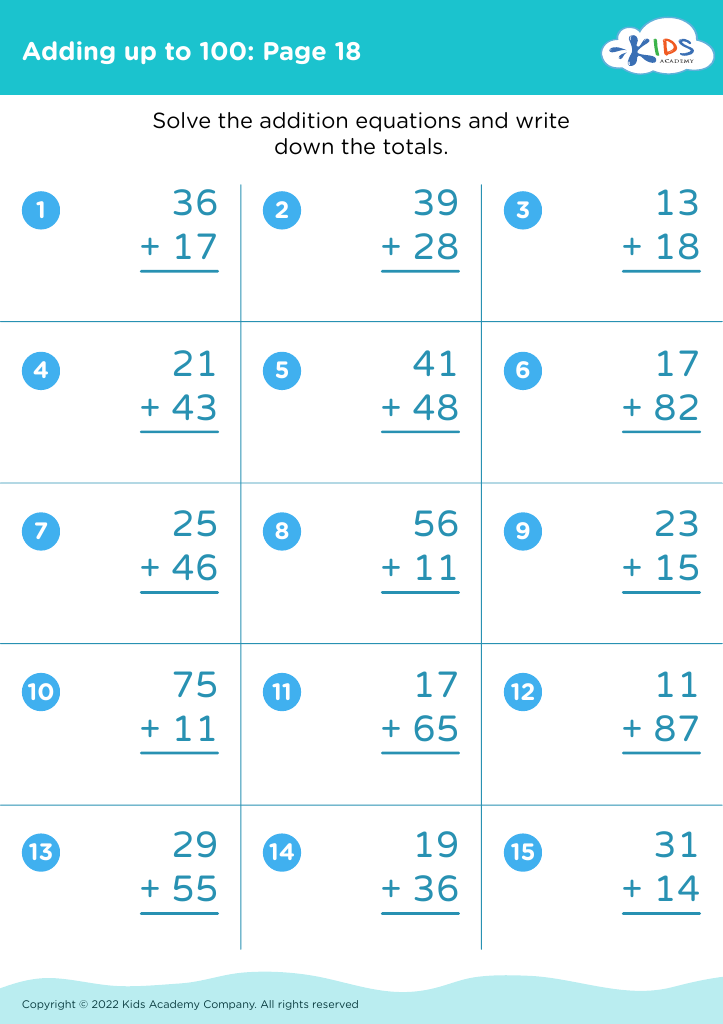
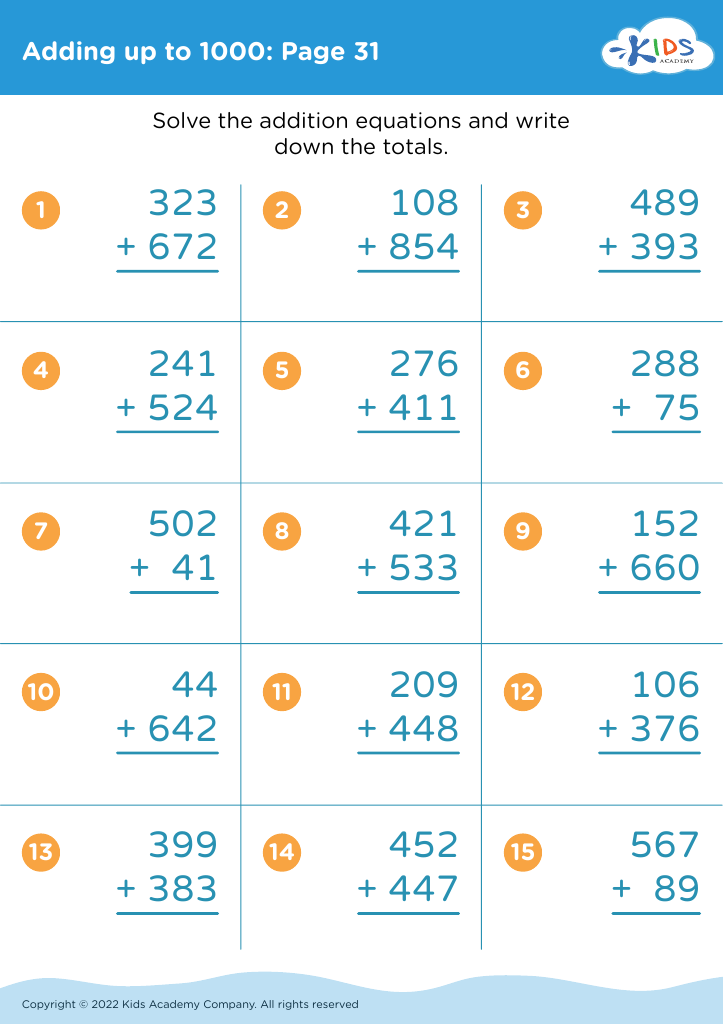
Practice writing numbers Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 7-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child’s math skills with our "Practice Writing Numbers Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 7-8"! These engaging and colorful printable worksheets focus on basic arithmetic, reinforcing number writing, addition, and subtraction concepts tailored for early learners. Designed by educators, each worksheet combines fun exercises with effective learning strategies to enhance problem-solving skills. Ideal for classroom use or homeschooling, these worksheets help children build confidence in math through practice and repetition. Dive into our collection to make mastering numbers an enjoyable experience for your young mathematicians! Visit our website to download and start practicing today.
Parents and teachers play a pivotal role in the foundational development of children, and mathematics is a cornerstone of that process. Ensuring that children ages 7-8 practice writing numbers, addition, and subtraction is essential for their cognitive development and future academic success. This practice helps solidify their understanding of basic number concepts, which are the building blocks for more advanced mathematical thinking.
Children at this age are typically in the second or third grade, a critical period for obtaining basic arithmetic skills. Regular practice enhances their numerical fluency, aiding them in performing calculations more quickly and accurately. These skills also foster a child's confidence, as proficiency in arithmetic can reduce math-related anxiety and increase their enjoyment of the subject.
Moreover, early arithmetic practice improves problem-solving skills and logical thinking, supporting overall academic performance. It assists in interdisciplinary areas such as reading (understanding word problems) and science (measuring and data collection). Writing numbers accurately develops fine motor skills and reinforces the relationship between numbers and quantities, which is crucial for understanding more complex mathematical concepts.
Thus, investing time in practicing these basic skills ensures children are not only proficient in arithmetic but also prepared for a future where math demands become increasingly sophisticated.