Reading comprehension Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 6-7
4 filtered results
-
From - To
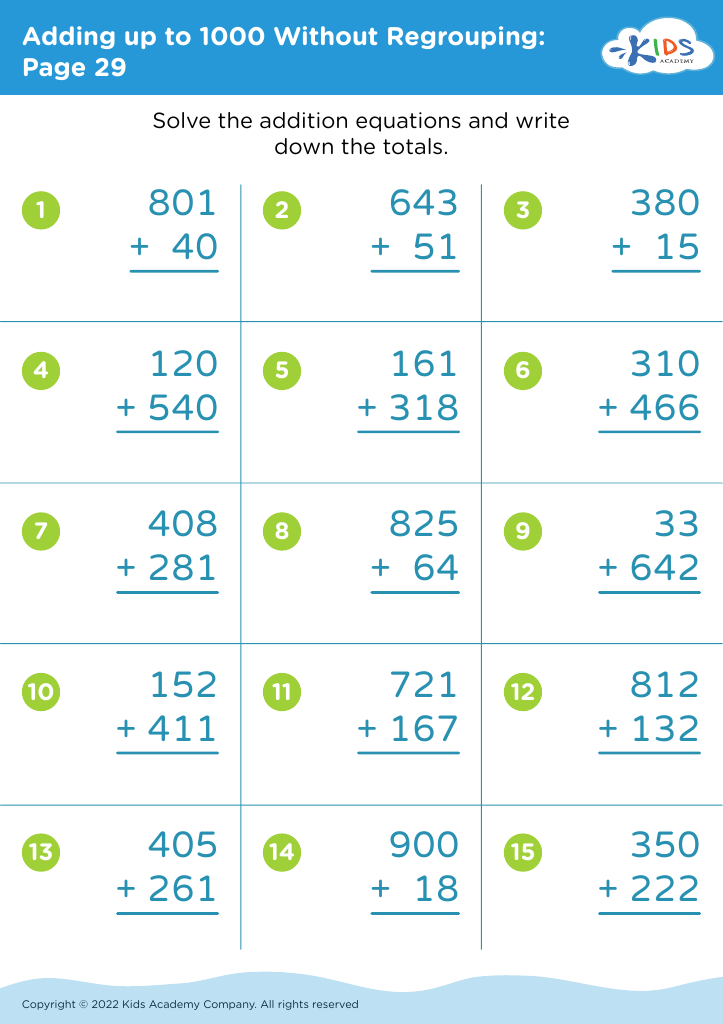
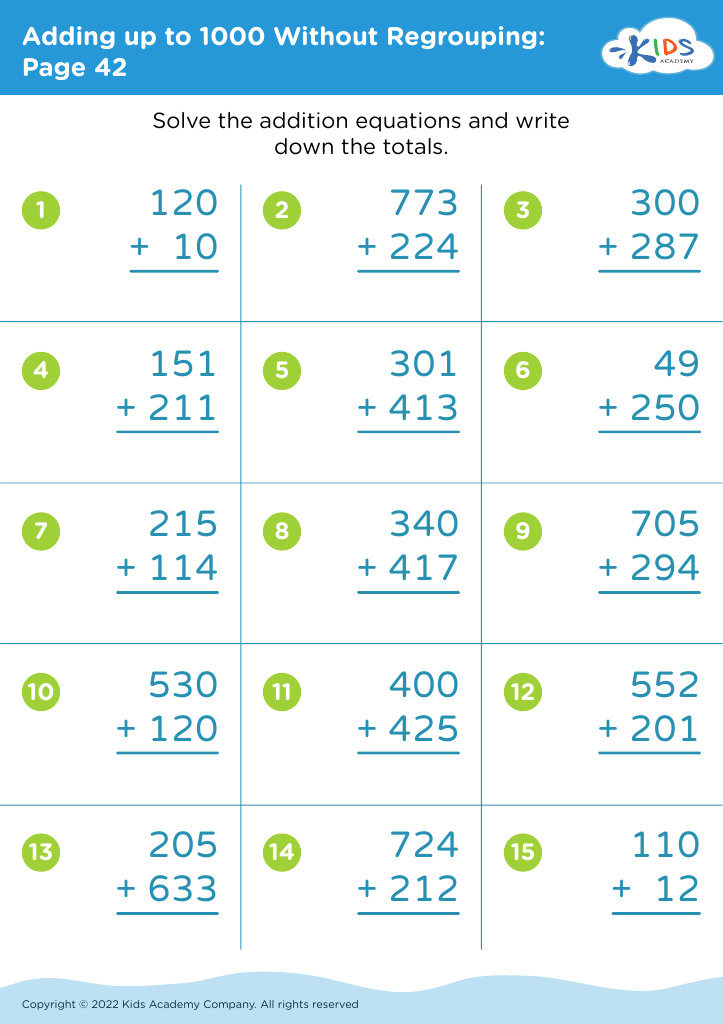
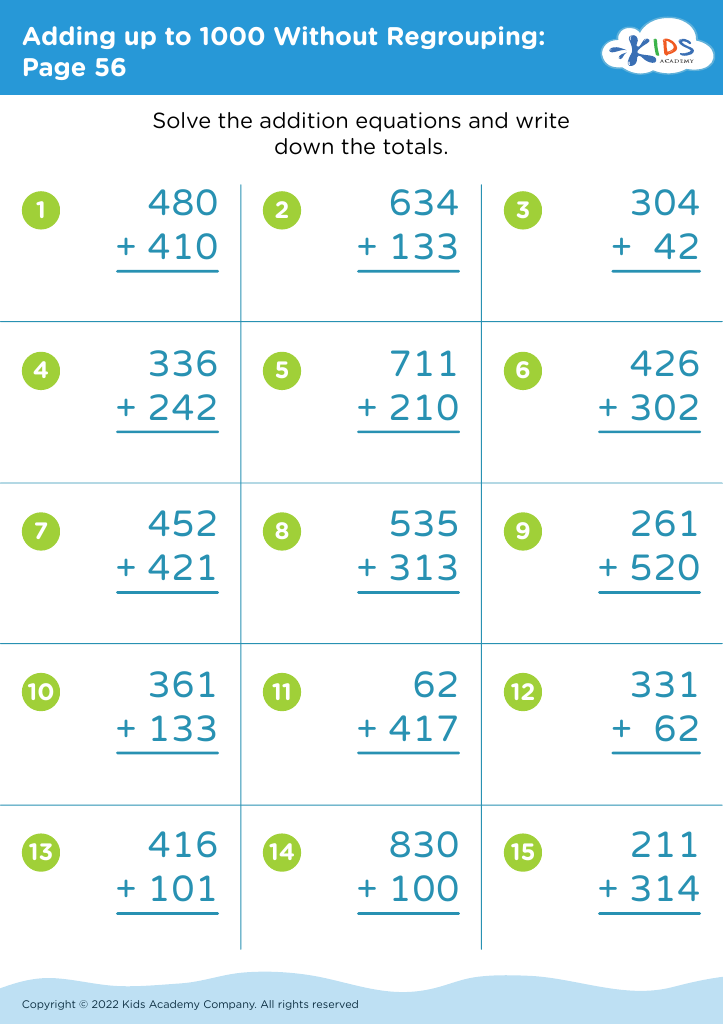
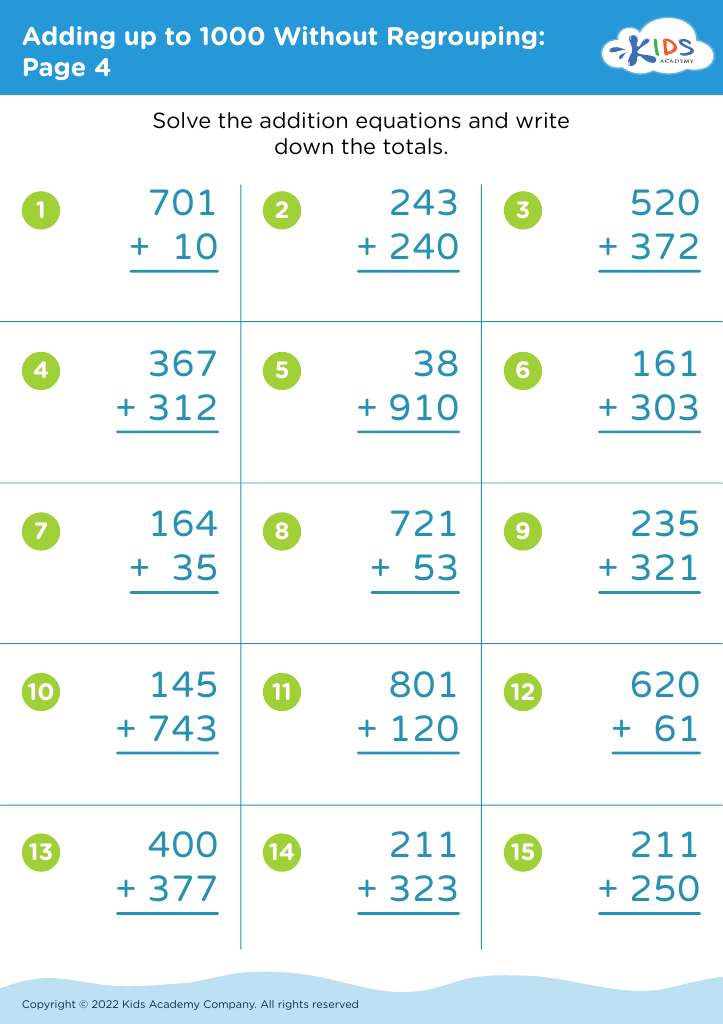
Unlock your child's reading potential with our engaging "Reading Comprehension Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets" designed for ages 6-7. These expertly crafted worksheets combine the essentials of basic arithmetic and reading comprehension to enhance both skills simultaneously. Each page offers fun math problems joined with intriguing stories and questions to ensure your young learner grasps adding up to 1000 without regrouping. Perfect for school or home use, these worksheets make learning enjoyable and effective, setting solid foundations in math and literacy. Give your child the confidence and skills they need to excel in both areas!
Reading comprehension and mastering basic addition are fundamental skills for young learners aged 6-7, bridging literacy and numeracy. Parents and teachers should care about these skills as they are foundational to a child's academic success and everyday problem-solving abilities. Let's explore why focusing on both areas is essential.
Reading comprehension requires students to understand and process text, fostering critical thinking, language development, and building knowledge across various subjects. When children comprehend what they read, they can follow instructions, gain new information, and become more self-reliant learners. This skill boosts their confidence and lays the groundwork for future learning and standardized testing.
Similarly, being able to add numbers up to 1000 without regrouping nurtures a child's understanding of basic mathematics. This competence not only helps in performing day-to-day tasks like handling money but also sets the stage for more advanced mathematical concepts. Proficiency in simple addition helps children grasp the principles of arithmetic, supporting a seamless progression to more complicated topics like multiplication or division.
Investing time and effort in these skills at this early age encourages a balanced development of cognitive abilities that are vital for both academic and real-world applications. Therefore, a joint focus on improving reading comprehension and basic arithmetic is key to fostering well-rounded, capable young learners.