Mental math practice Normal Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-4
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your toddler’s math skills with our Mental Math Practice Normal Addition Worksheets tailored for ages 3-4. These engaging worksheets are designed to help your preschooler master basic addition concepts effortlessly. Each worksheet promotes cognitive development and reinforces early math principles through fun, visually appealing activities that hold your child’s attention. Perfect for home or classroom use, our addition practices enhance your little one's problem-solving abilities, laying a strong foundation for future mathematical success. Download now and set the stage for a lifetime of love for numbers and mental math proficiency!
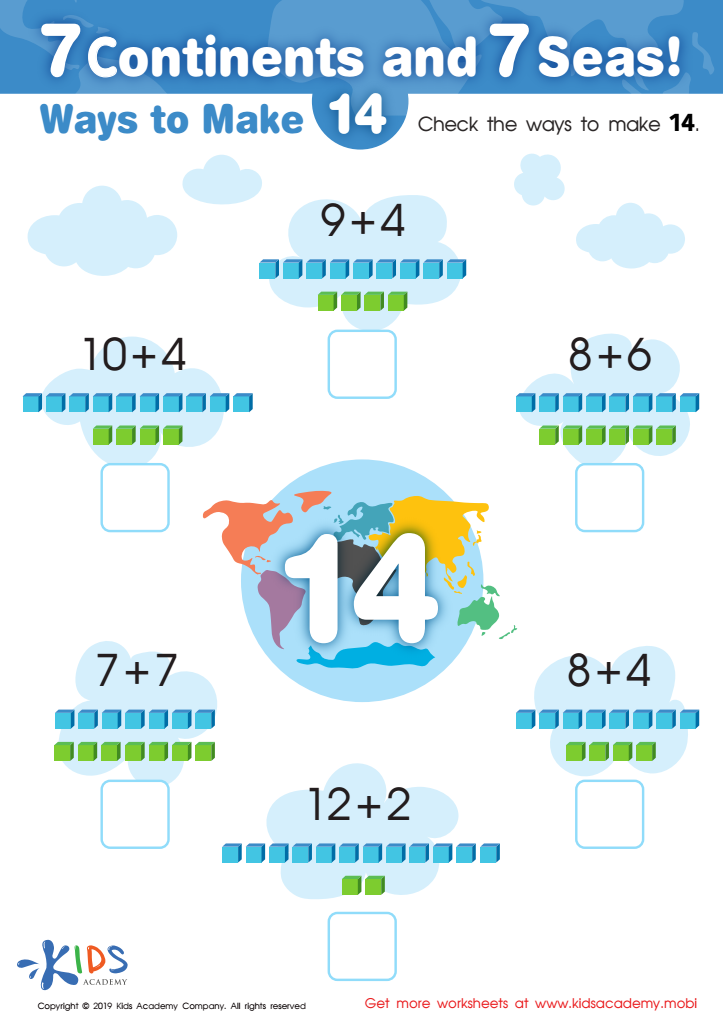

7 Continents and 7 Seas Worksheet
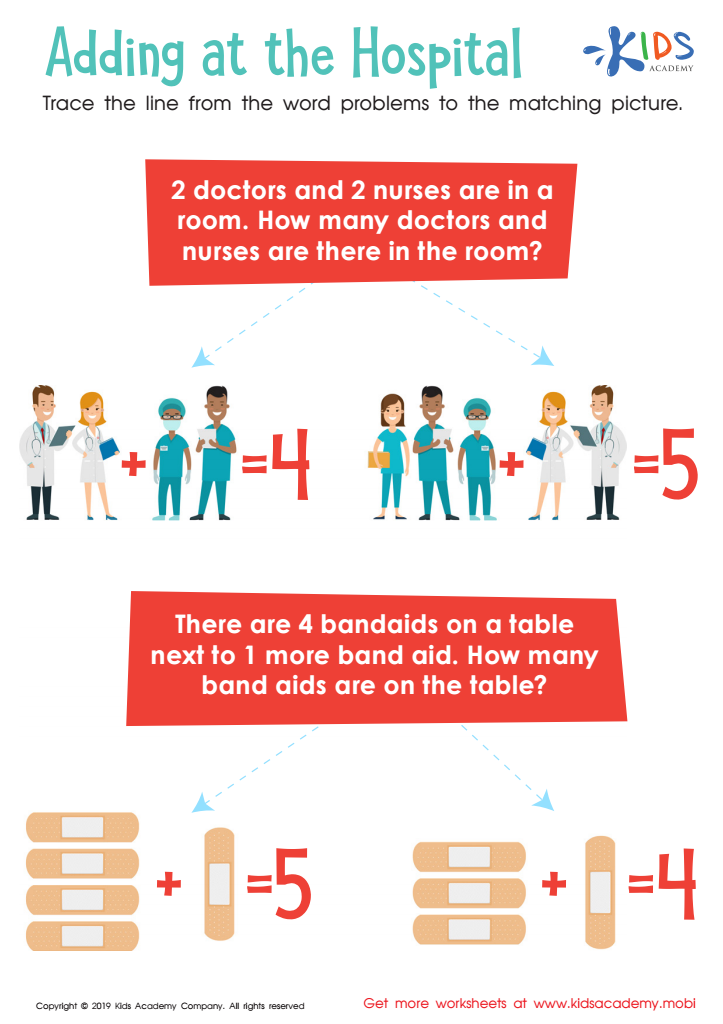

Adding at the Hospital Worksheet


Tricky Problems Worksheet: Part 2
Parents and teachers should place a high emphasis on mental math practice, particularly normal addition, for children ages 3-4 because it lays the foundation for essential cognitive development. At this tender age, children's brains are exceptionally receptive to new information and skills. Introducing mental math engages their brain in a way that fosters numeracy, problem-solving skills, and logical thinking.
Practicing addition at this early age promotes number sense, which is the ability to understand, relate, and connect numbers effectively. This foundational skill is crucial for future mathematical learning and overall academic success. Furthermore, early exposure to addition aids in developing concentration, memory, and the ability to perform mental calculations, reducing dependence on fingers or physical aids.
Engaging toddlers in math through fun and interactive activities boosts their confidence. It also nurtures a positive attitude towards math, counteracting any potential anxiety associated with the subject. Early mathematical practice not only supports cognitive abilities but also enhances everyday life skills. For instance, understanding quantities, following simple rules, and making decisions.
Ultimately, instilling these math foundations sets the stage for a child's educational journey. They will become more adept and comfortable with the increasing complexity of mathematical concepts they encounter as they grow.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















