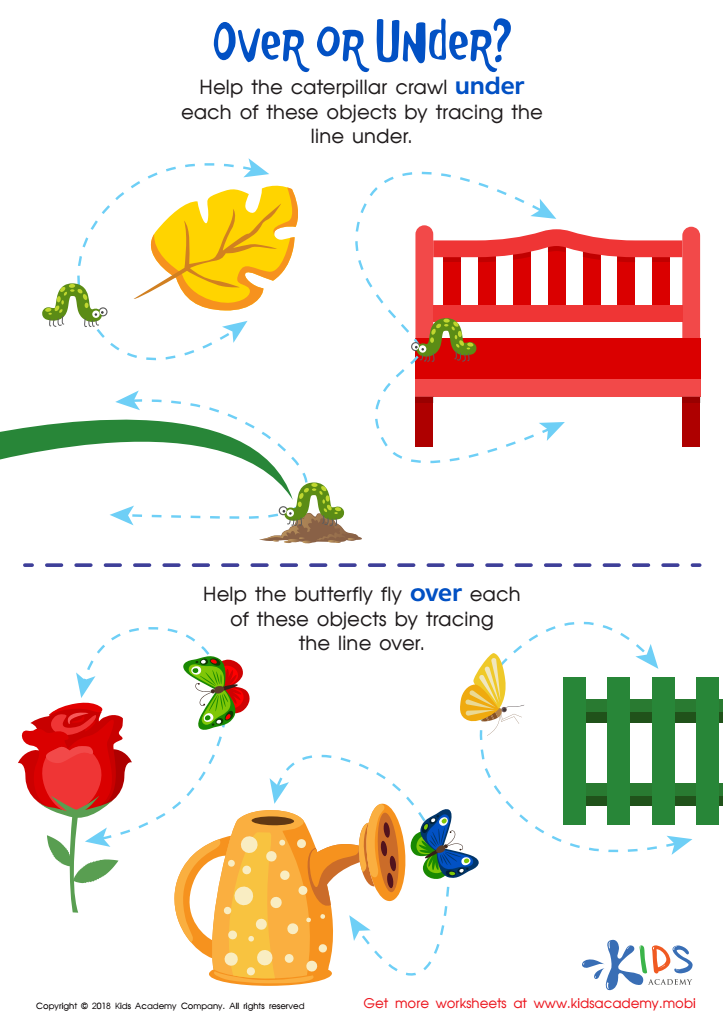

Over or Under? Worksheet


Over or Under Worksheet

In Front or Behind Worksheet
Understanding prepositions and basic geometry concepts is crucial for children ages 4-6 as it lays a foundational framework for their cognitive and linguistic development. Prepositions such as "on," "under," "in," and "beside" help children describe the relationships between objects in their environment, fostering critical thinking and spatial awareness. When children learn prepositions, they become better communicators, able to follow directions and appropriately express their thoughts, which enhances their social and academic interactions.
Geometry, on the other hand, introduces young learners to the properties and relationships of shapes and space. Simple activities like identifying and naming shapes, sorting objects, or constructing basic geometric figures with blocks help develop their problem-solving skills and ability to recognize patterns. These skills are essential for higher-level math comprehension and everyday tasks such as reading maps, organizing their personal space, or understanding the components of a story's setting.
Additionally, early exposure to these concepts promotes a positive attitude towards learning. When children successfully navigate basic geometric principles and prepositions, they experience a sense of accomplishment, which boosts their confidence and encourages a lifelong curiosity and enthusiasm for learning. Therefore, by focusing on these foundational skills, parents and teachers can significantly contribute to a child’s overall intellectual development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students