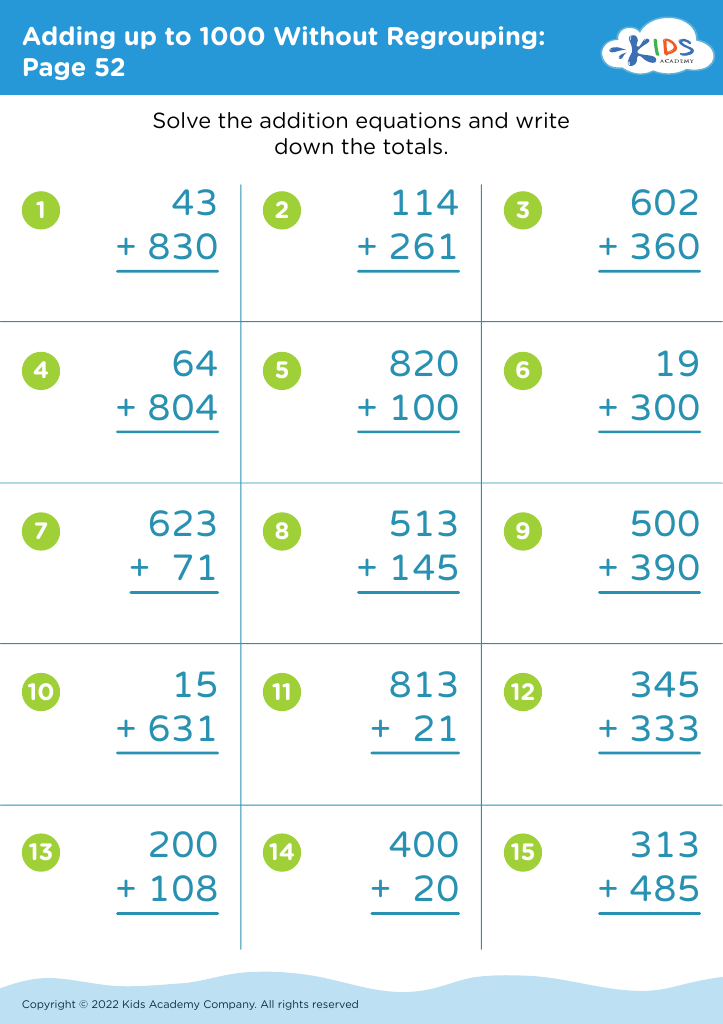
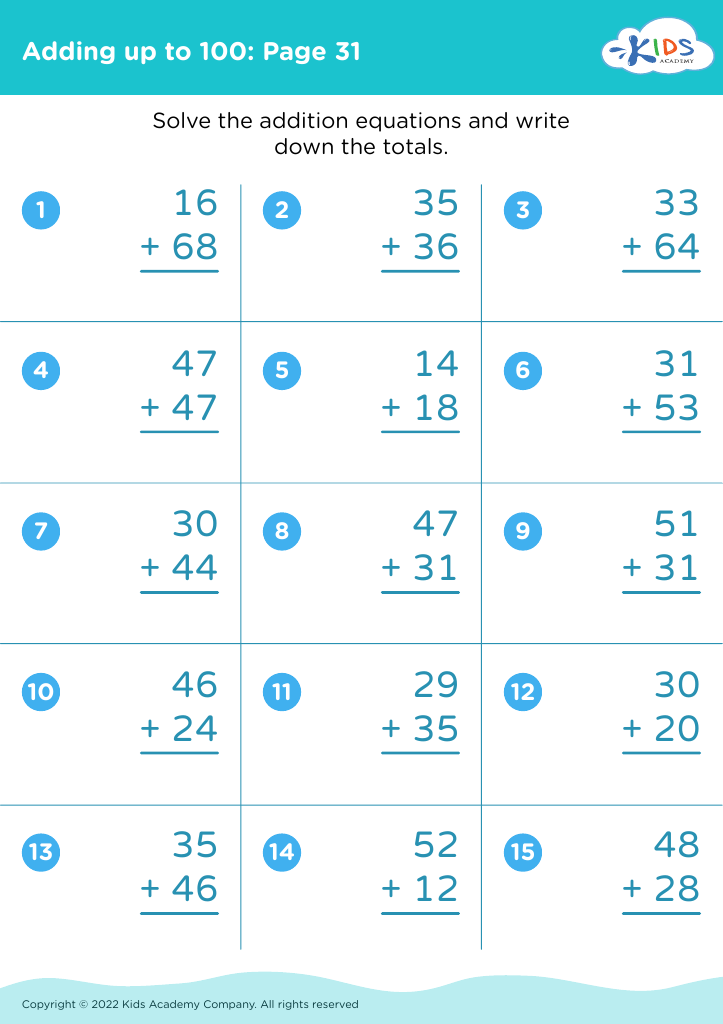
Improve fine motor skills Worksheets for Ages 5-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our engaging worksheets designed for ages 5-9. At Kids Academy, we offer a wide range of printable activities to support hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and precision in young learners. From tracing lines and shapes to practicing cutting and drawing, our worksheets provide diverse exercises to strengthen little hands for writing, crafting, and daily tasks. Created by education experts, these fun-filled resources are perfect for both classroom and home use. Empower your child’s development and boost their confidence through creative, skill-building activities tailored to their age and abilities.
Parents and teachers should care about improving fine motor skills in children ages 5-9 because these skills are crucial for everyday tasks and overall development. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, which are vital for activities like writing, cutting with scissors, buttoning clothes, and tying shoelaces. At this age, children are learning to perform these tasks independently, and their ability to do so can significantly impact their confidence and self-esteem.
Developing fine motor skills also plays a pivotal role in academic success. Children with well-developed motor skills tend to write more legibly and efficiently, which can enhance their learning and performance in school. These skills are also closely associated with cognitive development, as they involve planning, problem-solving, and dexterity.
Moreover, fine motor skills can affect social interactions. Children who struggle with tasks like drawing or playing certain games may feel excluded or frustrated, impacting their social engagement and relationships. By prioritizing the development of fine motor skills, parents and teachers can foster a child’s independence, boost their academic abilities, and support their social and emotional well-being, setting a strong foundation for future growth and learning.