Geometry application Worksheets for Kids
1 filtered results
-
From - To
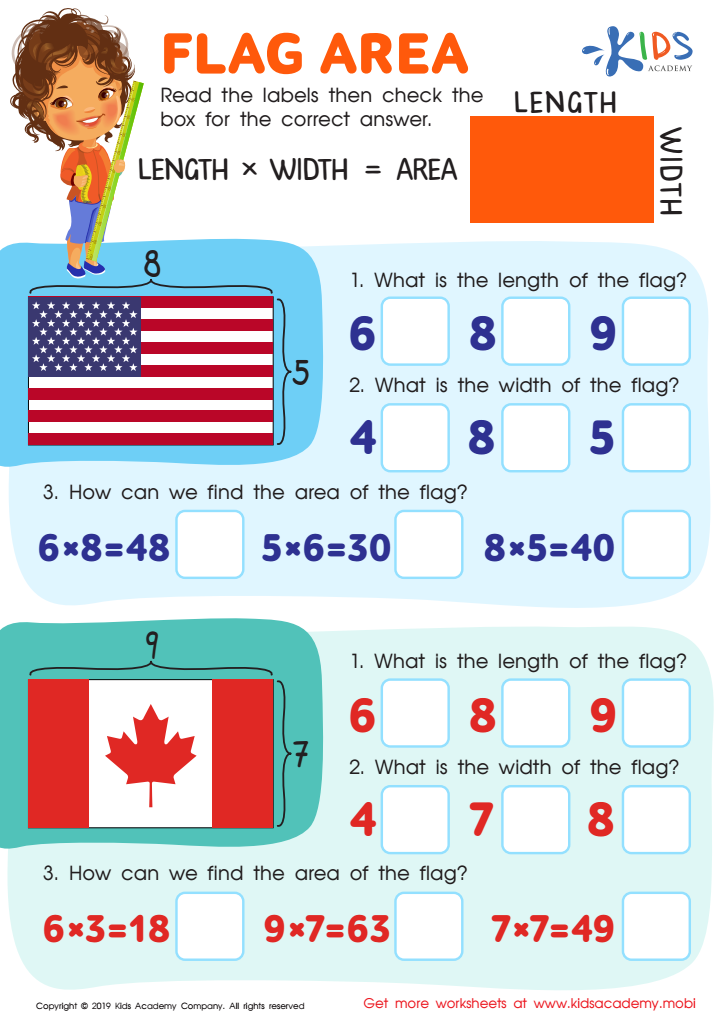

Flag Area Worksheet
Question/Answer
Why is the Geometry application skill important for Grade 3 students?
The Geometry application skill is important for Grade 3 students because it lays the foundation for understanding shapes, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving. It helps students visualize and manipulate objects in their environment, enhancing critical thinking and mathematical literacy. These skills are crucial for success in higher-level math, science, engineering, and daily life activities.
What does the Geometry application skill mean when it comes to Grade 3 Geometry learning?
The Geometry application skill in Grade 3 focuses on students' ability to recognize, categorize, and draw basic two-dimensional shapes, understand the concepts of area and perimeter, and relate geometric figures to real-world objects. It involves practical exercises such as constructing shapes using tools and identifying geometric properties in everyday contexts, enhancing their spatial reasoning and visualization skills.
How to test a Grade 3 student’s Geometry application skills?
To test a Grade 3 student's Geometry application skills, create tasks that require them to use geometric shapes in practical contexts. Include activities like drawing and identifying shapes, understanding symmetry, measuring angles with a protractor, and solving problems involving perimeter and area.
 Assign to the classroom
Assign to the classroom