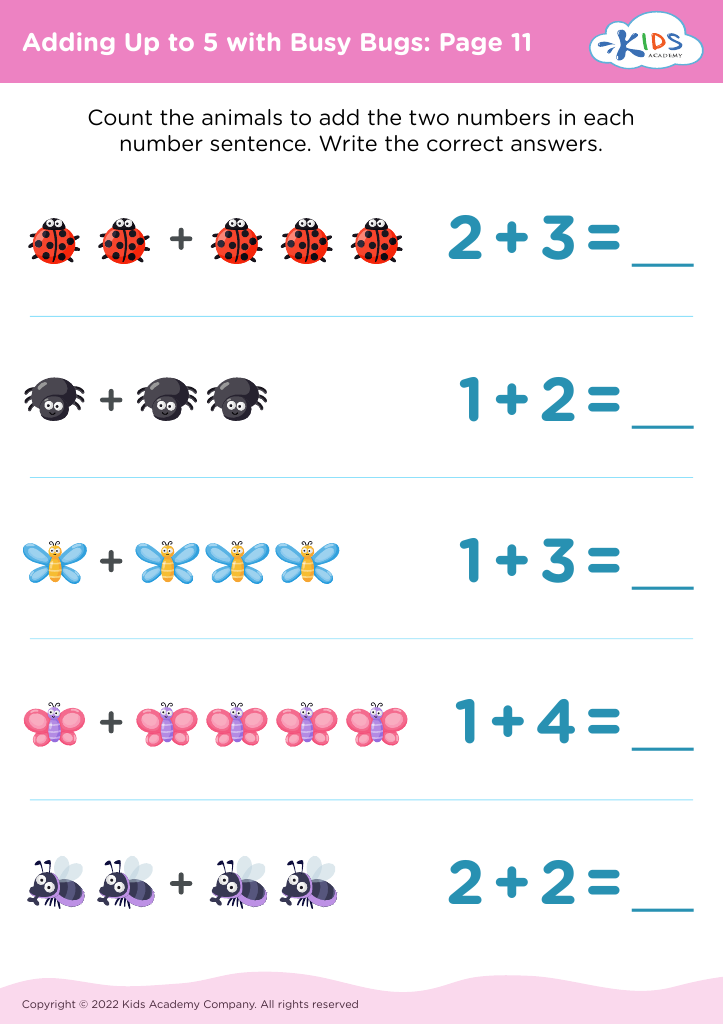
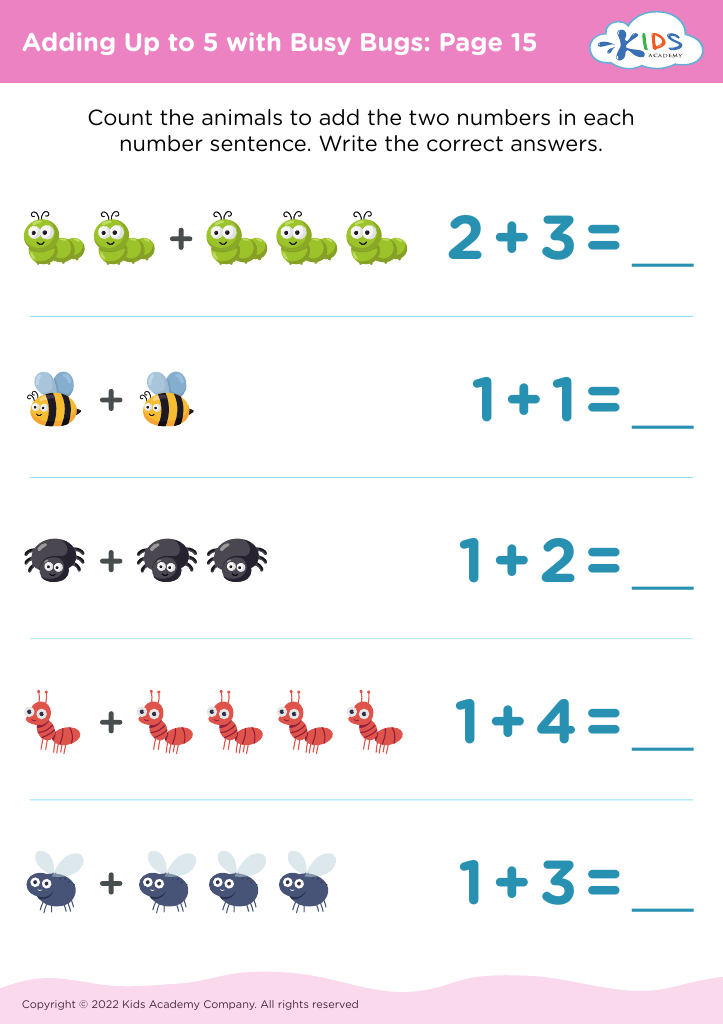
Counting skills Addition Worksheets for 4-Year-Olds - Page 6
Parents and teachers should prioritize counting skills and basic addition for 4-year-olds because these foundational mathematical abilities are crucial for cognitive development and future academic success. At this age, children's brains are highly receptive to learning new concepts, and early exposure to counting and simple addition helps them develop a strong number sense.
Counting teaches children to recognize numeric symbols and understand the sequential order of numbers. This skill is essential for more complex mathematical operations they'll encounter later. In addition to enhancing numerical understanding, counting activities can improve a child's memory and build concentration.
Introduction to basic addition furthers their mathematical comprehension by illustrating relationships between quantities. It also helps children grasp the concept of combining sets, which is a fundamental arithmetic principle they will build upon in later grades.
Moreover, early math skills correlate with better problem-solving abilities. When children learn to count and add, they also learn to think logically and sequentially, strengthening their analytical skills.
Incorporating counting and addition into playful and everyday activities ensures that learning feels intuitive and enjoyable. This approach not only prepares children for formal education but also fosters a positive attitude toward learning and curiosity, forming a critical foundation for lifelong intellectual engagement.