Fine Motor Skills Kindergarten Numbers 0–10 Worksheets - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To
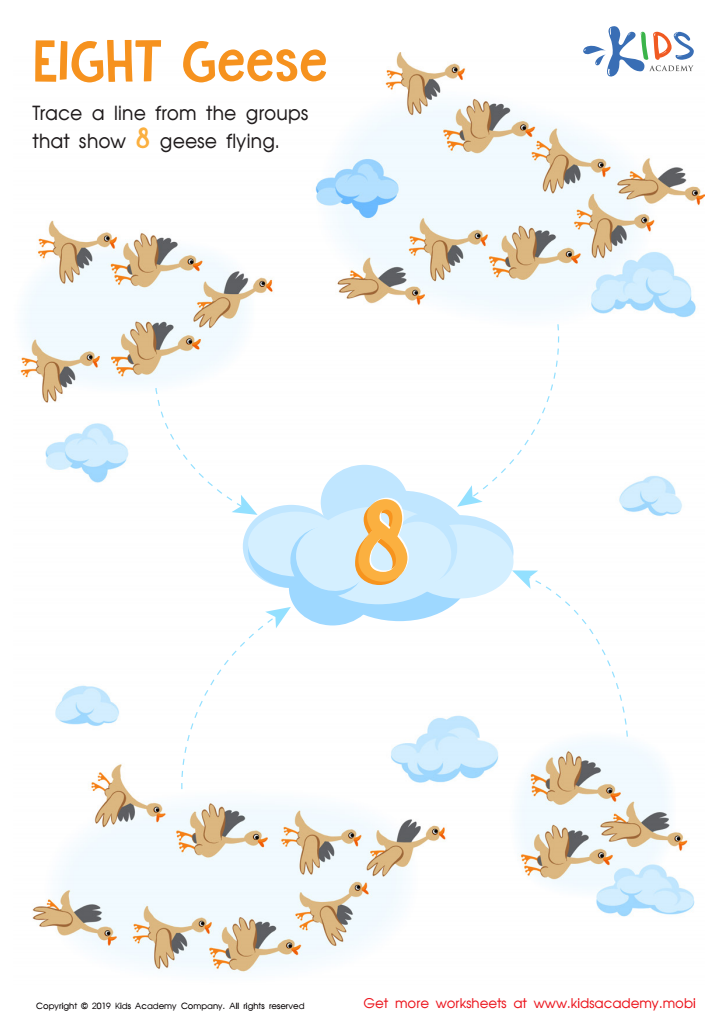

Eight Geese Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet
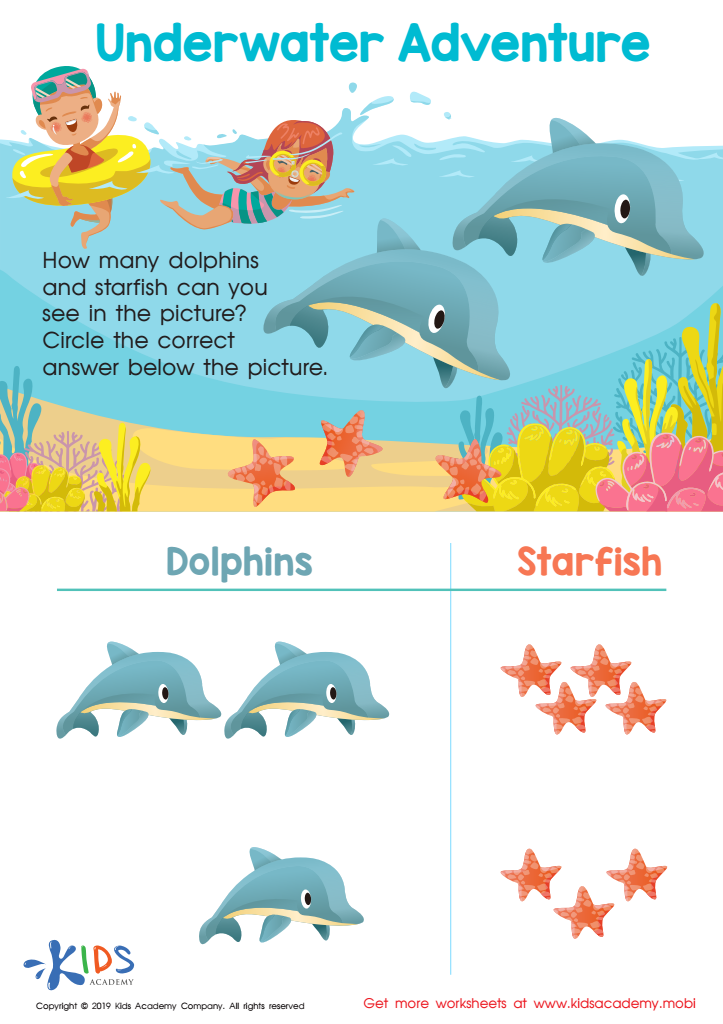

