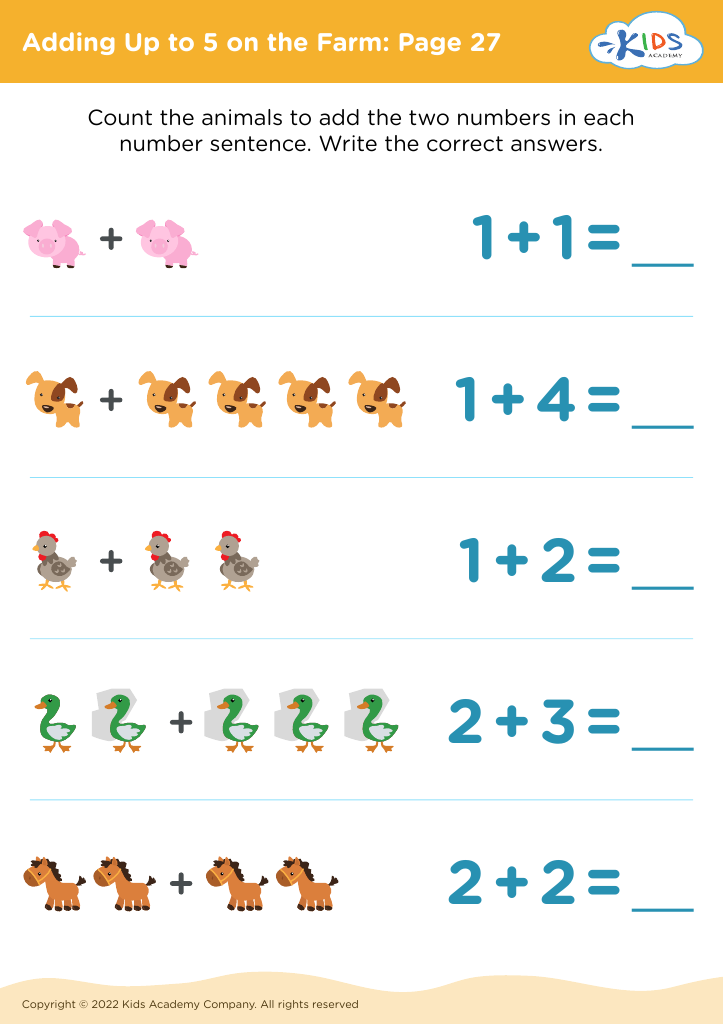Visual perception improvement Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-4
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your preschooler’s math skills with our Visual Perception Improvement Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for ages 3-4! These engaging worksheets focus on enhancing early math understanding, targeting both addition and subtraction fundamentals. Designed specifically for young learners, each activity also strengthens their visual perception abilities, crucial for overall cognitive development. Through vibrant and fun exercises, children practice counting, recognizing numbers, and simple arithmetic in an enjoyable and supportive way. Perfect for at-home practice or classroom use, these worksheets lay a strong foundation for future math success while making learning an exciting adventure! Download and start their learning journey today!
Visual perception is a fundamental skill for young children, especially when it comes to learning mathematics such as addition and subtraction. At ages 3-4, children are in a critical period of cognitive development, where they are developing the ability to interpret and understand visual information from their environments.
Improving visual perception helps children recognize patterns, differentiate between objects, and understand spatial relationships. These skills are essential for performing basic mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. For instance, when a child sees two groups of objects and counts to add them, they rely on their visual perception to understand the groups as distinct yet parts of a whole. Similarly, subtracting requires the ability to visually discern the original group and the removed part accurately.
Focusing on visual perception improvement can lead to stronger foundational math skills, bridging visual understanding with numerical concepts seamlessly. As these children progress in their education, the cognitive skills rooted in strong visual perception will aid in more complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and spatial reasoning tasks.
Additionally, a solid grasp of early math concepts builds confidence and fosters a positive attitude towards learning. By investing time in improving visual perception related to addition and subtraction, parents and teachers set children on a path of academic success and lifelong learning.