Visual-motor skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 4-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
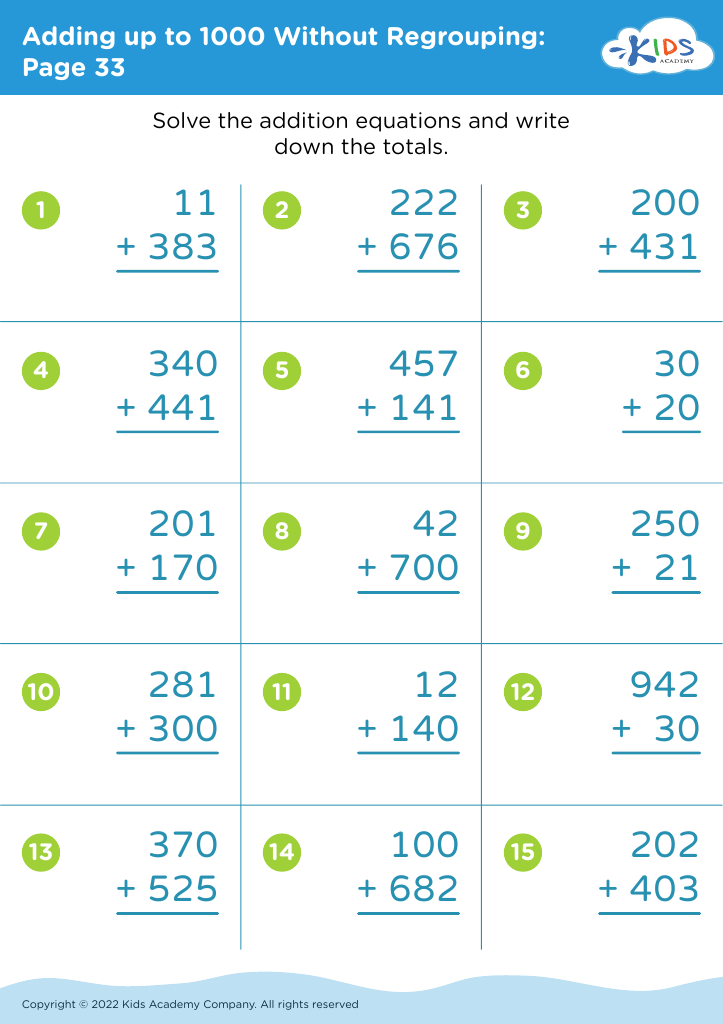
Enhance your child's learning experience with our tailored Visual-Motor Skills Addition and Subtraction Worksheets, designed specifically for kids aged 4-8. These engaging resources help young learners develop essential math skills while improving their fine motor abilities. Our worksheets feature colorful illustrations and creatively structured exercises that not only make math fun but also boost hand-eye coordination and pencil control. By integrating visual learning with foundational math concepts, children will gain confidence in their arithmetic skills and enjoy the learning process. Perfect for home or classroom use, these worksheets provide a balanced approach to early learning that fosters essential skills for lifelong success.
Visual-motor skills play a crucial role in the developmental stages of children, particularly in relation to addition and subtraction for ages 4-8. These skills encompass the ability to coordinate visual perception with fine motor control, which is essential for writing numbers, manipulating objects, and copying shapes. As children engage in math activities, strong visual-motor skills enable them to interpret problems accurately, maintain proper number formation, and navigate the spatial relationships between numbers.
Additionally, proficient visual-motor skills support overall academic success by laying a strong foundation for more complex concepts later in math and other subjects. Children with developed skills in this area are more likely to build confidence in their abilities, as frustration and difficulties often emanate from poor coordination between visual input and physical output.
Parents and teachers should actively promote activities that enhance visual-motor skills, such as tracing numbers, using manipulatives, and engaging in interactive games. Such engagement not only supports mathematical fluency but also fosters a positive attitude towards learning. By recognizing the significance of developing visual-motor skills early on, caregivers can ensure children are equipped with the necessary tools to succeed academically and develop essential problem-solving skills.