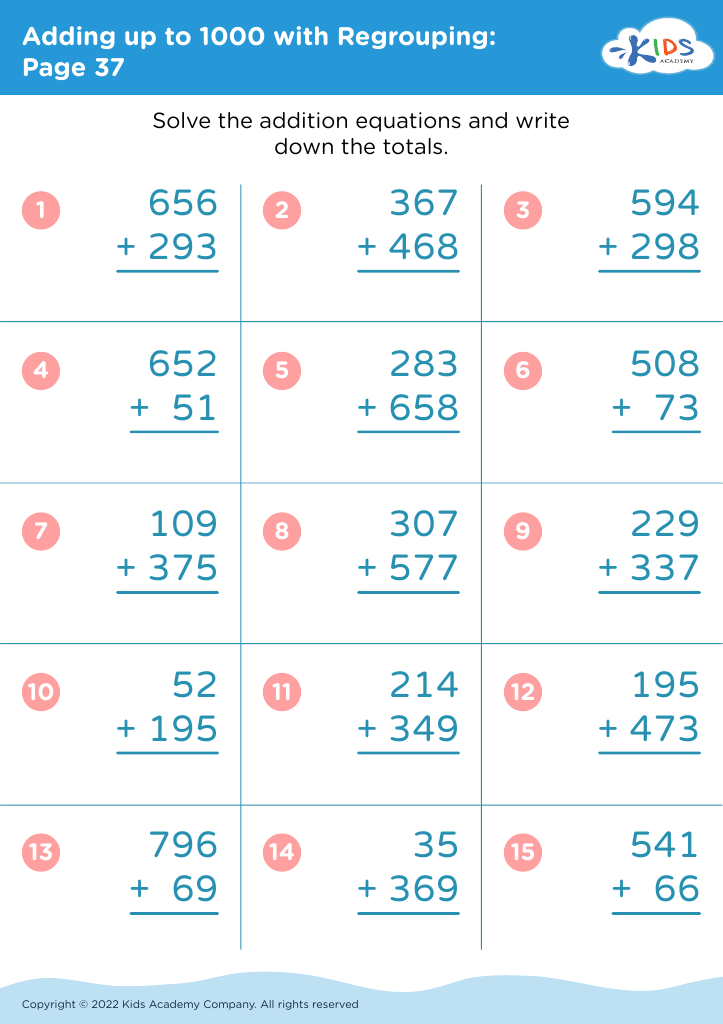
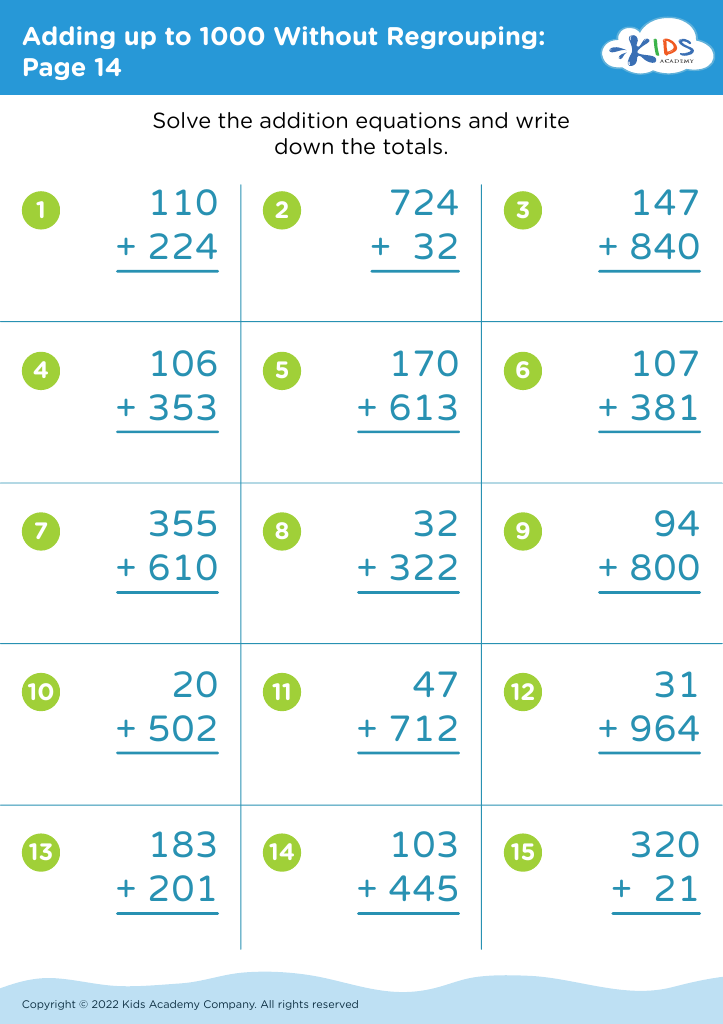
Fine motor skills development Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child's potential with our Fine Motor Skills Development Addition Worksheets designed for ages 4-7. These engaging activities combine the excitement of learning addition with the crucial development of fine motor skills. Children will enjoy tracing, counting, and manipulating colorful visuals to strengthen hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Our worksheets are thoughtfully created to cater to various learning styles, making math both fun and educational. Perfect for homeschooling or classroom settings, these resources empower young learners to build confidence in their math abilities while enhancing their motor skills. Join us in fostering a love for learning through creative and interactive addition practice!
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of fine motor skills in children ages 4-7 because these skills are foundational for a child’s overall development and academic success. Fine motor skills involve the small muscles in a child's hands and fingers, which are essential for tasks like writing, drawing, cutting with scissors, and using classroom tools.
During this critical age, children are refining their hand-eye coordination and dexterity, which significantly aids in academic activities. Strong fine motor skills enhance a child's ability to participate in schoolwork, improving their engagement and confidence. Additionally, these skills support cognitive development, as children learn to manipulate objects, which fosters problem-solving and critical thinking abilities.
Moreover, engaging in activities that develop fine motor skills, such as crafting, building, and threading, can also boost creativity and encourage perseverance. These experiences can serve not just as playful pastimes, but as essential building blocks for future learning. By investing time in fine motor development, parents and teachers can equip children with the tools necessary for school readiness, promoting independence and self-efficacy that resonant well into their later years. Ultimately, fostering these skills lays the groundwork for a child's lifelong learning journey.