Underwater Adventure Worksheet
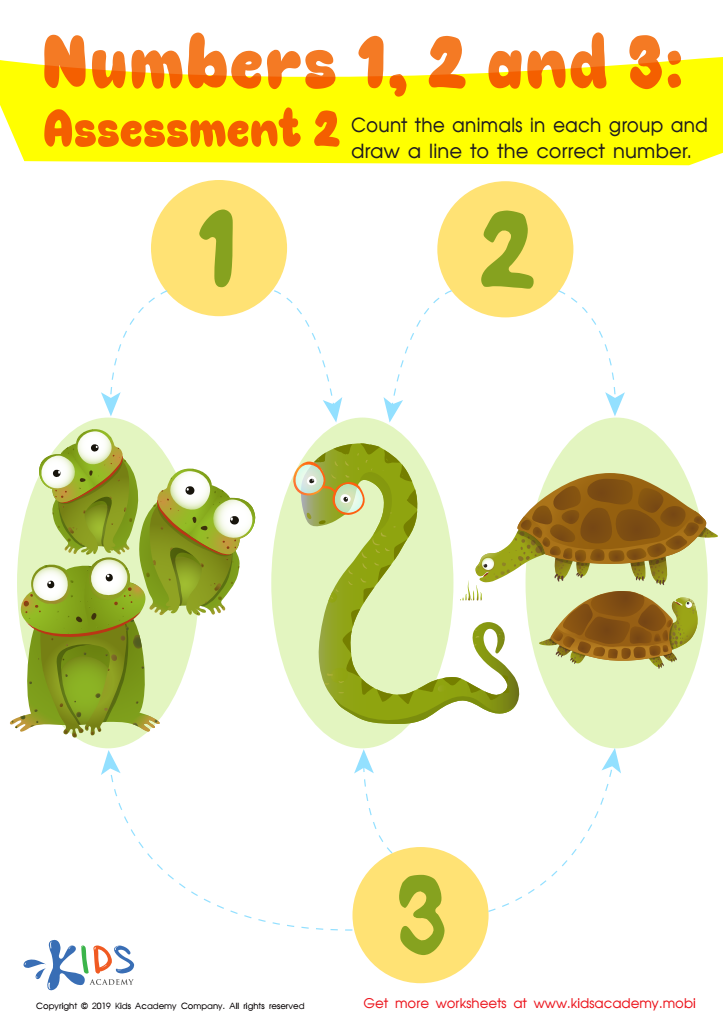

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet


Sloth – Coloring by Numbers


Count the Cucumbers and Trace the Number 8 Printable


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Sea Adventure – Coloring by Numbers


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


In the Treetops – Coloring Page


Great Hornbill – Coloring by Numbers


Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers


Little Chef – Coloring by Numbers


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet


A Fox and a Bird – Coloring by Numbers


Little Pilot – Coloring by Numbers


Little Red Riding Hood – Coloring by Numbers


In the Garden – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children's overall development and academic success. These skills involve the coordinated use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for various daily activities. Focusing on fine motor skills in relation to kindergarten numbers 0–10 offers multiple benefits.
Firstly, fine motor activities, such as tracing or drawing numbers, enhance hand-eye coordination and muscle control, foundational skills for writing. When children engage in activities like counting manipulatives or forming numbers with clay, they also improve their dexterity and grip strength, vital for holding pencils and performing tasks with precision.
Secondly, understanding and practising numbers 0–10 through hands-on activities bolster cognitive development. It encourages children to think quantitatively, promoting early numeracy skills crucial for later mathematical learning. Associating fine motor tasks with number recognition helps children make meaningful connections between the physical action and abstract concepts.
Finally, fine motor development boosts a child’s confidence and independence, leading to better self-esteem and a positive attitude towards learning. Activities that build fine motor skills can also promote concentration, patience, and persistence—traits that benefit academic pursuits and everyday life.
Thus, integrating fine motor skills with early number education provides a well-rounded approach that supports developmental milestones across cognitive, physical, and emotional domains.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students