Mathematical thinking Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-4
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's early math skills with our "Mathematical Thinking Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-4". These expertly designed worksheets promote engaging, interactive learning, helping young minds grasp foundational concepts easily. Through fun activities and vivid illustrations, children develop mathematical thinking, improve problem-solving abilities, and build confidence in addition and subtraction. Ideal for home or classroom use, our worksheets meet educational standards and are perfect for sparking a love for mathematics in your little ones. Download now to give your child a head start on their learning journey.
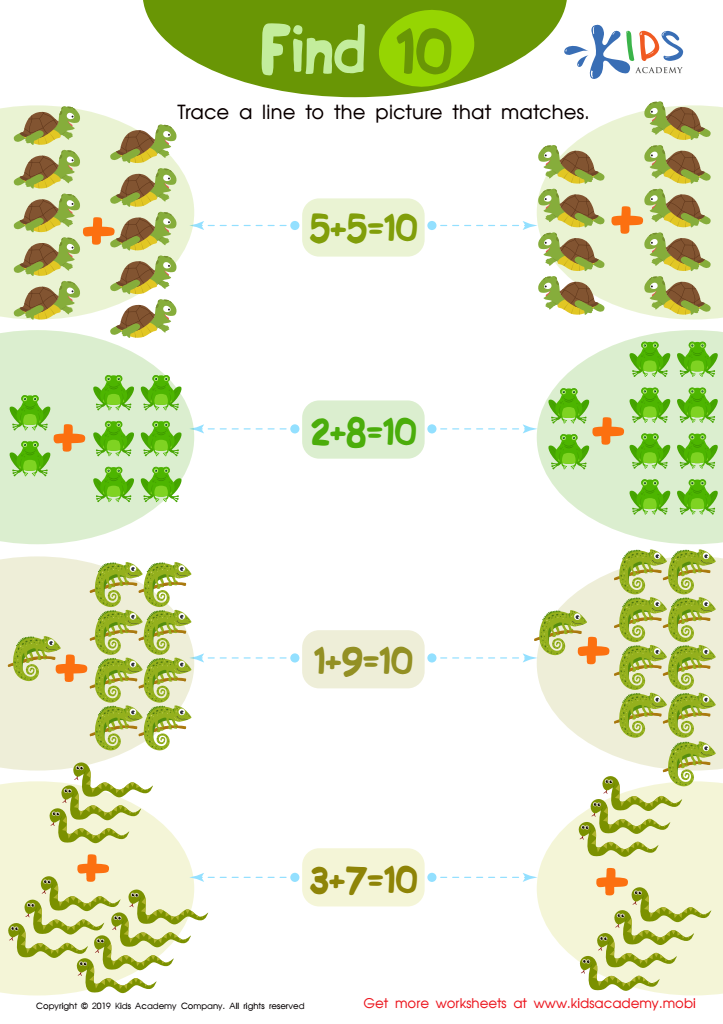

Find 10 Worksheet
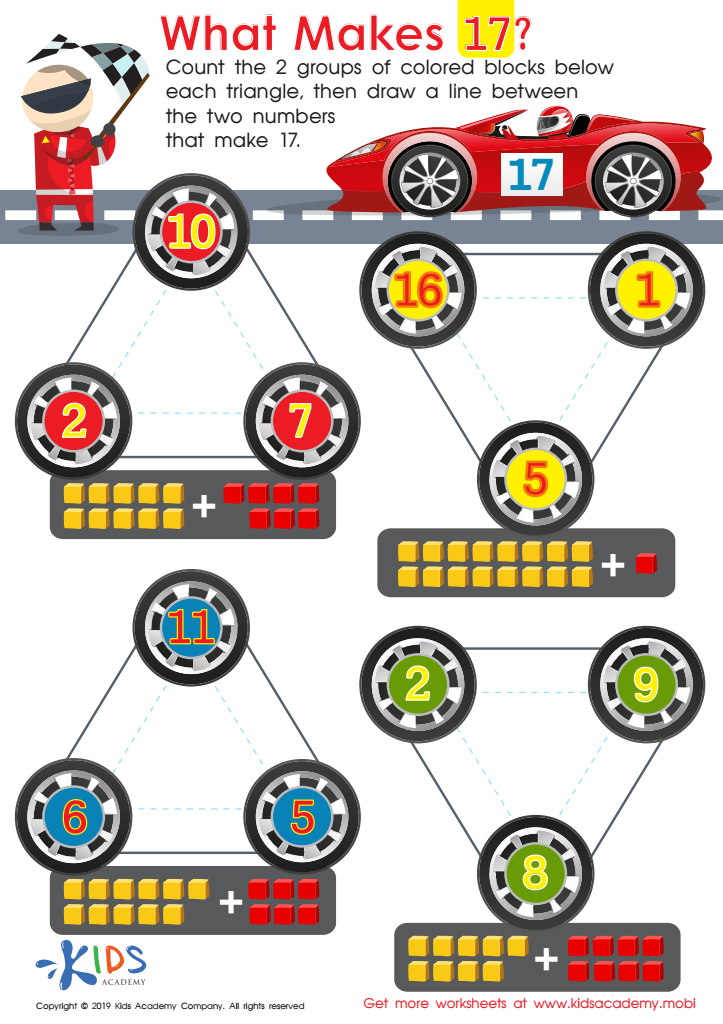

What Makes 17 Worksheet
Mathematical thinking, particularly the concepts of addition and subtraction, is crucial for young children aged 3-4 as it forms the foundation for their future academic and everyday life skills. At this early age, children are naturally curious and rapidly developing cognitive abilities. Introducing them to the basic principles of addition and subtraction allows them to make sense of the world around them in a quantitative manner.
Learning these skills helps enhance their problem-solving abilities and logical reasoning. For example, when children understand that combining two groups of objects results in a larger group (addition), or that taking some away makes a smaller group (subtraction), they develop important cognitive skills such as recognizing patterns and understanding numerical relationships.
Moreover, early exposure to these mathematical concepts boosts confidence, encouraging a positive attitude towards learning and making them more likely to engage in complex mathematical tasks later on. Parents and teachers have a shared role in nurturing these abilities by providing supportive and engaging environments where children can explore numbers through play, everyday activities, and structured learning.
In summary, fostering mathematical thinking in young children equips them with essential life skills and lays a solid foundation for their academic success and critical thinking in various real-world scenarios.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students

















