Fine Motor Skills Normal Science Worksheets for Ages 4-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Develop your child's fine motor skills with our engaging science worksheets tailored for ages 4-7. Created by educational experts, these carefully designed activities help young learners build essential motor skills while exploring fundamental science concepts. Through coloring, tracing, and cutting exercises, children enhance their dexterity, hand-eye coordination, and precision. Our worksheets not only foster scientific curiosity but also support overall development, setting a strong foundation for academic success. With vibrant illustrations and age-appropriate tasks, learning becomes a fun and rewarding experience. Empower your little one with the tools they need to thrive academically and develop crucial motor skills effortlessly!


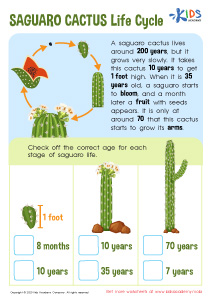
Prickly Nature Worksheet


Underwater Creatures with Shells Worksheet
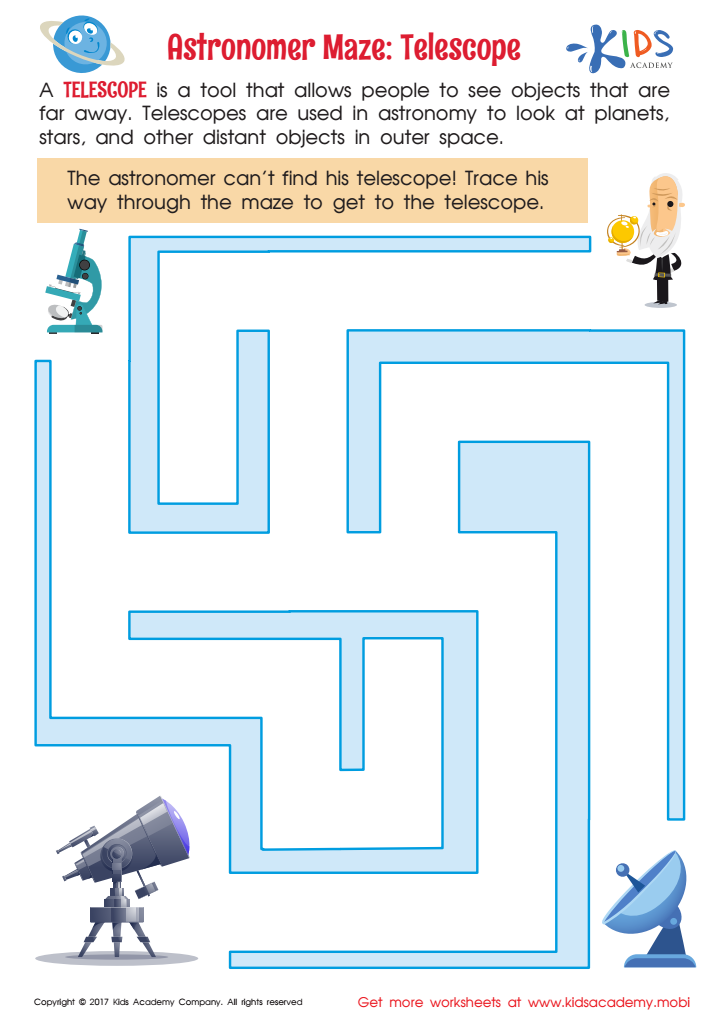

Astronomer Maze: Telescope Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 4-7 as they underpin many everyday tasks and are a fundamental part of early childhood development. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers with the eyes ("hand-eye coordination"), and are essential for activities such as writing, buttoning clothes, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. Well-developed fine motor skills contribute to greater independence and self-confidence in young children, allowing them to perform everyday tasks effectively and confidently.
In the context of academics, fine motor skills are vital for learning to write. The proper formation of letters, numbers, and the ability to stay within lines requires dexterity and control that are gained through fine motor exercise. Moreover, these skills also affect a child’s ability to use computers or tablets—important tools in modern education environments.
Fine motor skill development is also linked to cognitive abilities. Tasks requiring fine motor skills often involve problem-solving, concentration, and the use of language, all of which stimulate brain development. Attention to nurturing fine motor skills by parents and teachers ensures a well-rounded development, setting a strong foundation for future academic success and practical life skills necessary in adulthood.
Thus, caregivers must proactively support activities that enhance a child’s fine motor skills, such as drawing, crafting, and playing with building blocks, to foster overall growth and development.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students



.jpg)