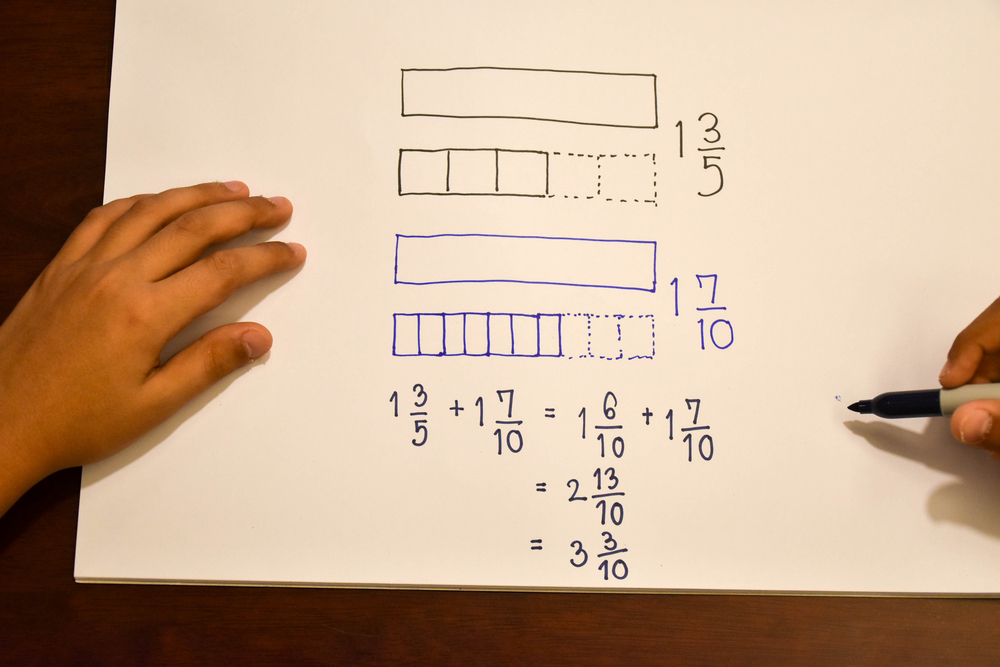
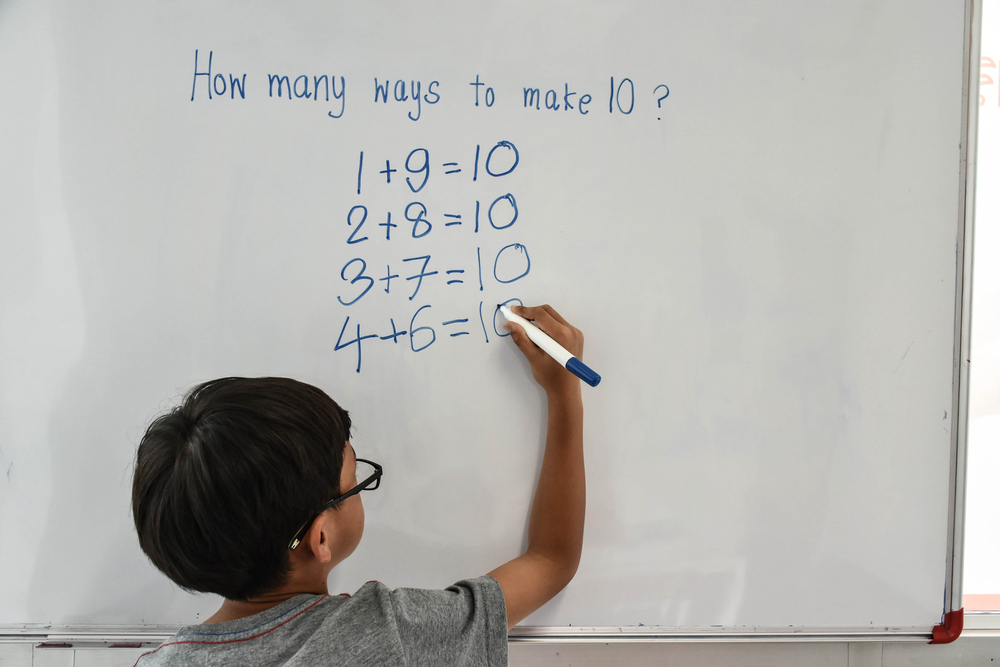Basic Math Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 7
148 filtered results
-
From - To
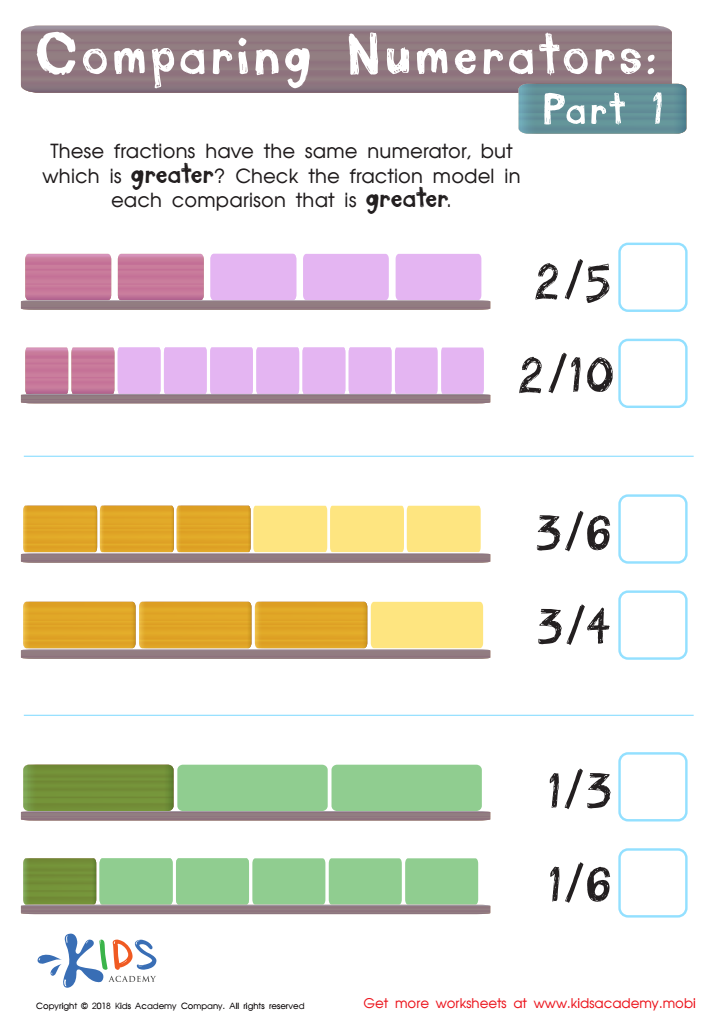

Comparing Numerators Part 1 Worksheet
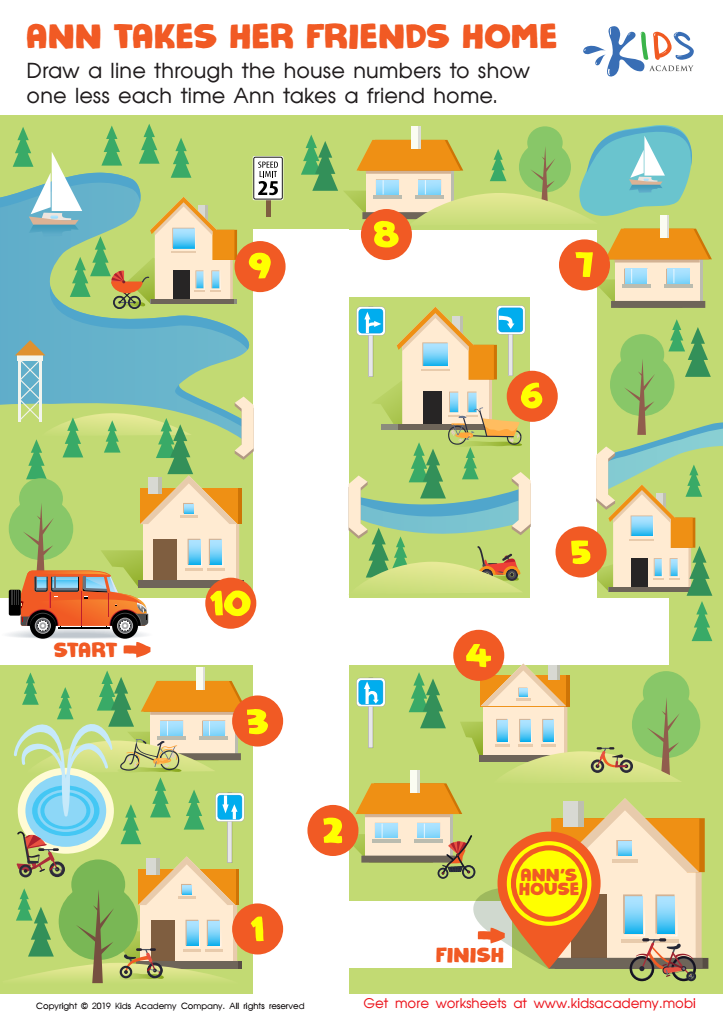

Ann Takes her Friends Home Worksheet
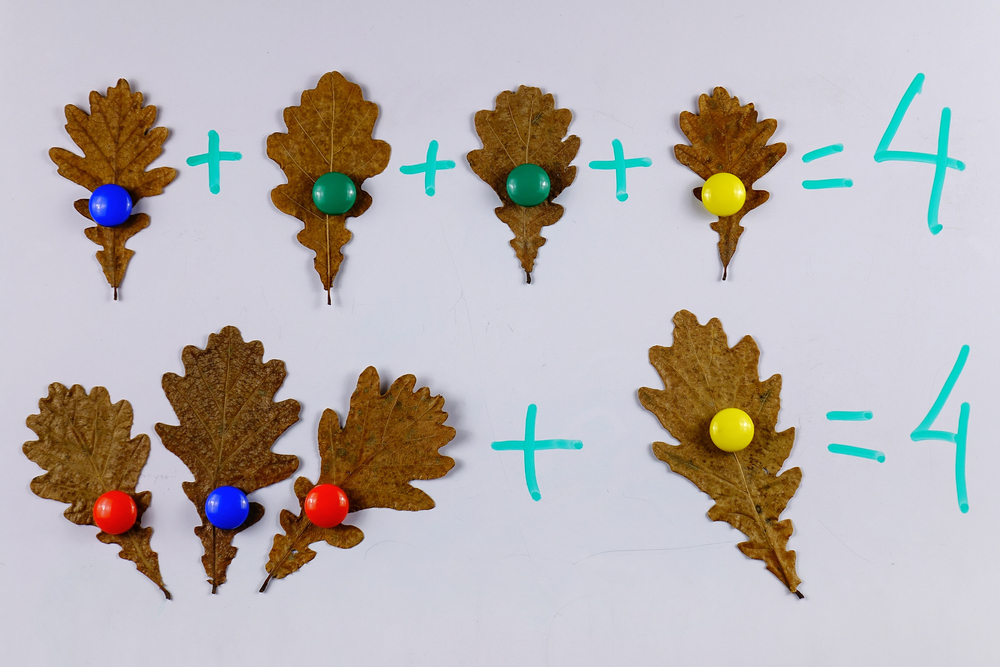
Basic math skills are foundational for children's academic success and everyday life. For children aged 6-8, developing these skills is especially critical, as this is a key period for cognitive growth and understanding mathematical concepts. Early math proficiency not only boosts children's confidence but also fosters logical thinking and problem-solving abilities that are essential in all areas of study.
Parents and teachers should prioritize basic math because these skills, including addition, subtraction, and understanding numbers, set the groundwork for more complex math topics in the future. Engaging children in hands-on activities and real-life situations, like shopping or cooking, helps them make connections between math and their world, enhancing retention and interest.
Additionally, children with strong math skills are more likely to excel in standardized testing and have increased opportunities in STEM fields later in life. Moreover, establishing a positive, supportive environment around math during these formative years can mitigate math anxiety and promote lifelong learning.
In summary, nurturing basic math skills for ages 6-8 is crucial for academic growth, everyday problem-solving, and preparing children for future educational and career opportunities. Engaged parents and teachers can make a significant impact on a child's lifelong relationship with math.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students