Alphabet sequencing Worksheets for Ages 4-8
10 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Alphabet Sequencing Worksheets, perfect for children aged 4-8! Tailored to build foundational literacy skills, these worksheets feature colorful and fun activities designed to help young learners master the order of the alphabet. From identifying the next letter in a sequence to filling in missing letters, each exercise enhances alphabet recognition, cognitive development, and fine motor skills. Ideal for both classroom and at-home learning, these printable worksheets support parents and educators in fostering early learning success. Watch as your child's confidence grows while they enjoy these interactive and educational resources!


Find Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


Lowercase Letters p q r Worksheet
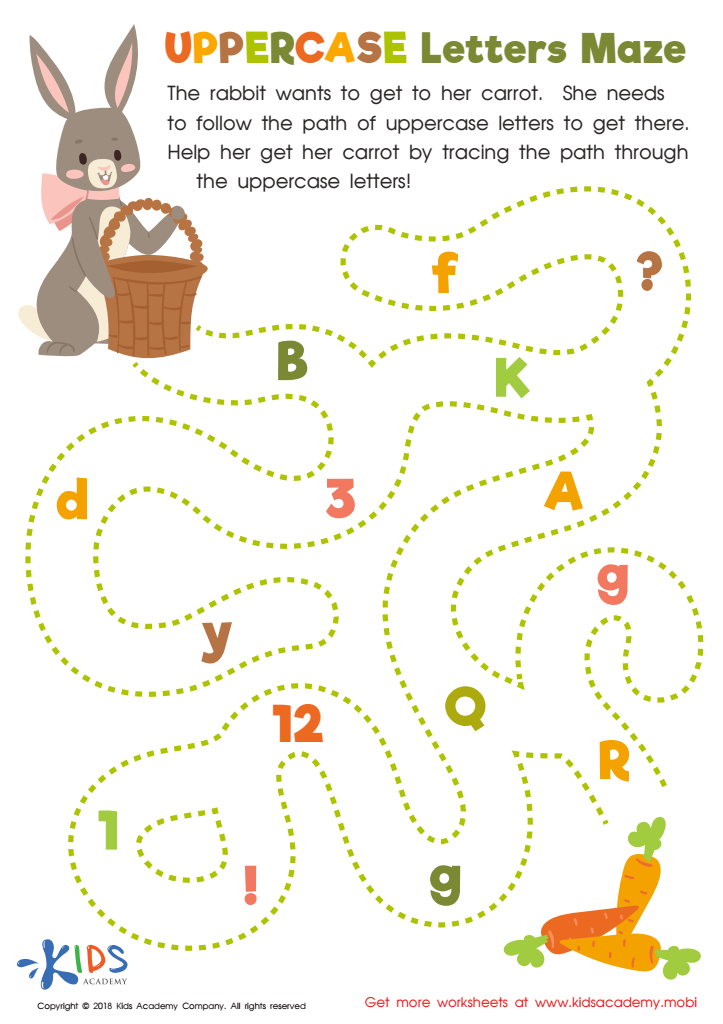

Uppercase Letters Maze Worksheet
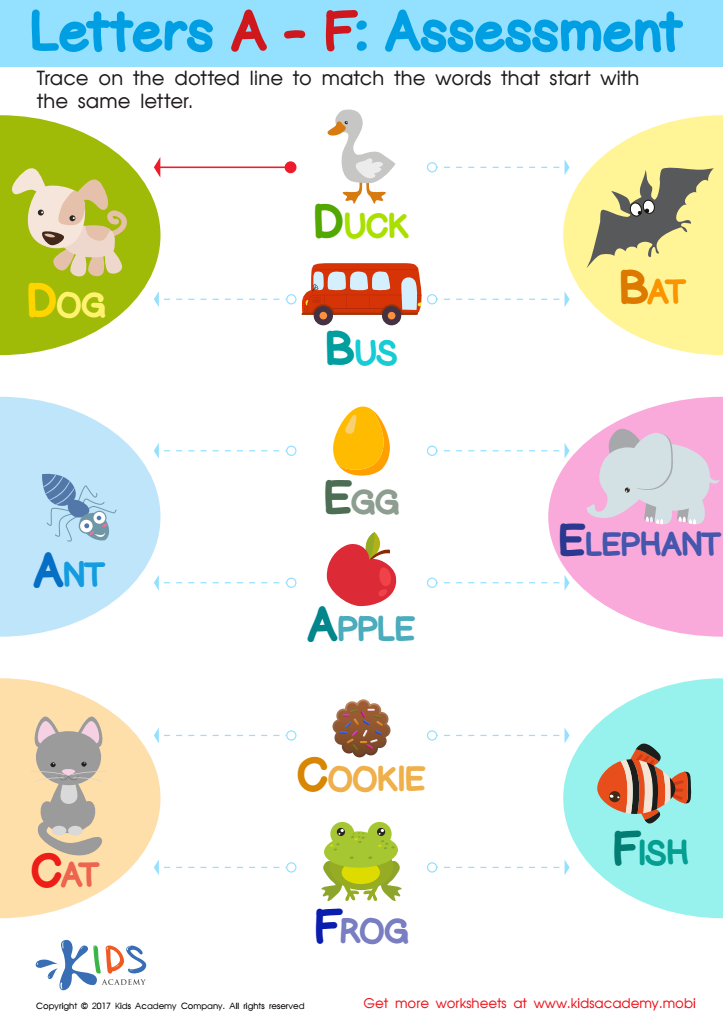

Letters A - F Worksheet


Lowercase Letters j k l Worksheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet

Easter: Chick in the Basket Worksheet


Letter Y Tracing Worksheet


Missing Letter Worksheet
Alphabet sequencing for children aged 4-8 is crucial as it forms the foundational pillar for early literacy skills. Knowing the alphabetical order helps children in recognizing letters quickly and aids in phonemic awareness, which is the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds in words. This is essential for learning to read and write effectively.
Firstly, fluency in alphabet sequencing supports vocabulary development. When a child can sequence letters easily, they can also comprehend and sort through words in dictionaries or glossaries. This enhances their ability to find, understand, and use new words appropriately.
Secondly, alphabet sequencing strengthens cognitive development. It encourages memory skills, improves concentration, and enhances logical thinking as children learn to arrange letters in a specific, repeated order.
Furthermore, strong skills in alphabet sequencing foster early reading confidence. When children understand that letters form the base of words and can consistently sequence them, they feel more secure in their reading abilities. This early confidence is crucial as it motivates them to engage more with books and texts, promoting a lifelong love for reading.
In summary, proficiency in alphabet sequencing is imperative for early literacy development, cognitive skills, and reading confidence, laying the groundwork for future academic success. Therefore, both parents and teachers should actively encourage and support this foundational learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students