Practice writing numbers Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's math skills with our "Practice Writing Numbers Addition Worksheets" designed for ages 4-8. These engaging worksheets combine number writing and foundational addition exercises to build essential skills. Perfect for early learners, each sheet features vibrant images and interactive problems that make learning fun and effective. Kids will improve their number formation, enhance counting abilities, and develop confidence in addition. Our worksheets cater to varying skill levels, ensuring every child can progress at their own pace. Ideal for home or classroom use, provide the perfect blend of practice and play to inspire young mathematicians!
Parents and teachers should prioritize practicing writing numbers and simple addition for children aged 4-8 because these skills lay the foundation for future academic success and everyday mathematical competence. At this critical developmental stage, children's minds are incredibly receptive, eager to absorb new concepts and skills. Mastering number writing enhances their fine motor skills and ensures they understand number formation and recognition, which is essential for accurate mathematical calculations later on.
Addition practice, integrated early, helps children grasp basic arithmetic concepts, fostering a sense of confidence and competence as they solve simple problems. This practice builds cognitive abilities such as logical thinking, problem-solving, and sequencing. Establishing a strong numerical foundation early can mitigate struggles and frustrations in higher-level math subjects encountered in later grades.
Additionally, these early math skills are crucial for real-life situations—like counting money, following recipes, and