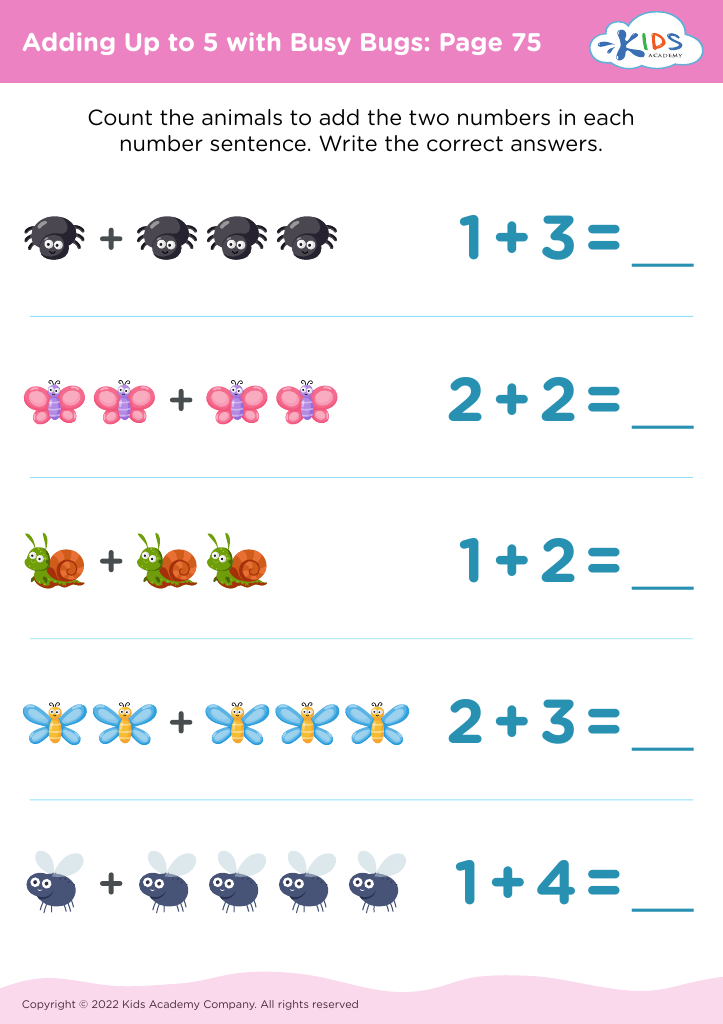
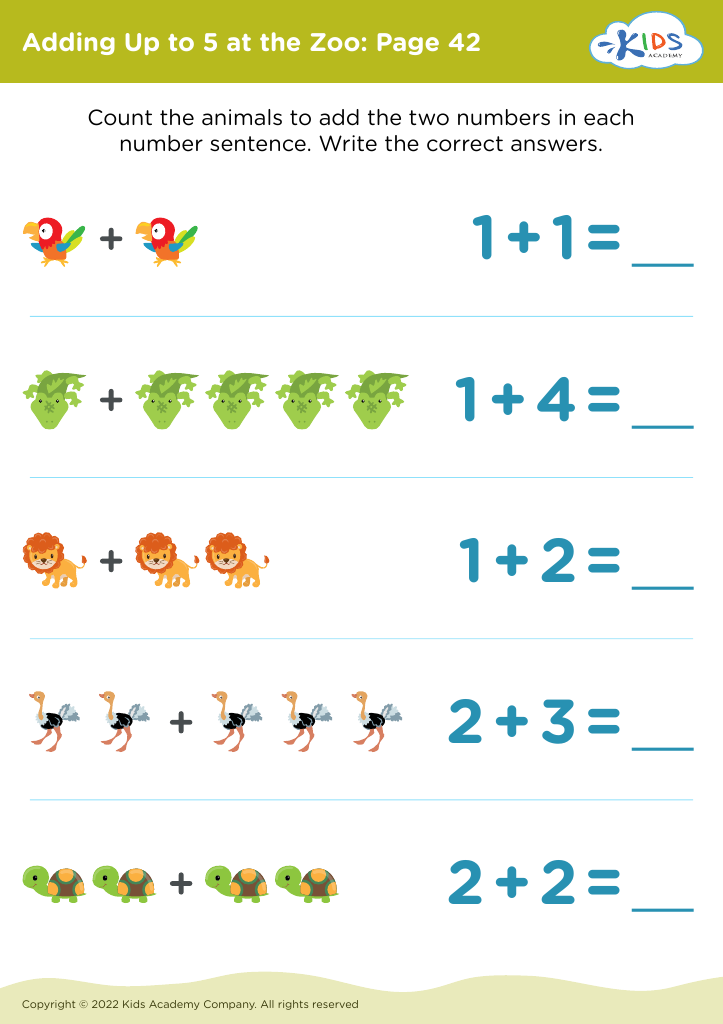Fine motor skills (writing) Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
33 filtered results
-
From - To
Fine motor skills are crucial for children's development, particularly in the early years when they are acquiring foundational skills for writing and mathematical concepts like addition and subtraction. For children aged 3-4, engaging in activities that strengthen fine motor skills—such as drawing, coloring, and manipulating small objects—promotes hand-eye coordination and dexterity. These skills are essential for forming letters and numbers accurately, which lays the groundwork for clear writing.
Incorporating early math concepts like addition and subtraction at this age can also foster a love for learning. Simple activities, such as counting toys or sharing snacks, introduce basic math in a playful context, making it understandable and enjoyable. Practicing these skills through fine motor activities enhances cognitive abilities and critical thinking, essential for problem-solving later on.
Moreover, teachers and parents can create a rich environment that encourages exploration through playful learning. By integrating fine motor tasks with early math concepts, caregivers facilitate not only academic growth but also social and emotional development. Children who develop strong fine motor skills and an early understanding of math concepts are more likely to approach future learning with confidence and enthusiasm. Hence, nurturing these skills in early education is vital for holistic development.