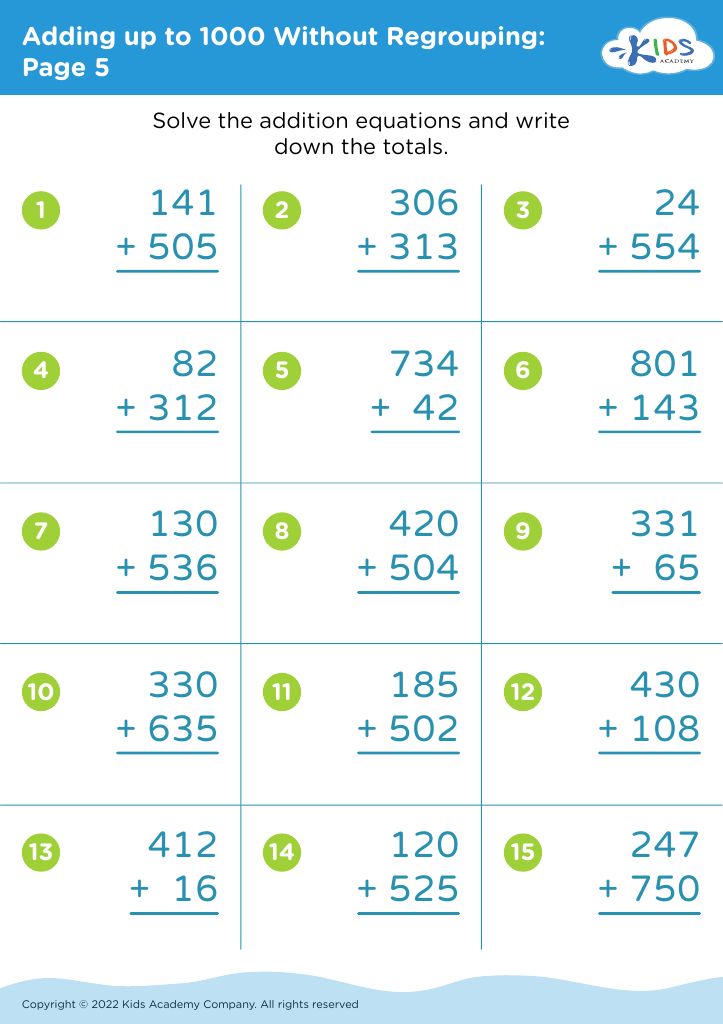
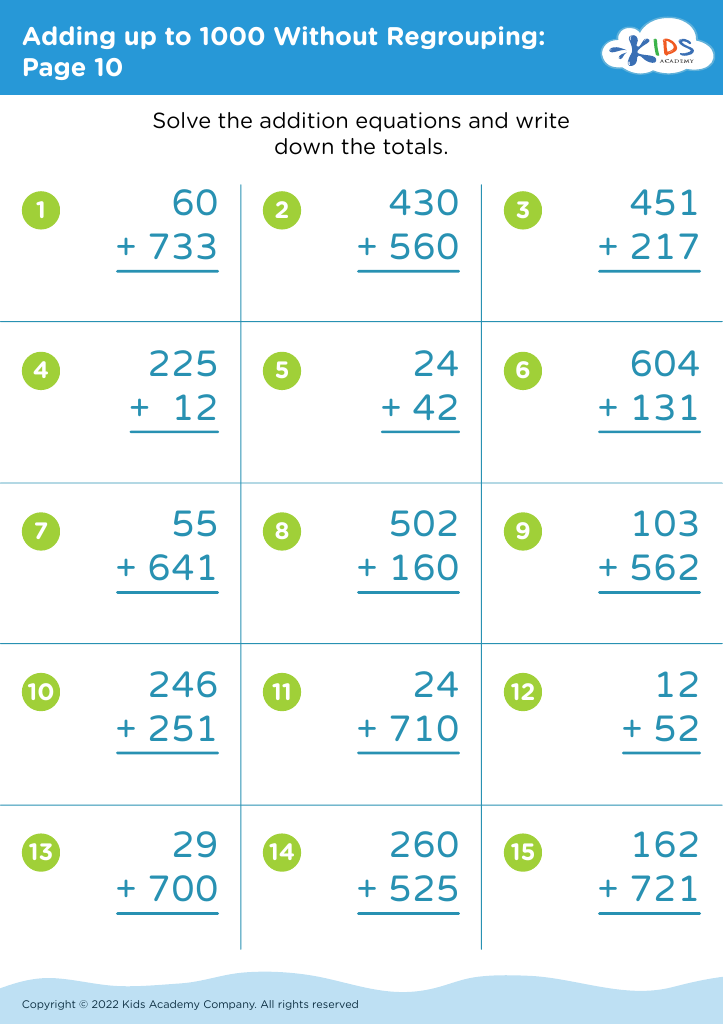
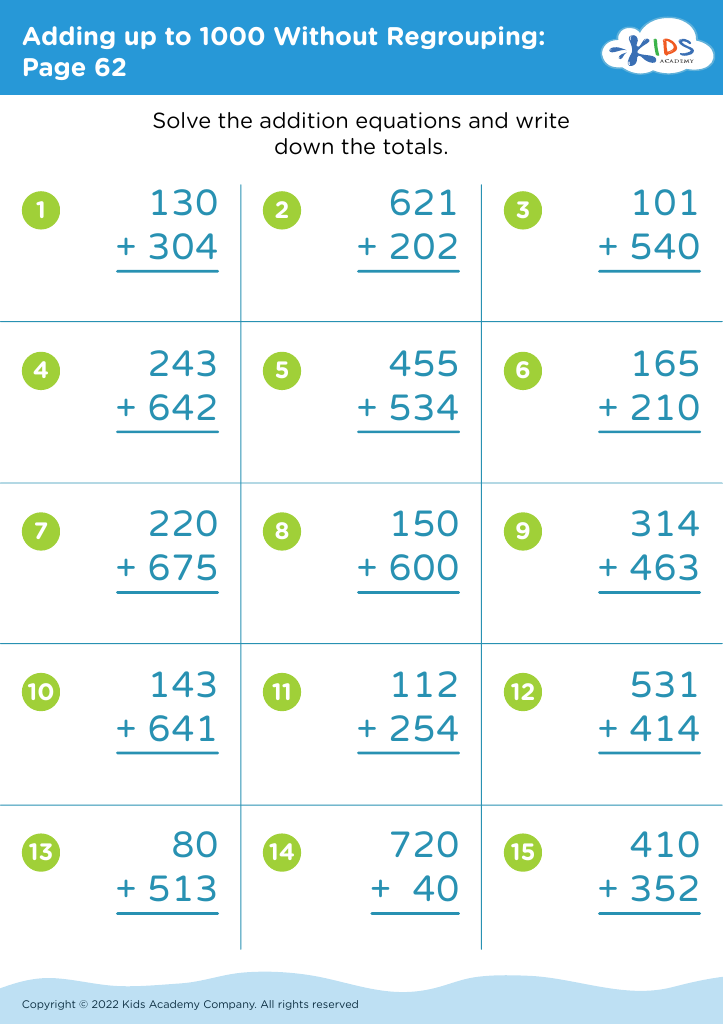
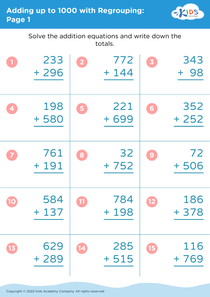
Basic Math Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Welcome to our engaging collection of "Basic Math Skills: Adding Up to 1000 Without Regrouping" worksheets, designed specifically for children aged 4-9. These worksheets aim to build a solid foundation in addition, helping young learners master the skill of adding numbers up to 1000 without regrouping. Our fun, interactive exercises promote confidence and ease in arithmetic, making math enjoyable! With colorful illustrations and varied problem sets, your child will enhance their problem-solving abilities while developing critical thinking. Perfect for home or classroom use, our worksheets are an excellent resource to support early math education and lifelong learning! Start your child's math journey today!
Basic math skills, such as adding up to 1000 without regrouping, are fundamental for children aged 4-9 for several reasons. First, these skills lay the groundwork for more advanced mathematical concepts, promoting a strong number sense. Understanding how to add numbers effectively helps develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, which are essential across all subjects and in everyday life.
Secondly, math skills foster confidence. Mastering addition in a straightforward manner equips children with the belief that they can tackle more complex problems in the future. This confidence can carry over to other learning areas, creating a positive attitude towards education.
Moreover, parents and teachers play a pivotal role in nurturing an environment conducive to learning. By emphasizing basic math skills, they provide children with tools that will serve them well in later academic pursuits and real-world situations, such as budgeting and time management.
Finally, the ability to add up to 1000 without regrouping supports the development of mental math skills. This promotes efficiency and accuracy, allowing students to process mathematical information quickly in various contexts. Overall, an emphasis on these foundational skills benefits children's academic journeys, fosters resilience, and prepares them for future challenges.