Problem-solving abilities Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
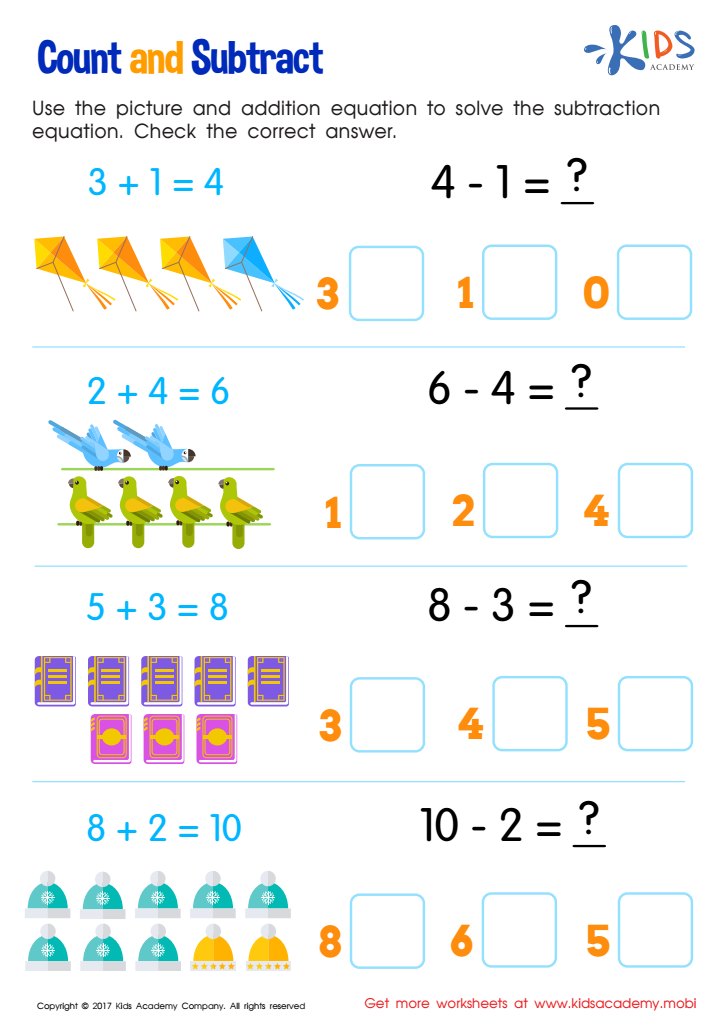

