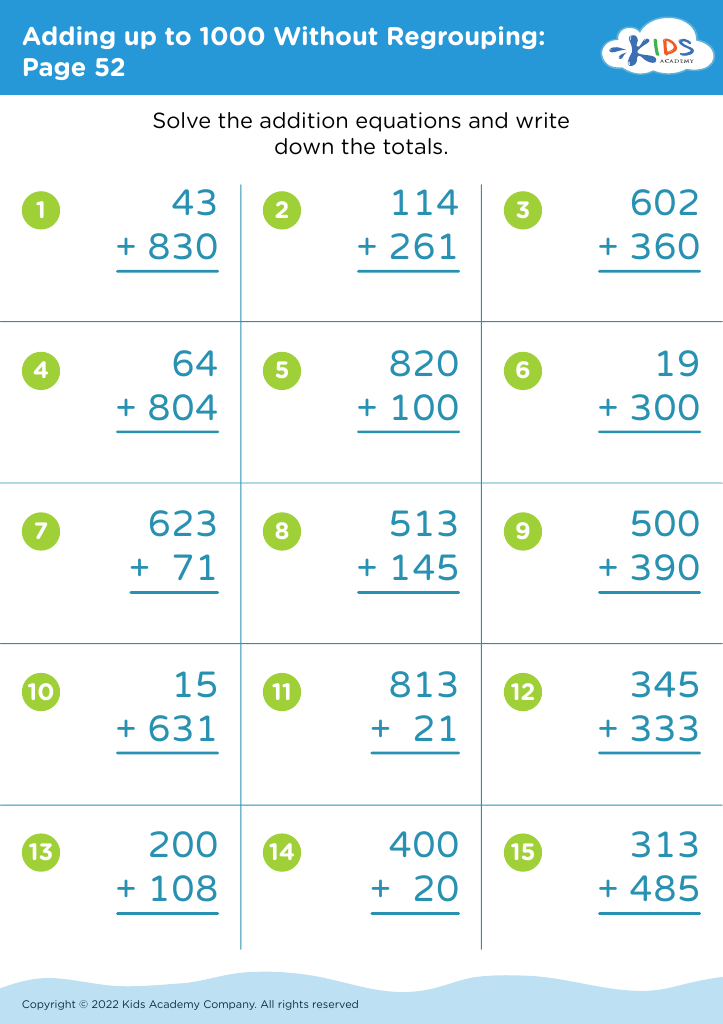
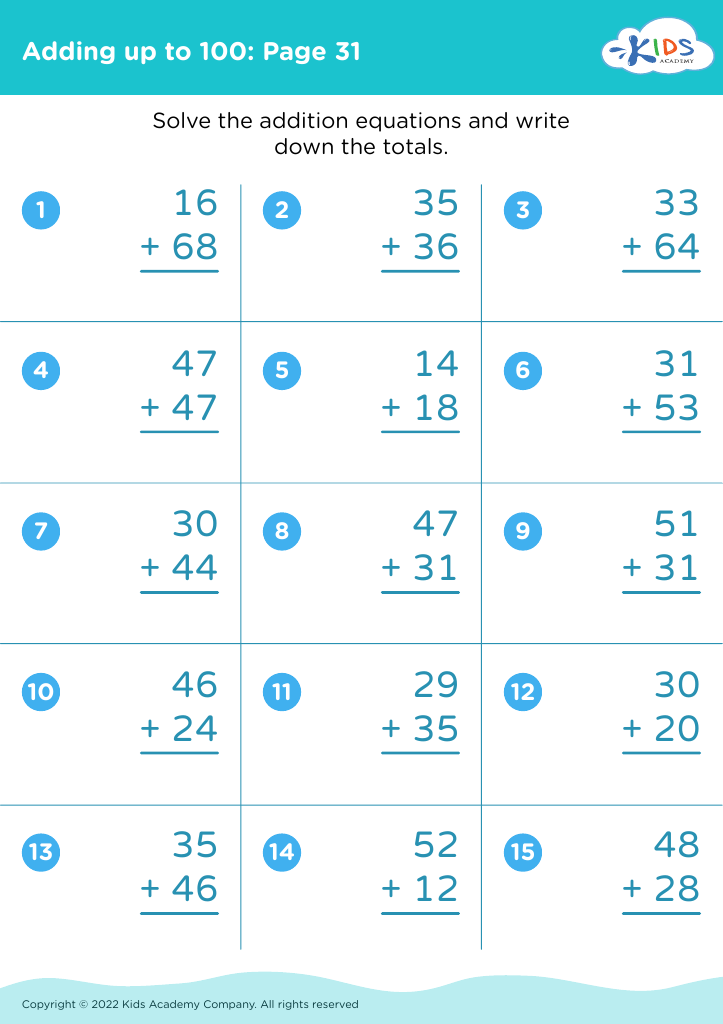
Improve fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's fine motor skills with our engaging math worksheets designed for ages 4-7! Our expertly crafted resources focus on fun and educational activities that enhance hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and pencil control. Through tracing numbers, connecting dots, counting exercises, and more, children develop crucial pre-writing skills while building a strong foundation in math. Ideal for young learners, these vibrant worksheets transform learning into an enjoyable adventure, helping little hands master the delicate movements needed for future academic success. Visit us for a collection tailored to support your child's growth in a playful, effective way!
