Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 4-7 - Page 2
26 filtered results
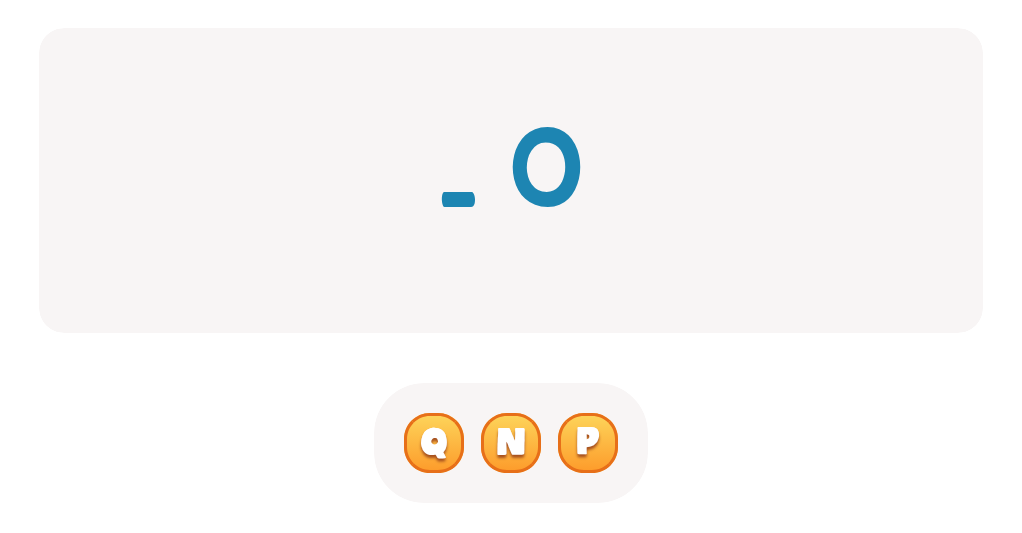
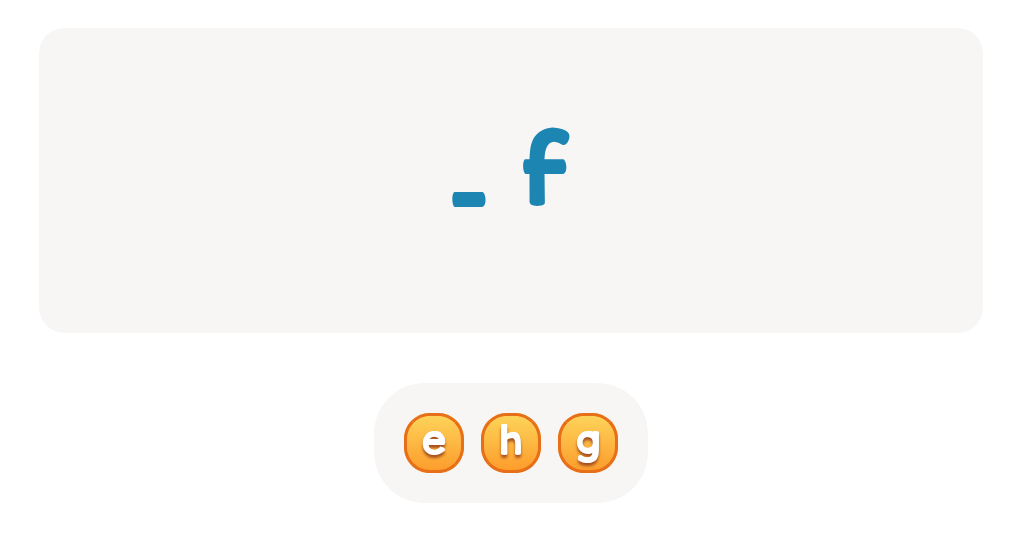
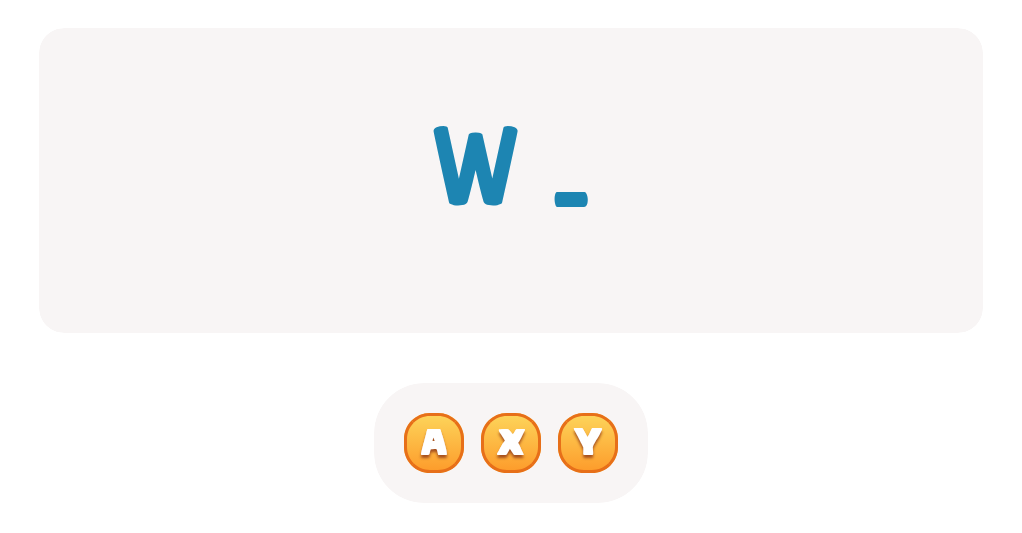
-
From - To


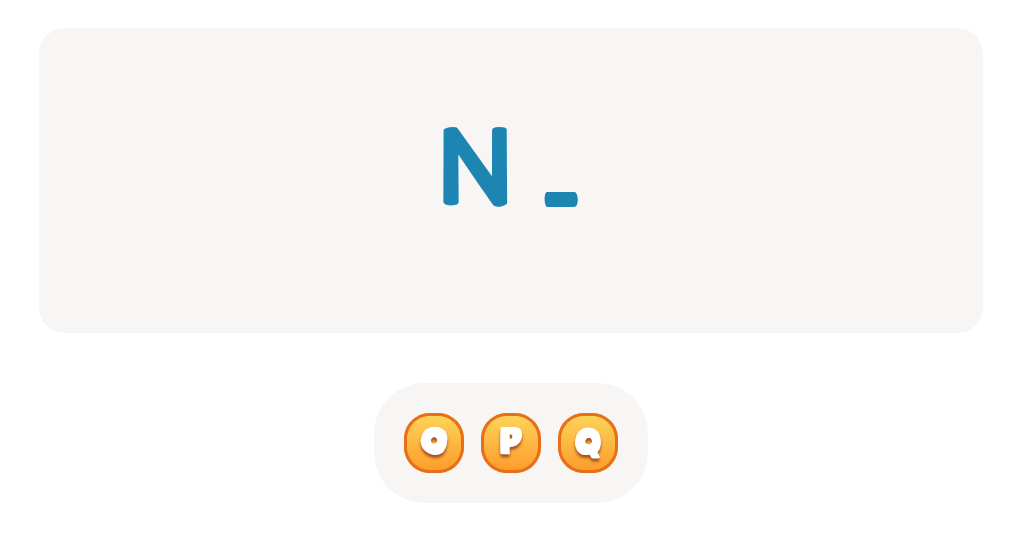
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice for ages 4-7 is crucial for several key reasons. Firstly, developing fine motor skills at an early age lays the foundation for future academic success. Writing the ABC letters helps strengthen hand muscles and improves hand-eye coordination, enabling children to undertake more complex tasks as they grow.
Secondly, handwriting practice enhances cognitive development. The process of learning to form each letter aids in letter recognition, phonemic awareness, and early reading skills, which are essential components of literacy. Kids who engage in regular handwriting practice often exhibit better memory retention and information processing, as forming letters encourages neural activity.
Thirdly, handwriting builds confidence and independence in young learners. Being able to write their own names, simple words, or sentences gives children a sense of accomplishment and bolsters their self-esteem. It also makes them more eager and willing to participate in more demanding academic activities.
Socially, handwriting can act as an emotional outlet for children. Expressing thoughts and ideas through writing can be comforting and can also improve communication skills. Overall, investing in developing handwriting skills during the formative years supports holistic development — academically, cognitively, and socially — making it a critical aspect of early education for parents and teachers alike.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students