Count and Subtract Worksheet
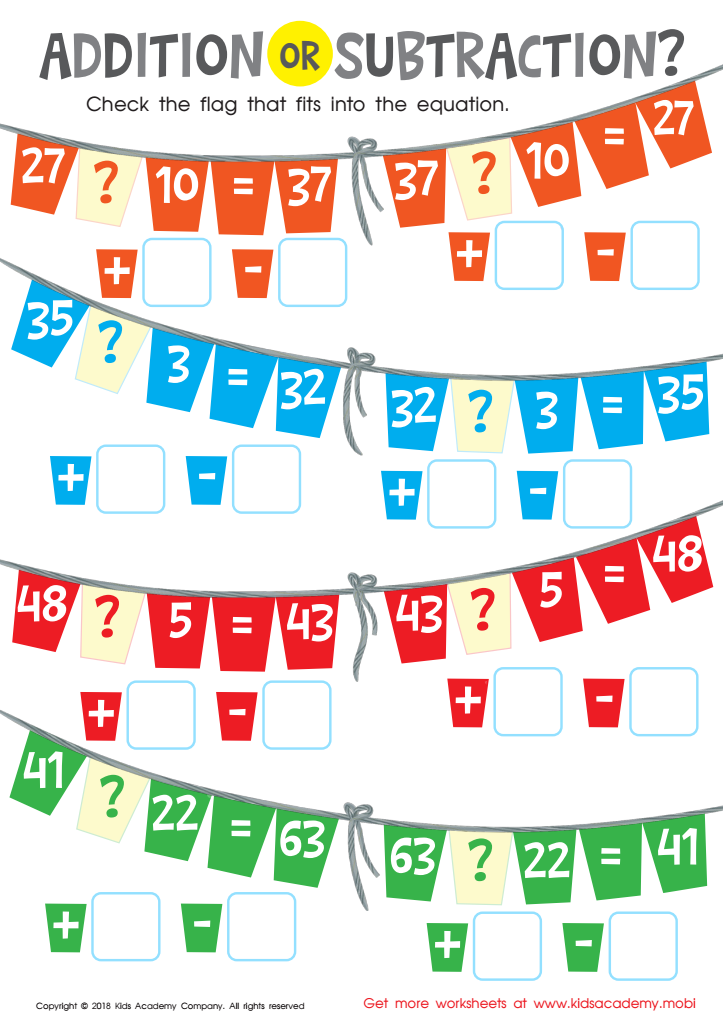

Addition or Subtraction? Worksheet
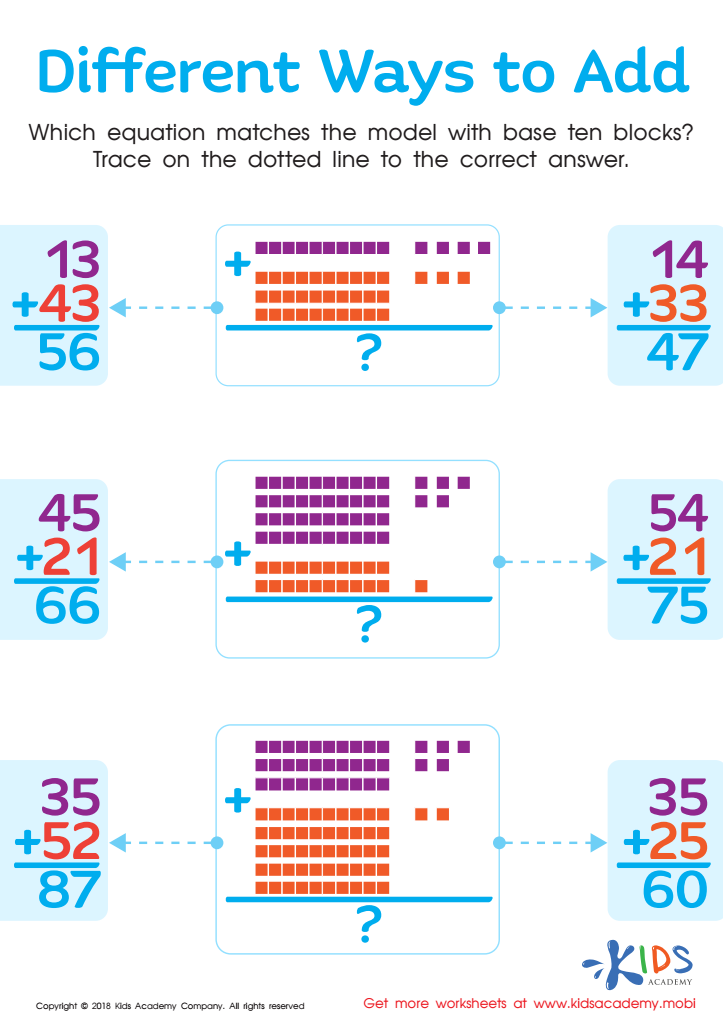

Different Ways to Add Worksheet
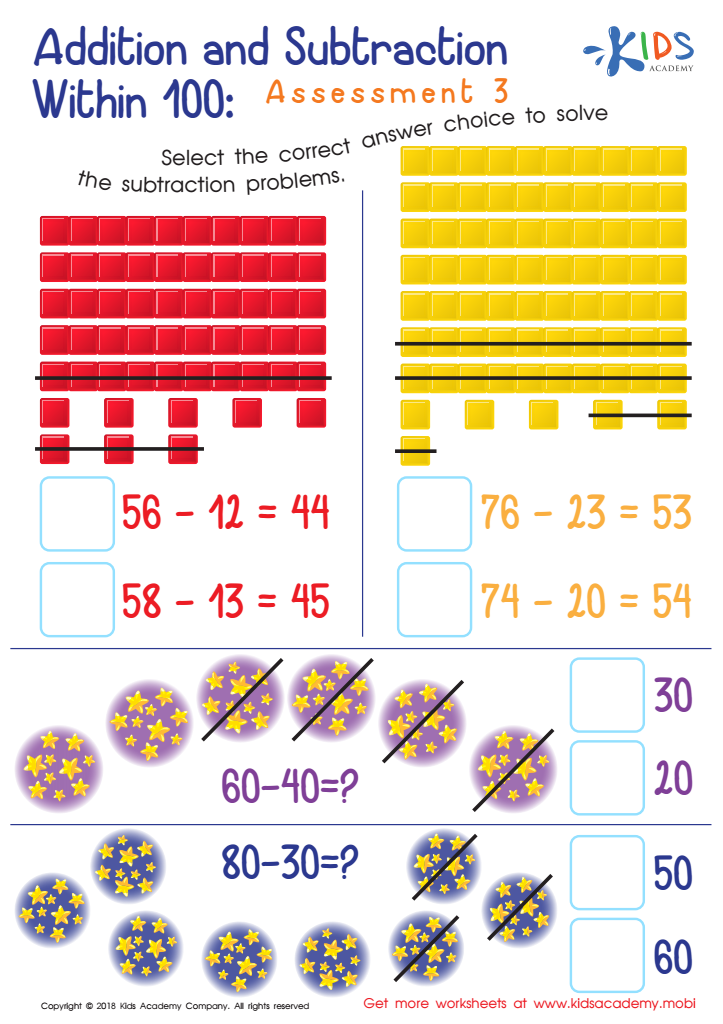

Addition and Subtraction Within 1: Assessment 3 Worksheet

Pyramid Math to Make 11 Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize problem-solving abilities in addition and subtraction for children aged 6 to 8 because these skills serve as foundational pillars for future learning in mathematics and beyond. At this age, children are transitioning from concrete understanding to more abstract thinking; thus, encouraging robust problem-solving in basic arithmetic not only enhances their numerical comprehension but also fosters critical thinking skills.
By engaging in problem-solving activities, children learn how to apply mathematical concepts to real-world situations. This practical application helps to solidify their understanding and boosts their confidence in tackling more complex problems as they advance in their education. Furthermore, developing these skills early enables children to recognize patterns, improve their logical reasoning, and enhance their analytical thinking—capabilities that extend well beyond math.
Additionally, strong problem-solving skills in addition and subtraction contribute to better performance in standardized testing and assessments, setting a positive precedent for future academic success. Supporting children in mastering these abilities lays the groundwork for perseverance and resilience, encouraging them to explore challenges and view mistakes as opportunities for growth. Ultimately, fostering problem-solving skills in young learners nurtures curiosity and a love for learning that lasts a lifetime.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















