Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
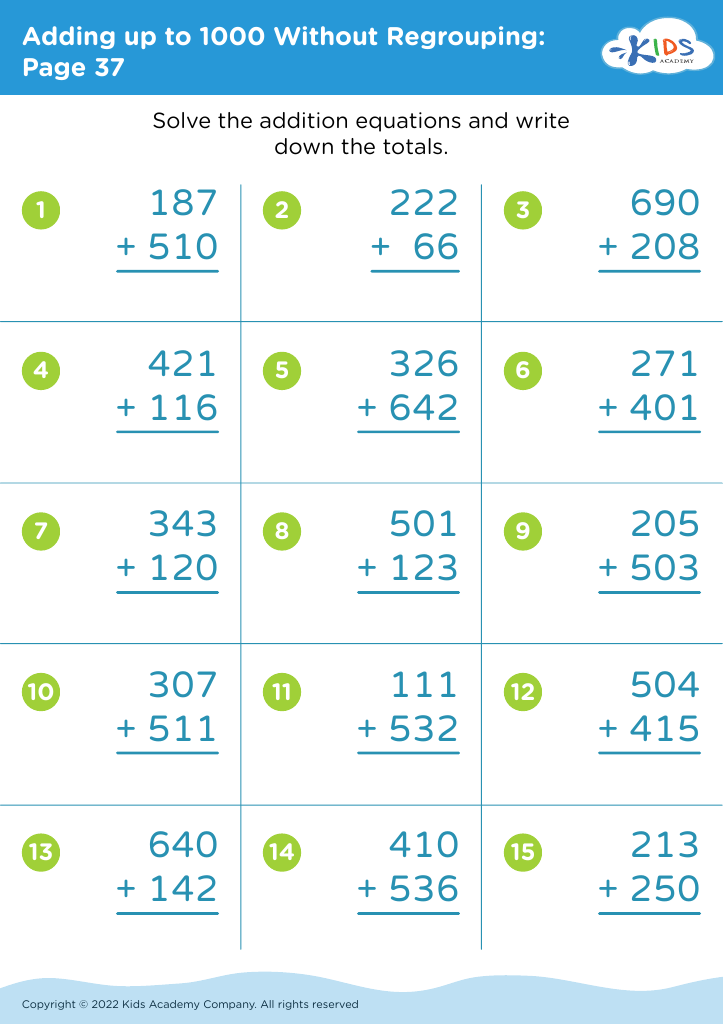
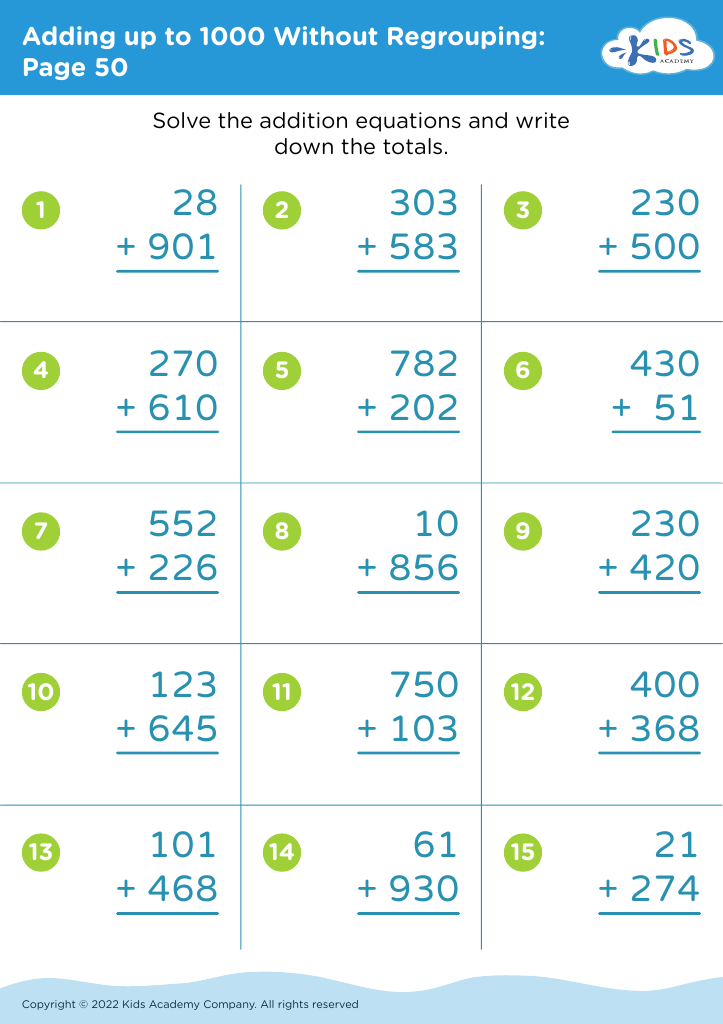
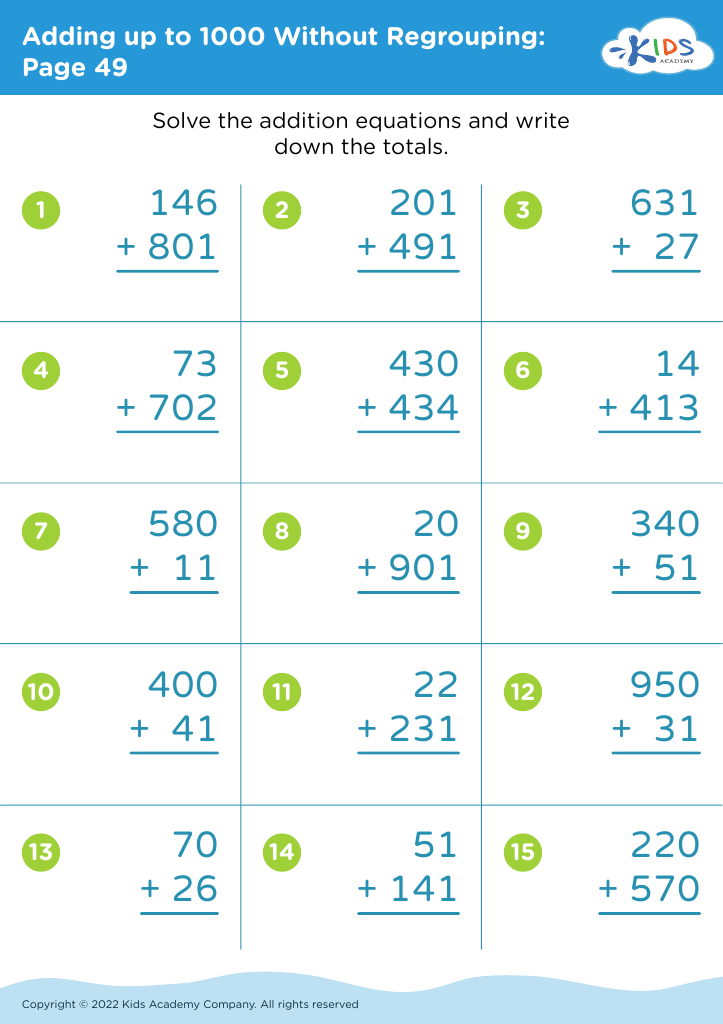
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while boosting their math abilities with our "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping" worksheets, perfect for ages 4-9. These engaging activities are designed to improve precision and hand coordination through writing and calculation exercises. Kids practice adding large numbers without regrouping in a fun, supportive environment. Our carefully crafted worksheets help build foundational math skills and confidence, preparing young learners for more advanced concepts. Ideal for home or classroom use, these resources make learning both effective and enjoyable. Empower your child to reach new heights in their academic journey today!
Fine motor skills are critical to a child's development and influence their ability to perform essential daily tasks like writing, buttoning, and using utensils. For children ages 4-9, introducing math activities that do not require regrouping, such as adding up to 1000 without regrouping, can positively impact both cognitive and fine motor development. These activities often involve using pencils, manipulatives, or technology that engage small hand muscles, thereby strengthening dexterity and coordination.
Mastery of basic math concepts also lays the groundwork for more advanced mathematical skills and critical thinking. When children practice addition within manageable limits, they experience less frustration and more immediate success, boosting their confidence in both math and broader academic pursuits.
Incorporating fine motor development into math instruction is particularly advantageous because it creates opportunities for multi-sensory learning. Children who draw numbers, move objects, or click through digital exercises are integrating tactile, visual, and auditory inputs, which can enhance understanding and retention.
Parents and teachers should prioritize activities that blend fine motor skills with basic math concepts to provide a holistic educational experience. These dual-focused activities not only promote proficiency in essential academic skills but also facilitate development of the fine motor abilities necessary for everyday life and future learning.