Grammar skills improvement Normal Reading Worksheets for Ages 5-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's grammar skills with our engaging Normal Reading Worksheets, designed specifically for ages 5-9. These worksheets help children build a solid foundation in grammar through fun and interactive exercises. Each activity is tailored to improve key language skills such as sentence structure, punctuation, and parts of speech. Ideal for both classroom use and home learning, these printable resources are easy to access and offer variety to keep young learners motivated. With our Grammar Skills Improvement worksheets, children will gain confidence in their reading and writing abilities while having fun along the way! Start their grammar journey today!


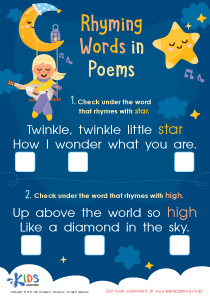
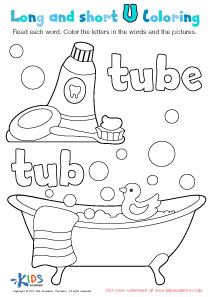
Scrambled Sentences Part 2 Worksheet


Adjectives Worksheet


Where Are Pronouns? Worksheet


Prefix Practice Worksheet: DIS, IM, UM
Parents and teachers should prioritize grammar skills improvement for children aged 5-9 as these foundational abilities play a critical role in a child's overall literacy development. Mastery of grammar enhances reading comprehension, enabling children to make sense of texts and grasp key ideas. When students understand the rules of language, they can decode sentences more effectively, fostering retention and critical thinking skills.
Moreover, strong grammar skills support effective communication. As children learn to construct sentences correctly, they gain confidence in expressing their thoughts and ideas, both verbally and in writing. This not only enriches their academic experience but also encourages social interactions and collaborative learning.
Early grammar instruction sets the stage for future writing success. Children who grasp grammatical conventions are better prepared for more complex language challenges as they progress through school, contributing to improved academic performance.
In summary, parents and teachers play a vital role in nurturing children’s grammar skills, as early proficiency leads to enhanced reading comprehension, increased confidence in communication, and a solid foundation for future learning. Investing time and resources to improve grammar at an early age ultimately leads to more competent and articulate young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students