playing games—promoting overall numerical literacy. For both social and academic contexts, developing robust math skills in early childhood can encourage a lifelong affinity for learning, critical thinking, and practical problem-solving, providing children with the tools they need to thrive in an increasingly complex world.

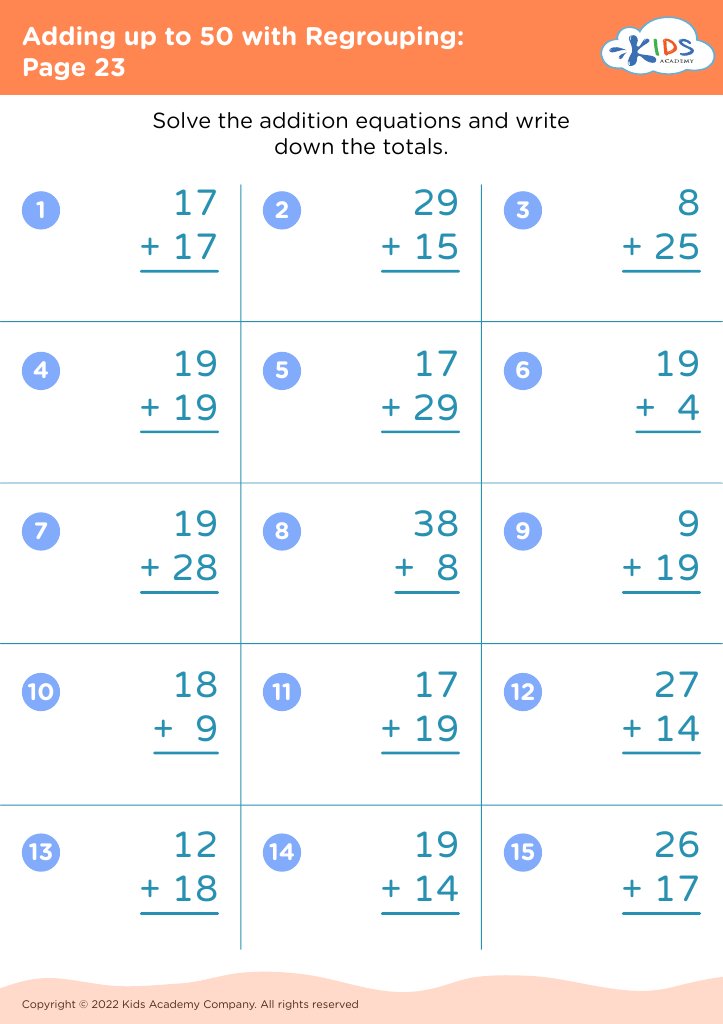
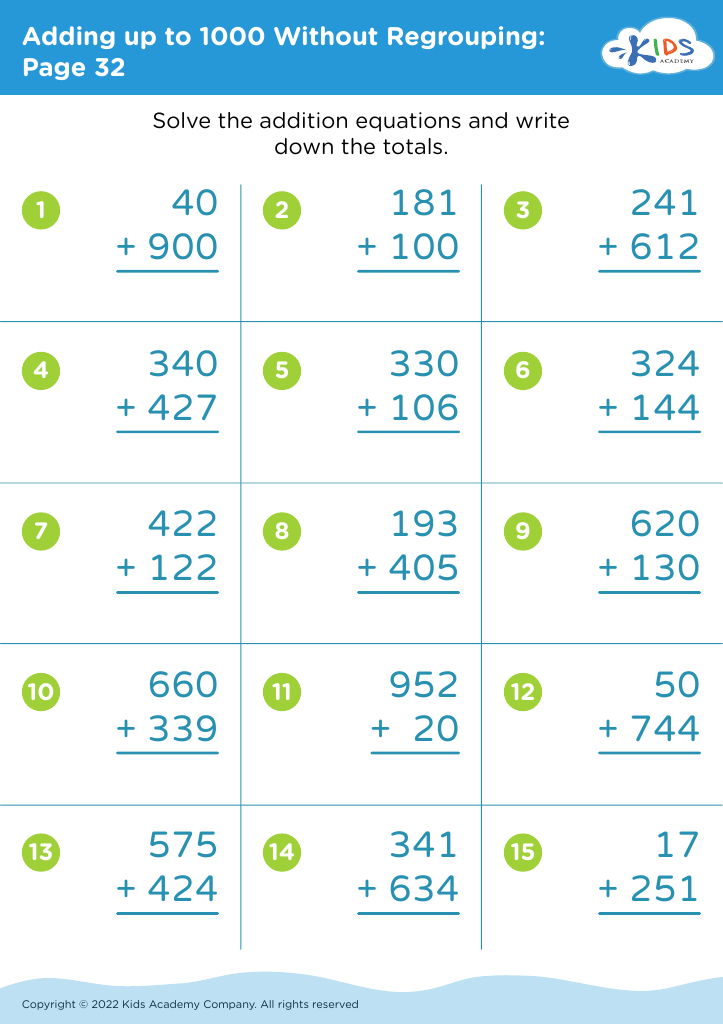
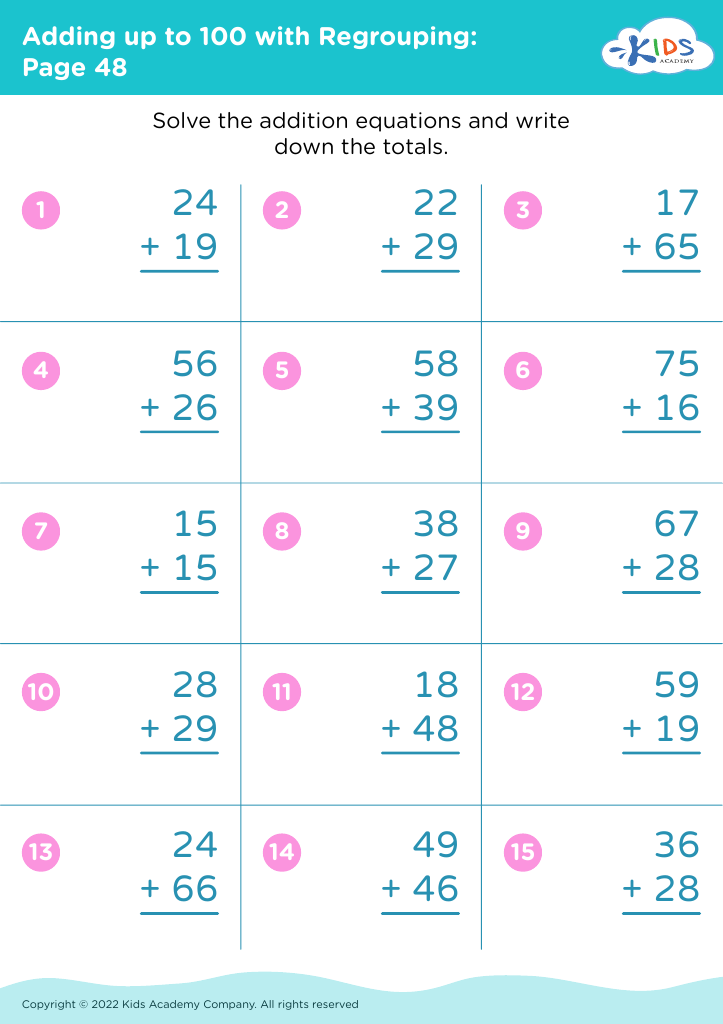
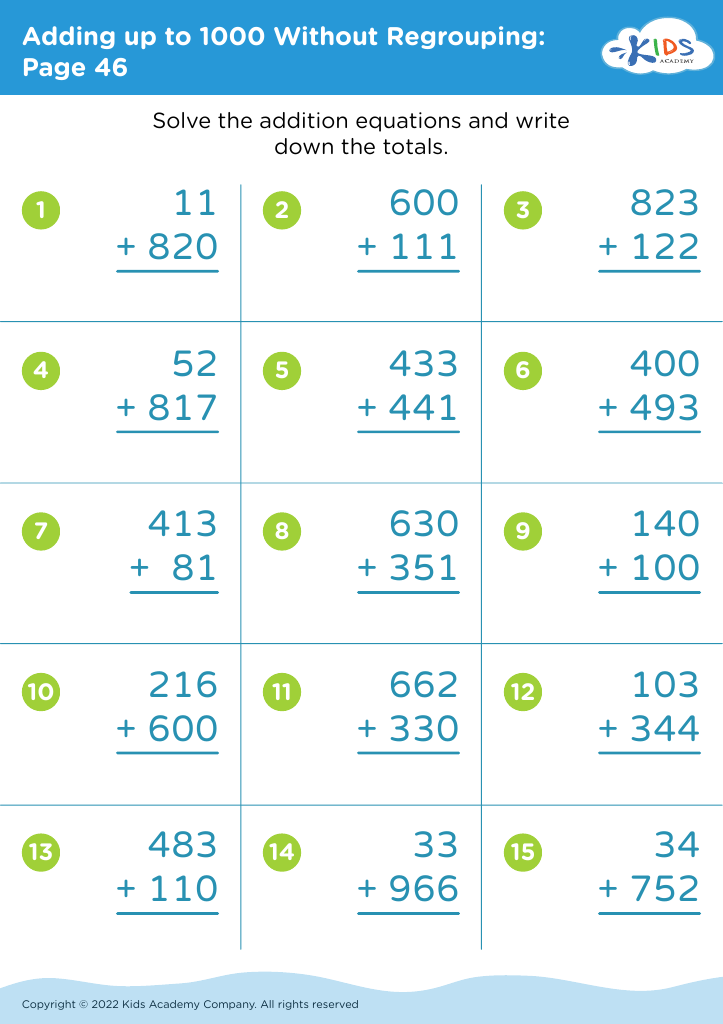
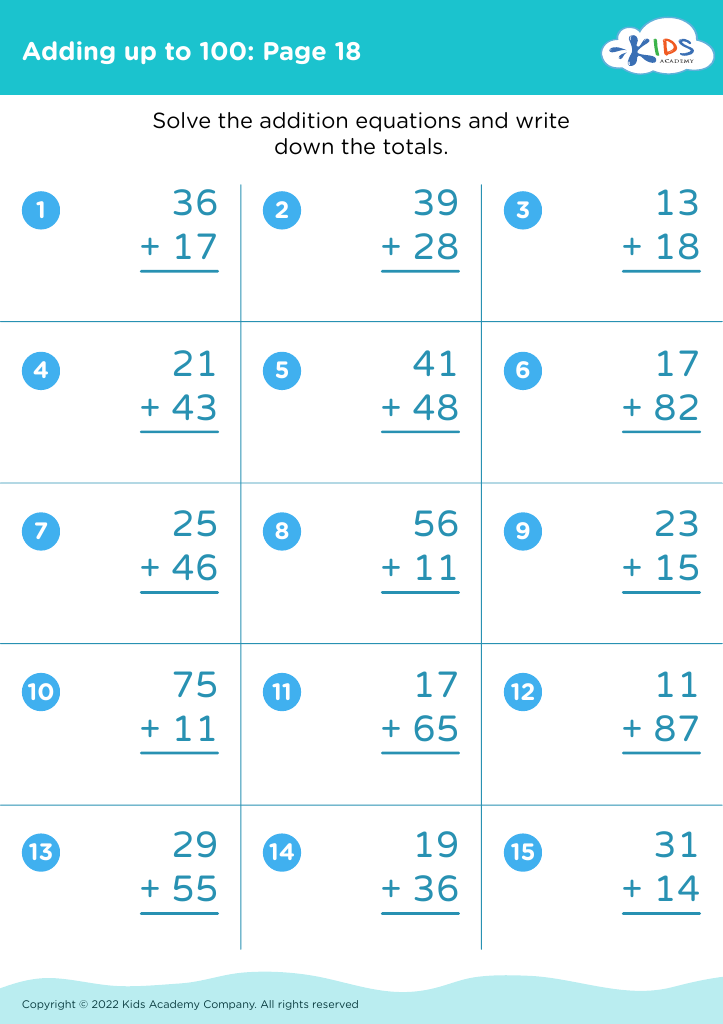
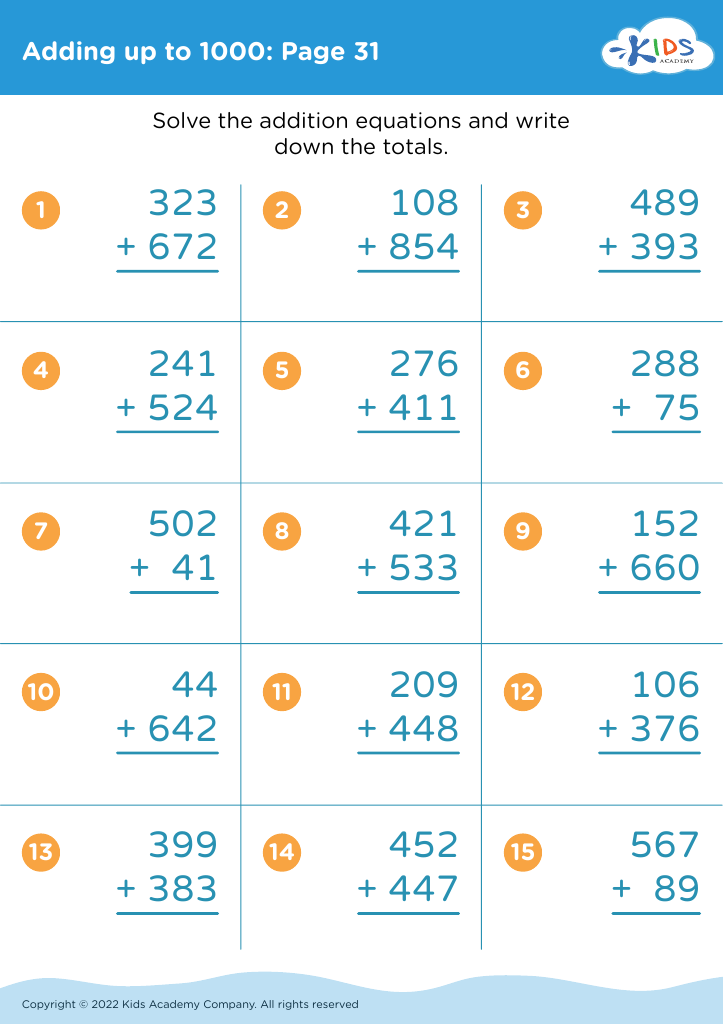



.jpg)












