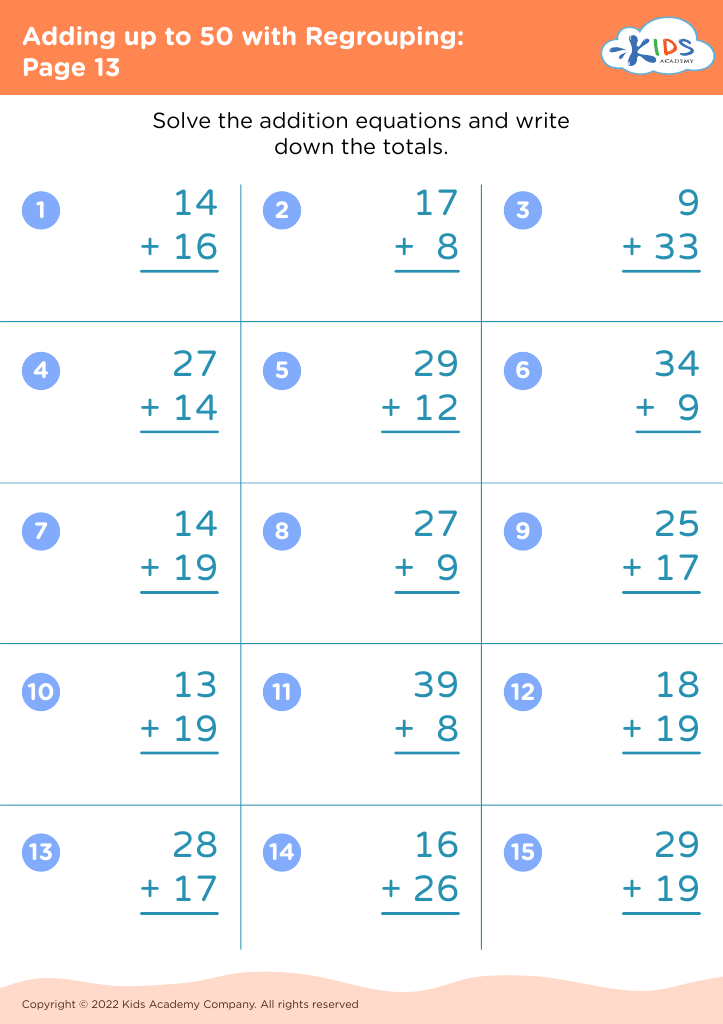
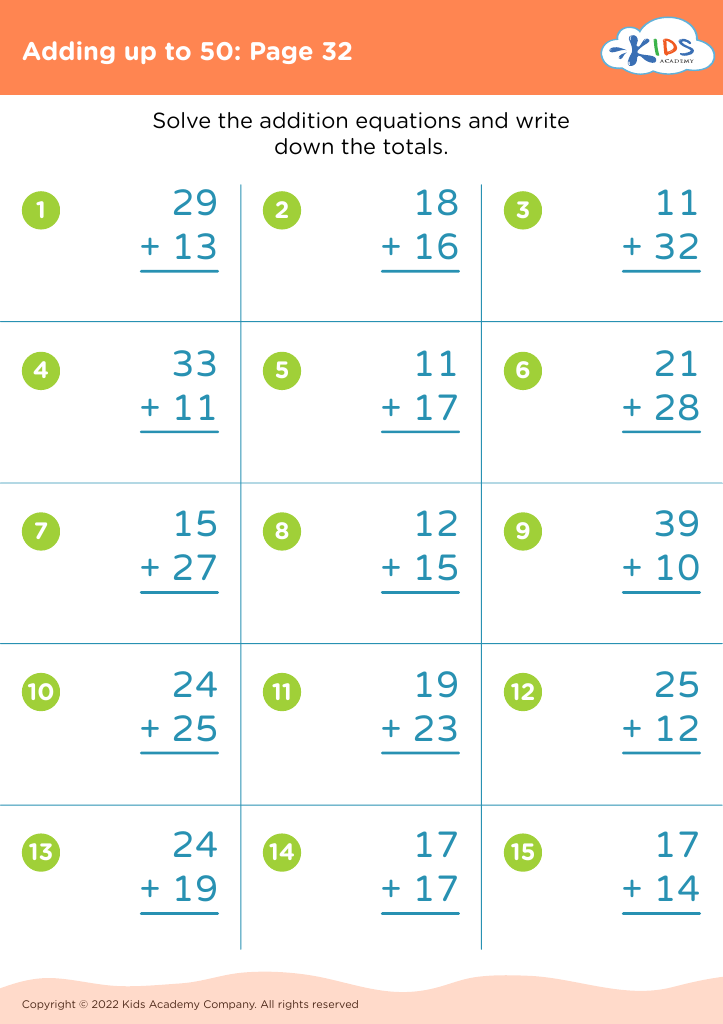
Counting skills Math Worksheets for Ages 8-9 - Page 7
150 filtered results
-
From - To
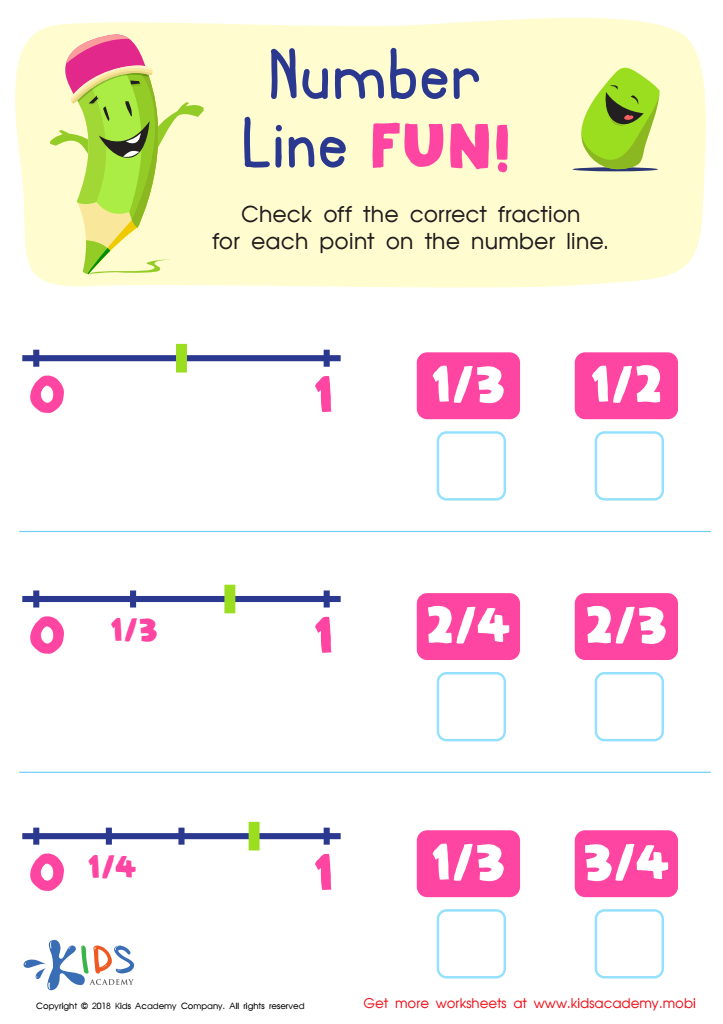

Number Line Fun Worksheet
Counting skills are fundamental building blocks for children aged 8-9, often at the key stage of primary education. Mastery of counting is crucial because it serves as the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. At this age, students transition from concrete to more abstract mathematical thinking; understanding counting helps them make this shift more smoothly.
For parents and teachers, ensuring that children are proficient in counting skills enables the development of logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities. Counting trains the brain to think sequentially and recognize patterns, both of which are essential not just for mathematics but for everyday decision-making and tasks.
Moreover, confidence in basic counting promotes a positive attitude towards math in general. When children understand and can manipulate numbers effectively, they are more likely to enjoy the subject and less likely to experience math anxiety. This can have long-term benefits, encouraging a proactive approach to learning and making children more resilient when facing academic challenges.
Lastly, counting skills also have practical uses in daily life, such as managing money, telling time, and following steps in a process, thereby promoting independence. Therefore, supporting strong counting skills helps set the stage for academic success and everyday competency.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students