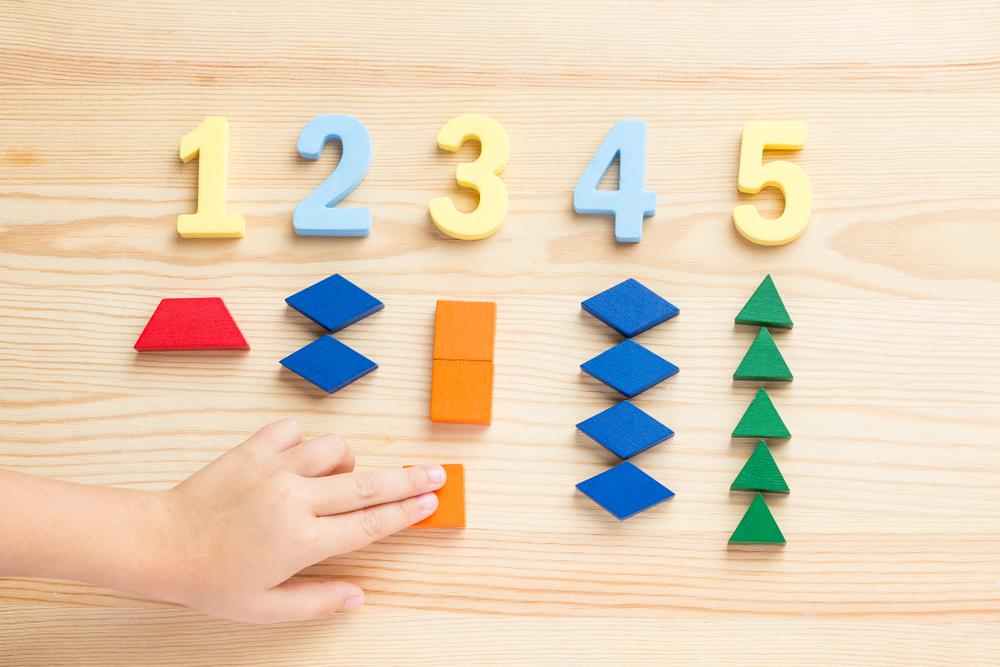
Improving fine motor skills and math skills for children aged 4-7 is essential for several key reasons. First, fine motor skills, which involve the use of small muscles in the fingers, hands, and wrists, are crucial for daily activities such as writing, dressing, and eating. Developing these skills at an early age sets the foundation for academic success; children who are adept with their fine motor skills find it easier to write legibly, which enhances their ability to learn and express mathematical concepts through written work.
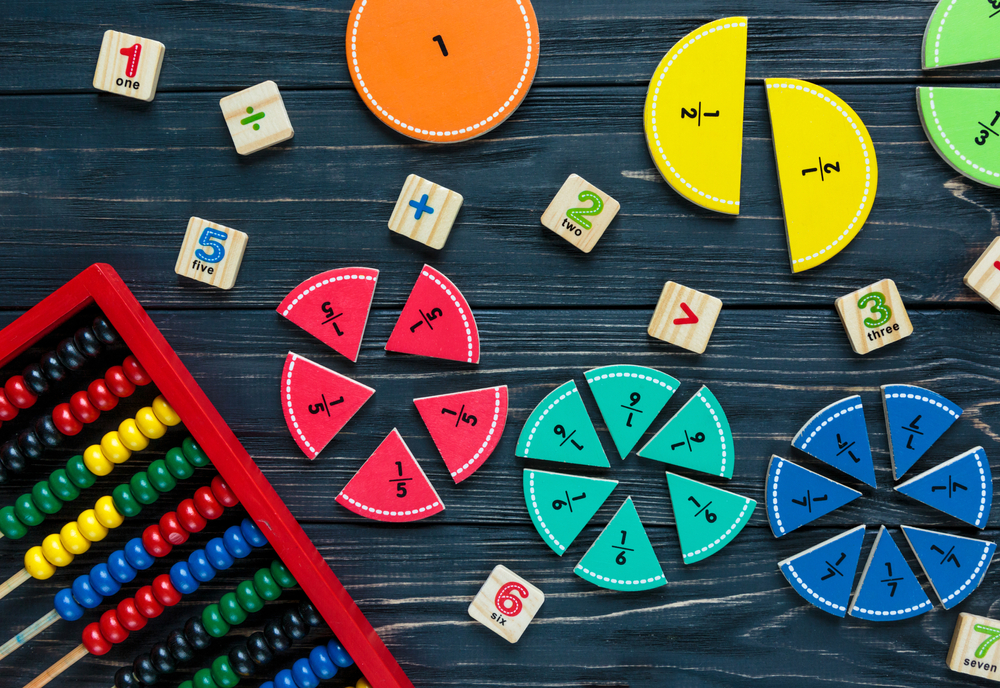
Second, introducing math at a young age nurtures critical thinking, problem-solving, and logical reasoning abilities. Mathematical concepts like counting, pattern recognition, and basic arithmetic form the basis upon which more complex mathematical ideas are later built. Integrating fine motor skill development with math to ensure these skills progress together enhances learning. For instance, sorting small objects into groups requires both math skills (counting and categorizing) and fine motor skills (grasping and manipulating objects).
Collectively, focusing on these areas supports a well-rounded development, boosts confidence, and prepares children for more structured academic settings. It also fosters a love for learning by making math more accessible and interactive, ensuring children gain essential skills that benefit them now and in their future educational endeavors.