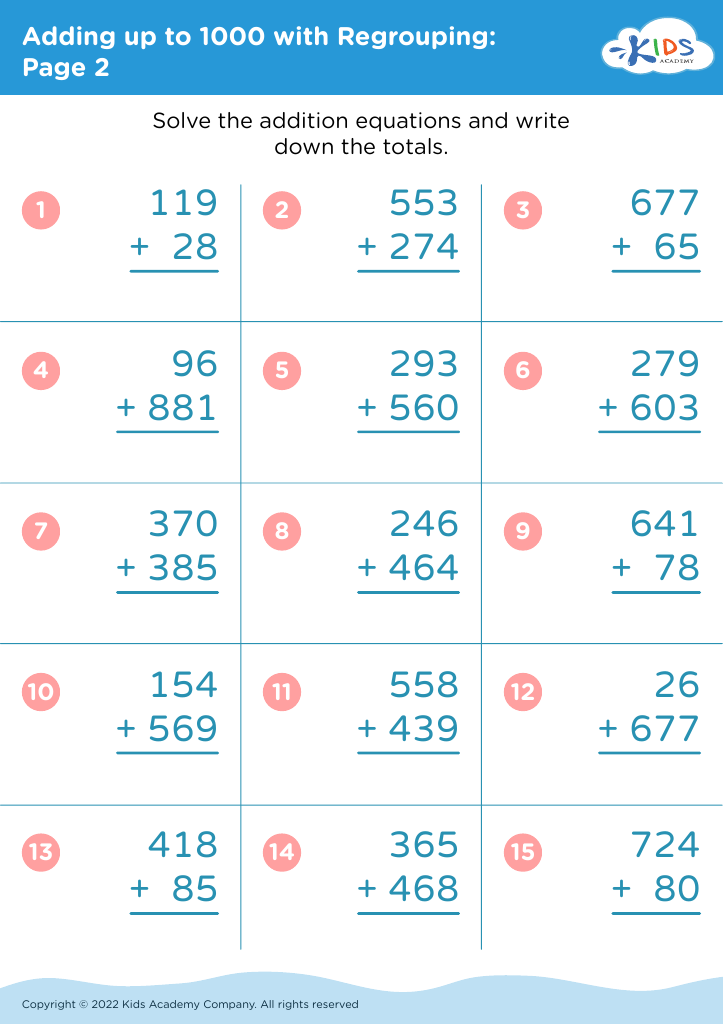
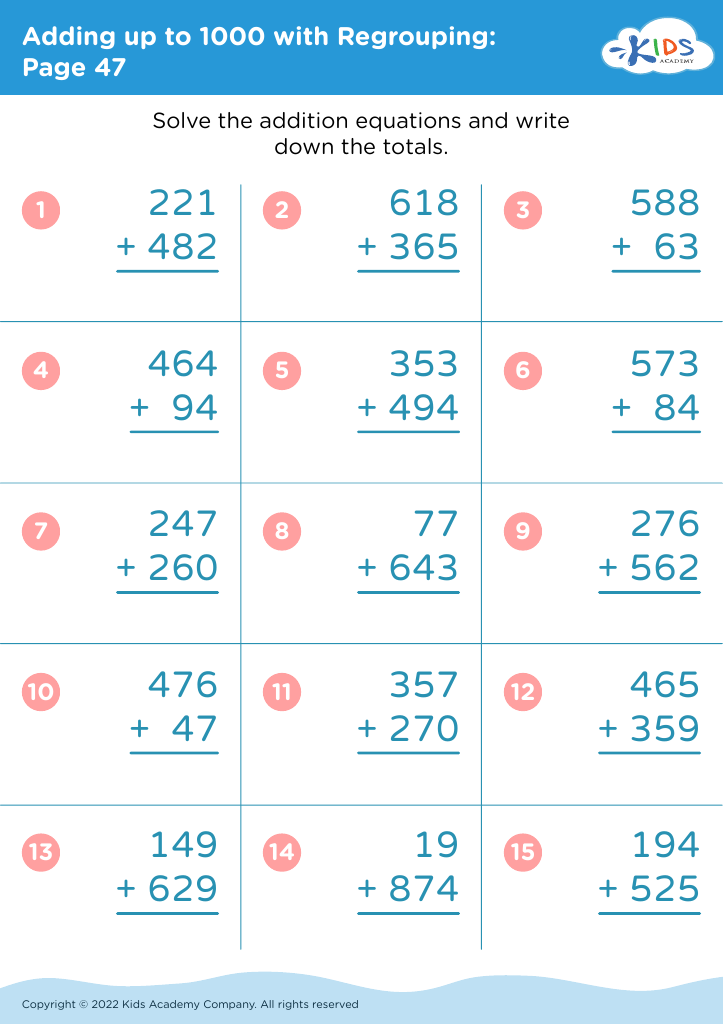
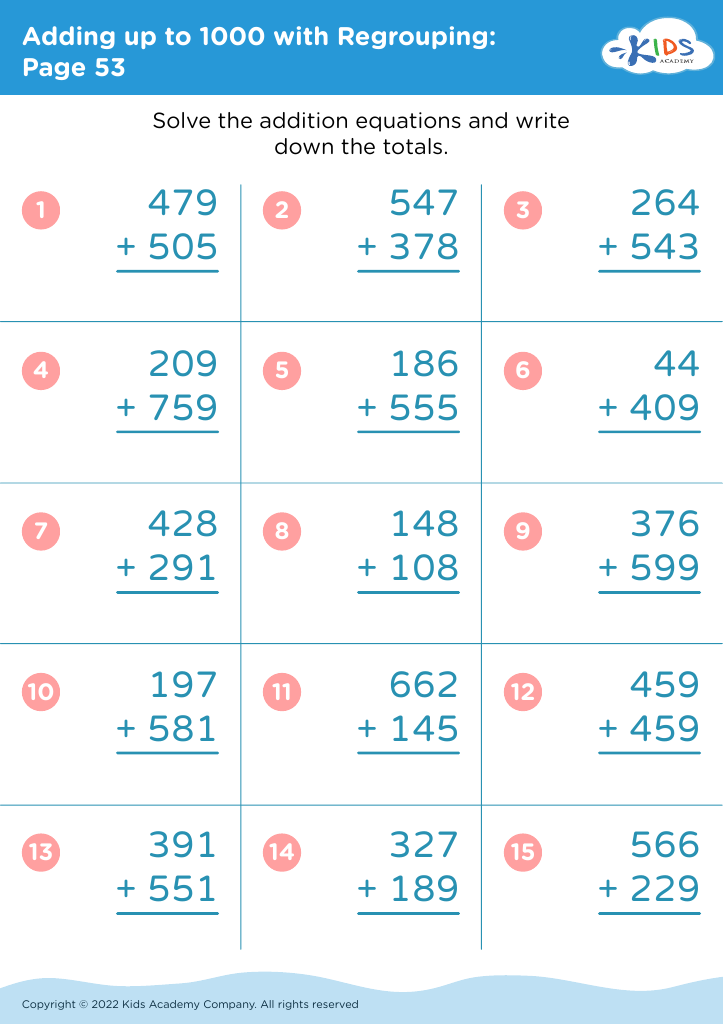
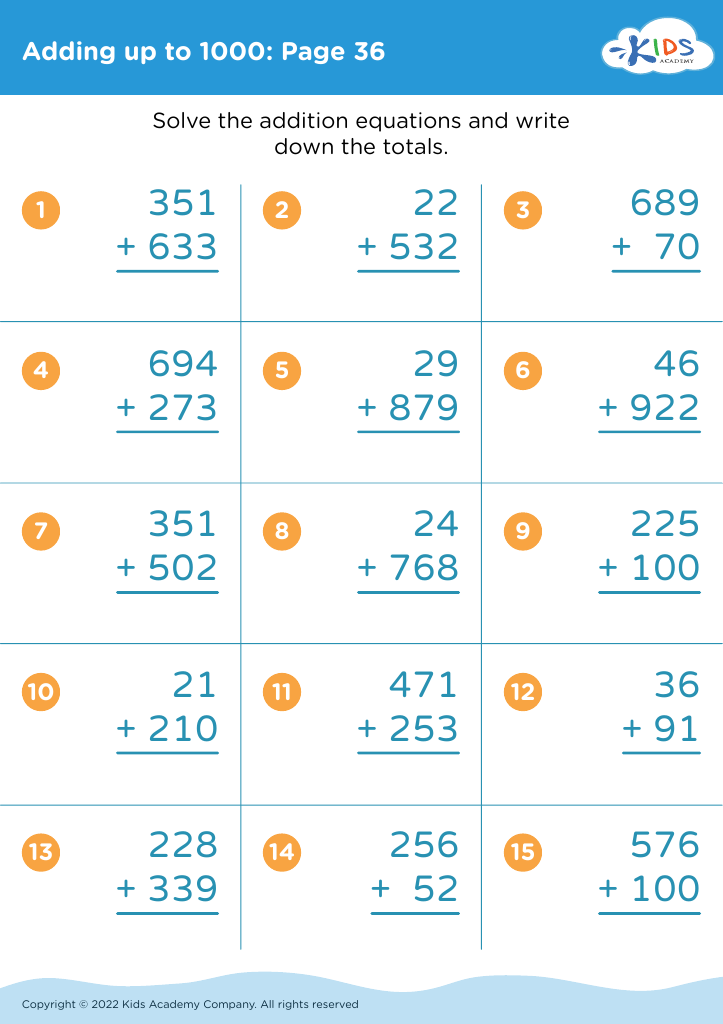
Number Recognition Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
31 filtered results
-
From - To
Number recognition and the ability to add up to 1000 by ages 4-9 are foundational skills that establish a solid basis for future mathematical learning and daily life tasks. At these formative ages, children's brains are highly receptive to learning new concepts. Grasping number recognition and addition builds their numerical literacy, enhancing their ability to understand more complex math problems later on.
For young learners, understanding numbers and simple addition promotes cognitive development by improving memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. In everyday scenarios, these skills translate to basic tasks like handling money, telling time, and even cooking, creating tangible connections between education and real-world applications.
Parents and teachers play a pivotal role in fostering these abilities. By encouraging numerical learning, they can inspire confidence and a positive attitude towards math within children. This early proficiency can mitigate math anxiety, a common barrier to learning as children grow older. Engaging young minds with fun and interactive number activities enriches their learning experience and keeps them motivated.
Ultimately, instilling strong number recognition and addition skills by the age of 9 lays a robust foundation for advanced education and critical thinking, equipping children for both academic success and practical life skills.