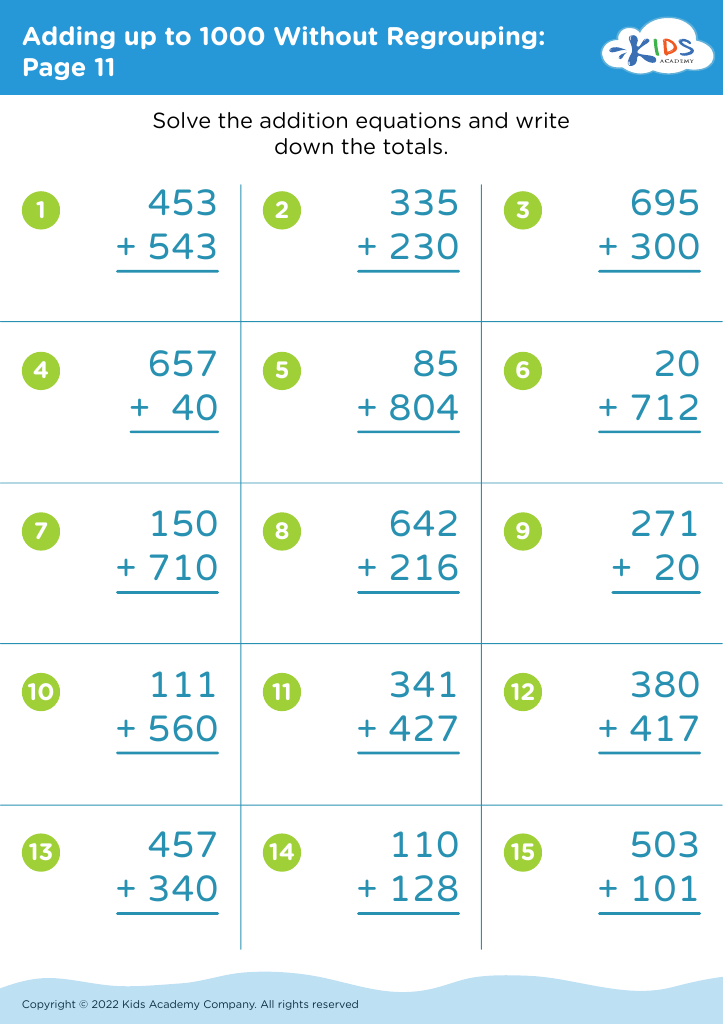
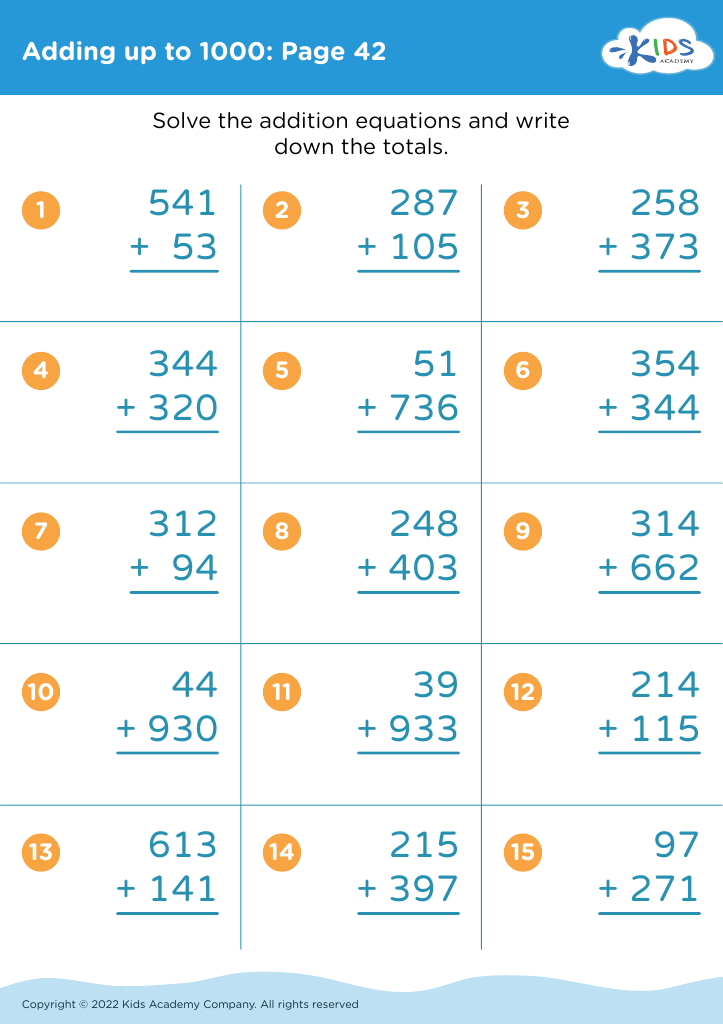
Counting skills are the earliest foundations of mathematical learning, vital for children aged 4-9. Mastering counting and adding up to 1,000 provides not just a numerical proficiency but fosters cognitive development, problem-solving skills, and logical thinking. During these formative years, a child's brain is making critical neural connections, and engaging with numbers stimulates intellectual growth. Basic counting introduces children to patterns and sequences, which are essential components of all mathematical concepts they will encounter later, including more complex arithmetic, geometry, and algebra.
Additionally, being proficient with numbers affects their ability to manage everyday tasks and increases their confidence in handling more technical subjects in future. Skills like addition are practical: whether tallying up allowances or understanding quantities while assisting in the grocery store, they lay a concrete groundwork for real-world transactions and decision making. Furthermore, competence in counting correlates strongly with overall academic achievement.
For teachers and parents, investing time in teaching counting up to 1,000 ensures children build a robust and pleasant relationship with mathematics early on. Positive early math experiences reduce math anxiety and engage children in creative and iterative thinking processes. Therefore, prioritizing these skills tailors a child's trajectory towards scholastic success and life-long numeracy.