Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets
3 filtered results
-
From - To
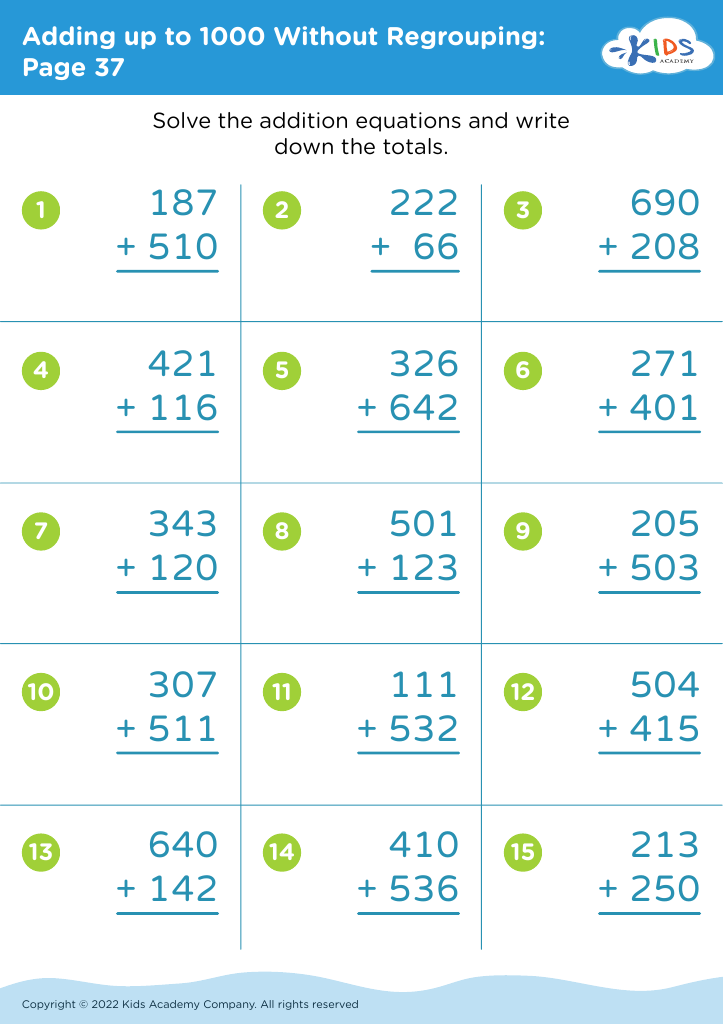
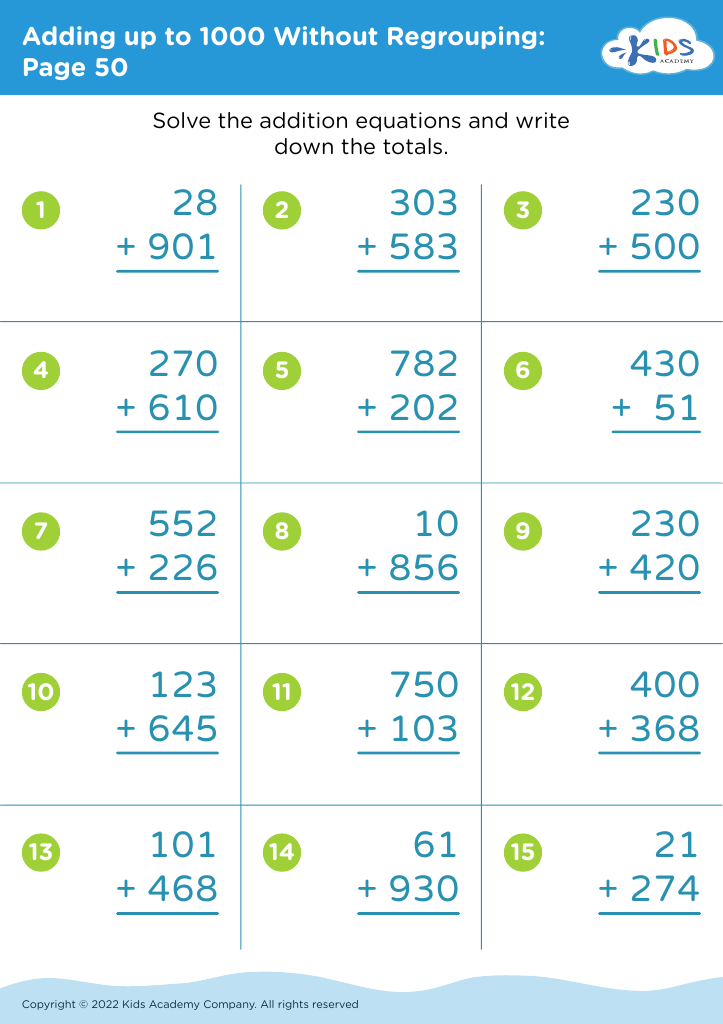
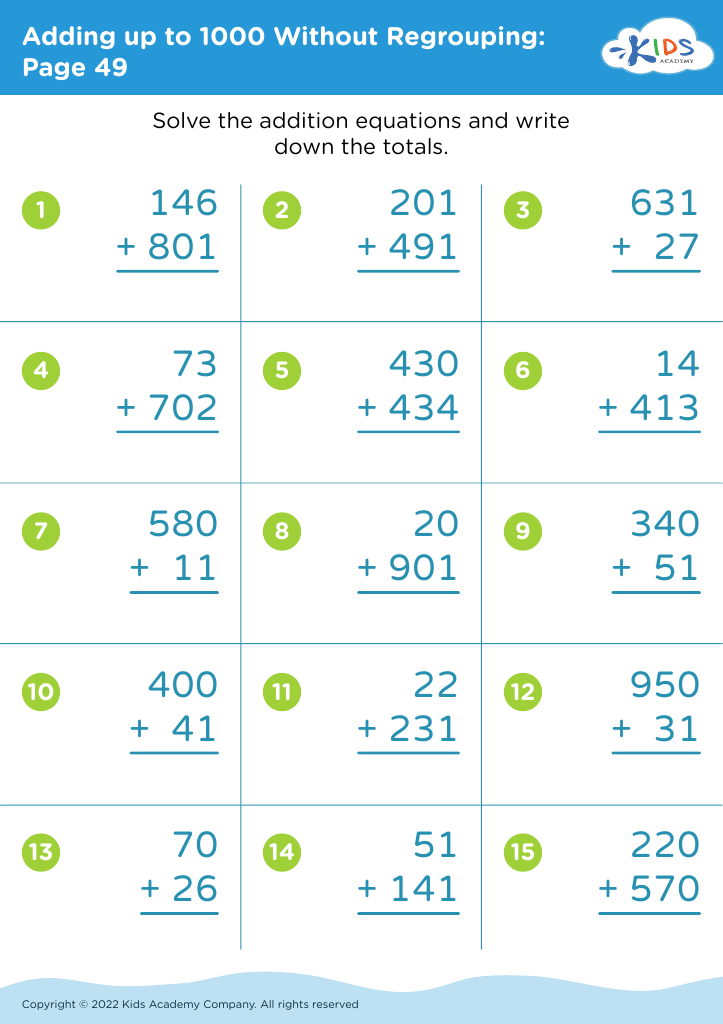
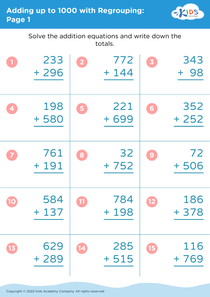
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while mastering addition with our "Fine Motor Skills Adding Up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets". Designed for early learners, these engaging worksheets combine mathematical practice and coordination exercises. Children will enjoy solving addition problems that require adding numbers up to 1000, all without regrouping, reinforcing their understanding of basic arithmetic. Additionally, our worksheets feature fun illustrations and activities that promote hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and control. Perfect for classroom use or at-home practice, these worksheets will not only improve your child's math abilities but also support their physical development in a fun and interactive way!
Fine motor skills are crucial for early childhood development, impacting a child's ability to perform everyday tasks and enhancing cognitive growth. These skills involve the precise movement of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers. Parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills because they lay the foundation for essential functions such as writing, using scissors, and buttoning clothing.
Additionally, developing fine motor skills directly contributes to children’s academic success. For example, mastering skills such as counting, sorting, and writing helps in various subjects, including math and language arts. When children learn to add numbers without regrouping, they engage in deeper cognitive processing, reinforcing both mathematical understanding and fine motor coordination through the physical act of writing numbers.
Moreover, fine motor skill development fosters independence and confidence in children. As they gain proficiency in tasks that require hand-eye coordination, children feel empowered to accomplish more complex challenges, which can positively influence their self-esteem.
In essence, focusing on fine motor skills not only fosters significant academic benefits but also influences a child’s overall growth, instilling a sense of achievement and encouraging lifelong learning. This is why it is vital for parents and teachers to actively support and nurture fine motor skill development in early education.