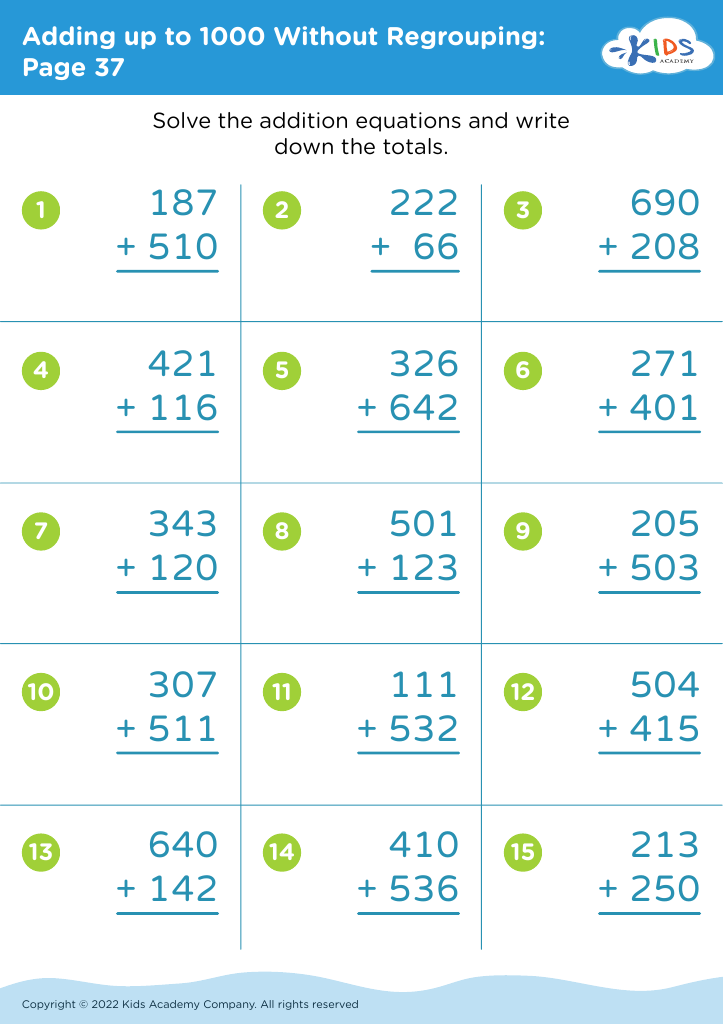
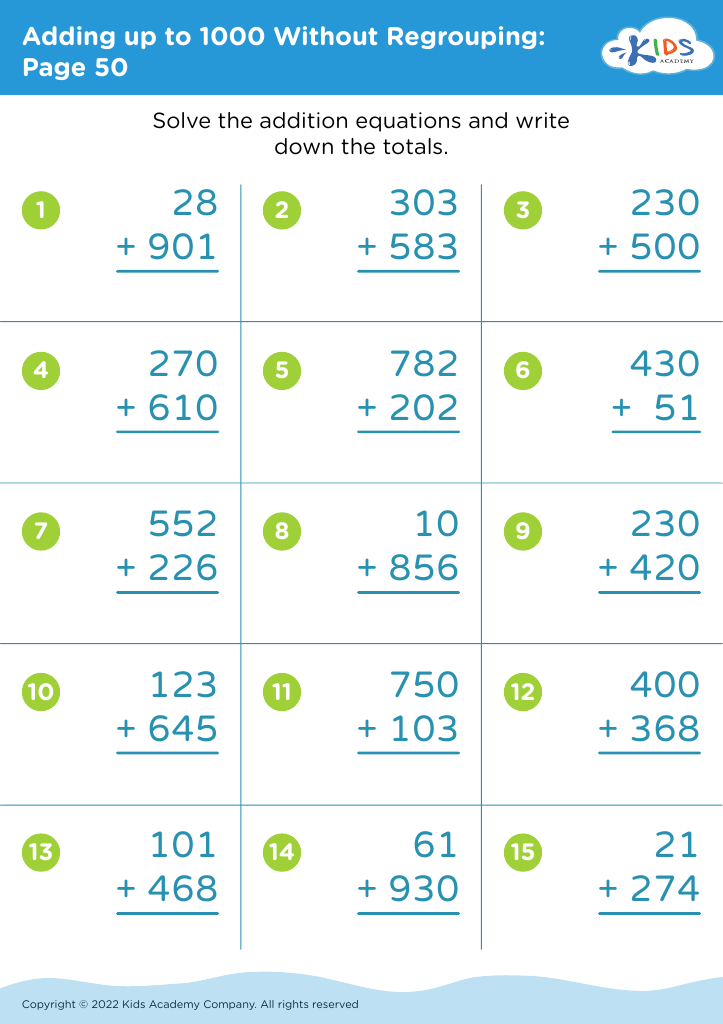
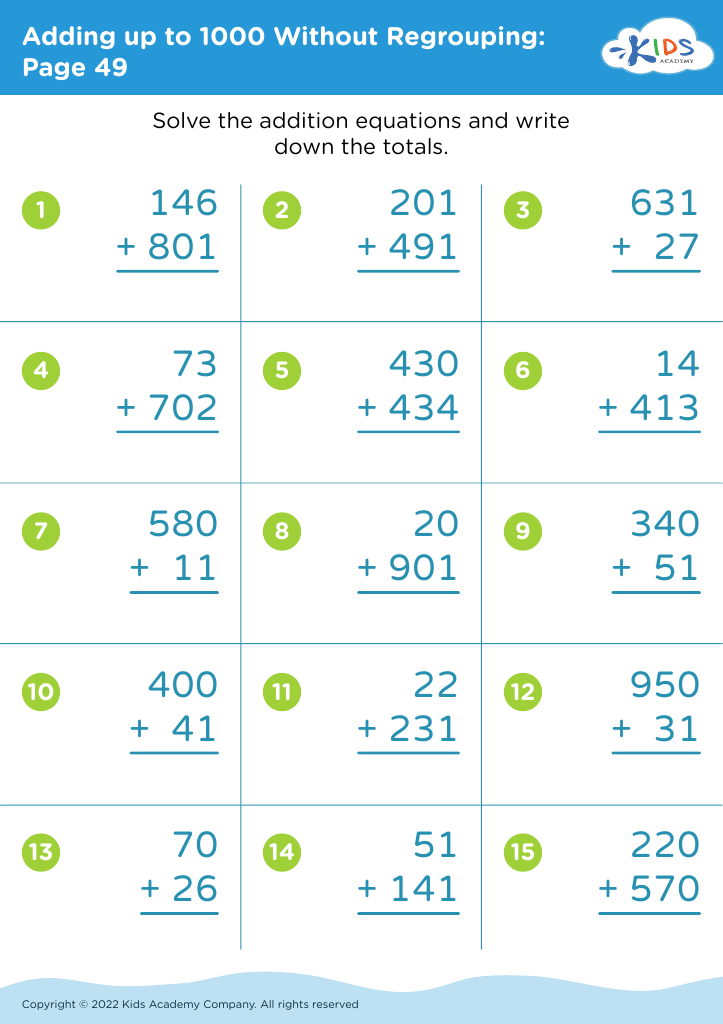
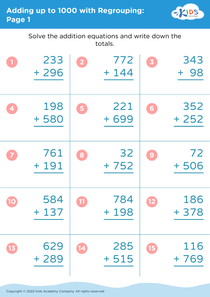
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 7-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets" specifically designed for children aged 7-8. These worksheets combine foundational math concepts with fine motor skill development, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience. By focusing on addition without regrouping, kids practice essential arithmetic while improving hand-eye coordination and pencil control. Perfect for reinforcing classroom learning, these worksheets make practicing math enjoyable and creative. With vibrant illustrations and interactive exercises, they help maintain children's interest and boost their confidence. Download now to support your child's growth in both mathematical skills and fine motor coordination! Ideal for homeschoolers and educators alike!
Fine motor skills and arithmetic mastery—such as adding up to 1000 without regrouping—are crucial for children ages 7-8, as they play a significant role in the overall development of young learners. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles for tasks like writing, drawing, and manipulating objects. Developing these skills enhances a child’s ability to perform daily activities, boosts confidence, and supports better academic performance.
When children master addition without regrouping, they gain a foundational understanding of numbers that is critical for future math concepts. This skill teaches them to break down tasks into manageable parts and improves their problem-solving abilities. Additionally, the integration of fine motor skills with mathematics reinforces the idea that learning is interconnected, allowing children to approach subjects holistically.
Moreover, encouraging tasks that require both fine motor skills and arithmetic, such as using manipulatives or engaging in interactive math activities, helps create a positive and stimulating learning environment. When parents and teachers emphasize the importance of these skills, they support children’s cognitive, physical, and emotional development, ensuring they are well-equipped for more challenging concepts in the future. Investing time in these areas ultimately fosters a love of learning and improves self-efficacy in various academic disciplines.