Fine Motor Skills Counting Worksheets for Ages 3-4
7 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's learning with our Fine Motor Skills Counting Worksheets designed for ages 3-4. These engaging, age-appropriate printables combine counting practice with activities that strengthen fine motor skills. By tracing numbers, connecting dots, and handling small objects, children improve their hand-eye coordination and precision. Perfect for at-home learning or in educational settings, our worksheets offer a fun and interactive way for little ones to develop early math skills while building essential fine motor abilities. Give your child a head start in math with our comprehensive and skill-building resources!
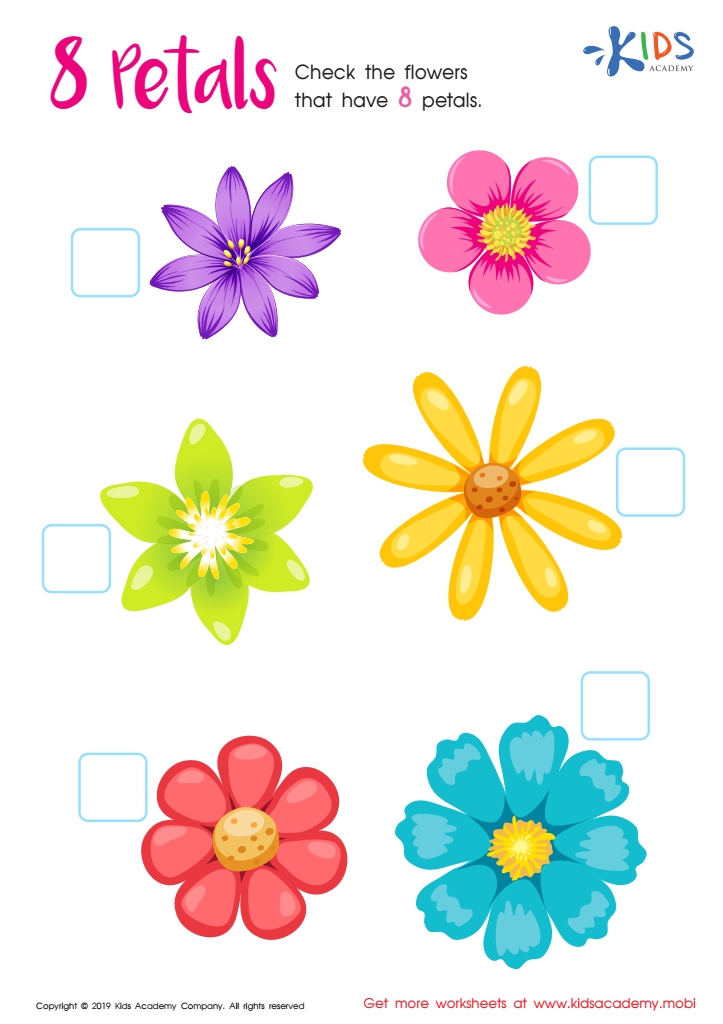


8 Petals Worksheet
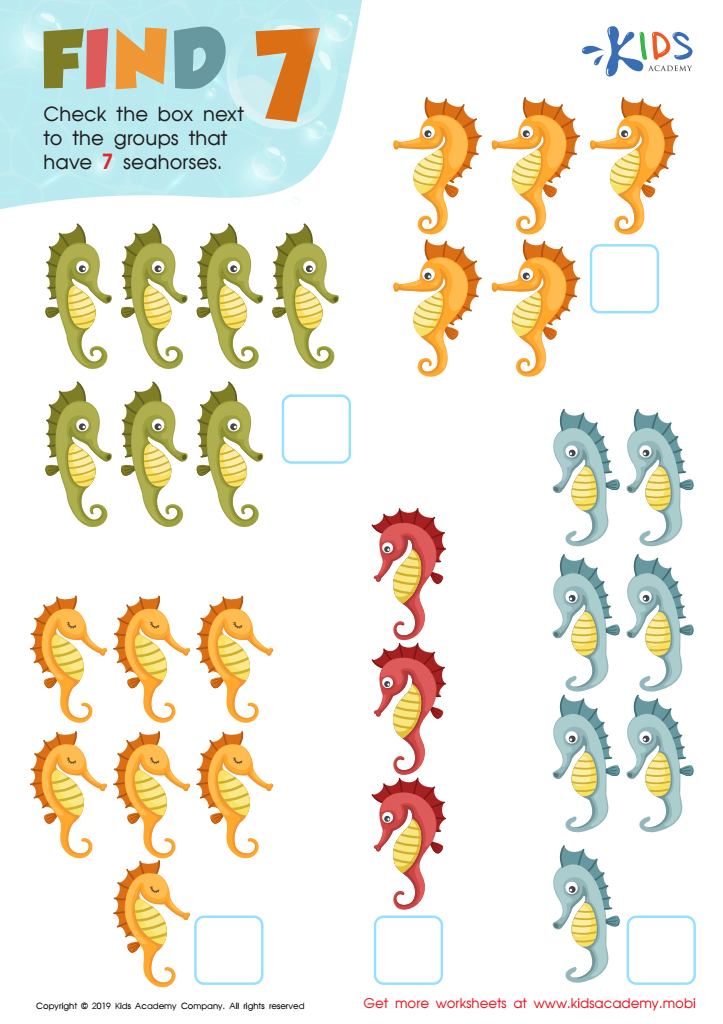


Find 7 Worksheet
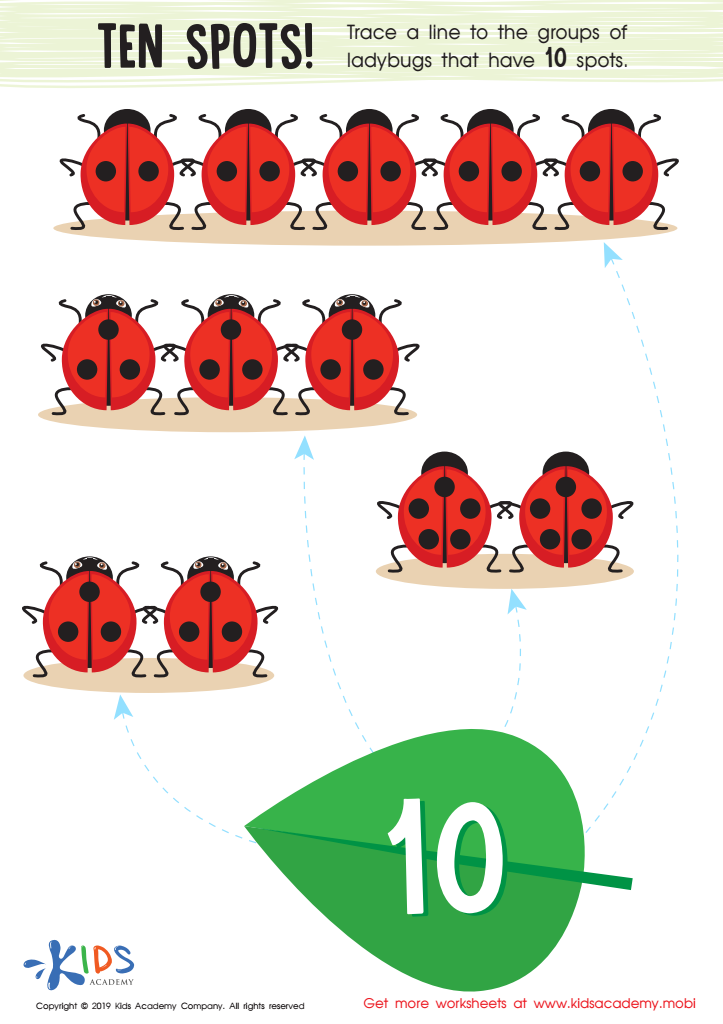

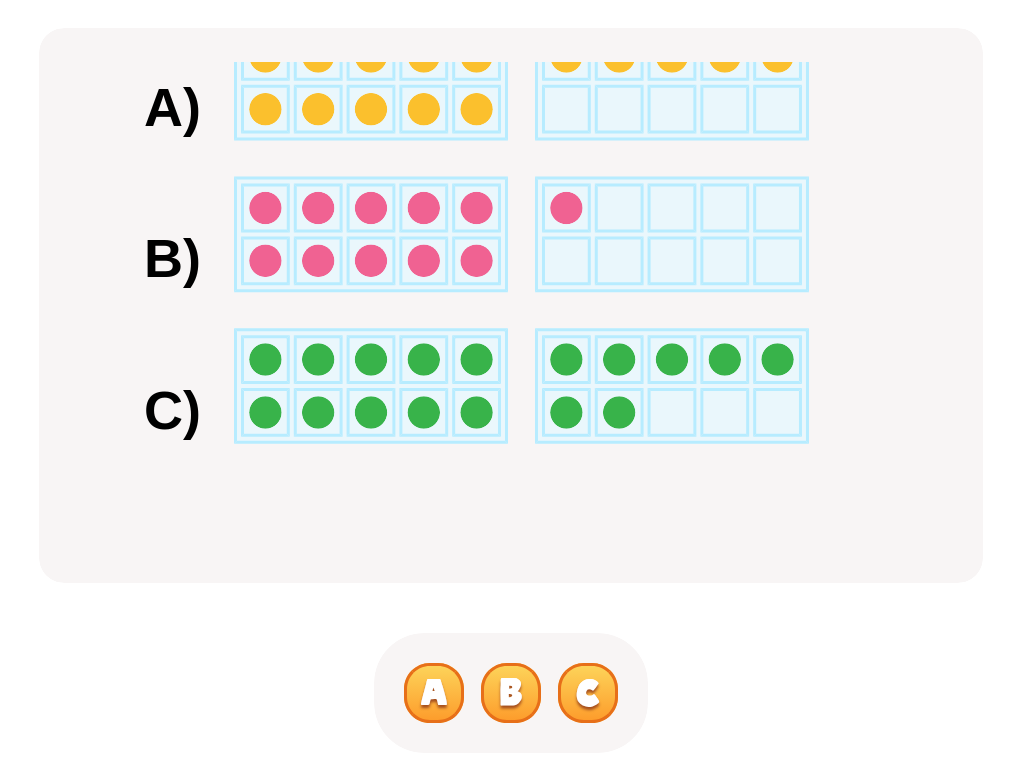
Ten Spots Worksheet
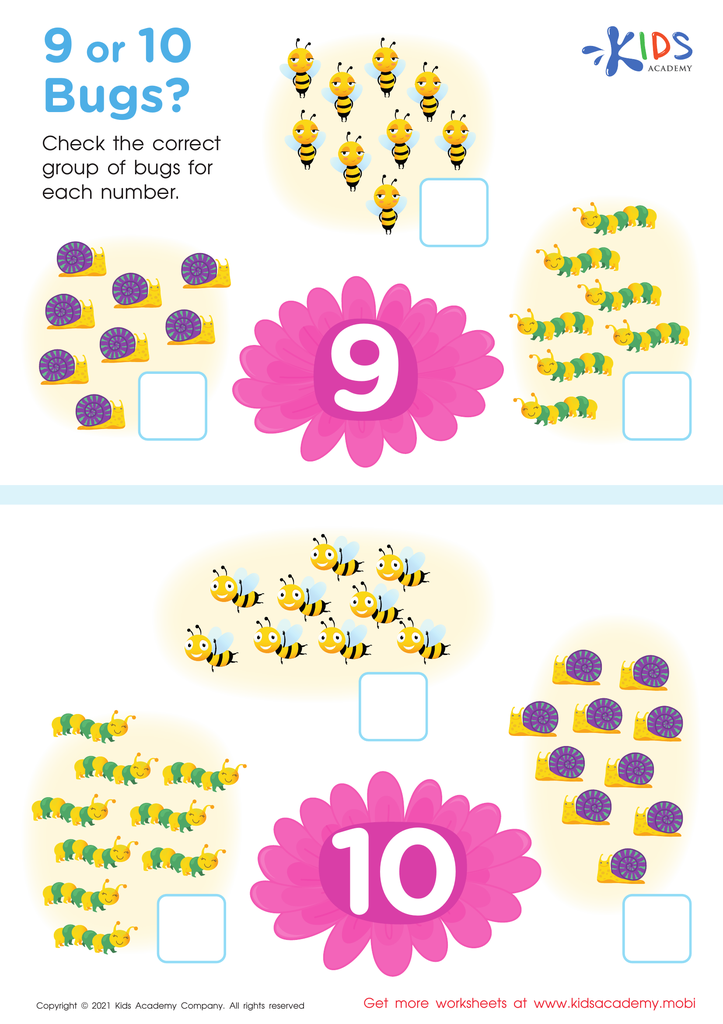

9 or 10 Bugs Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial in early childhood development, particularly for preschoolers aged 3-4. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are necessary for tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. When combined with counting activities, fine motor skills support both cognitive and physical development. Activities like threading beads or placing counters on specific numbers on a board can help children improve their hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and pincer grip—all vital for future writing proficiency.
Moreover, fine motor skills counting activities enhance cognitive skills such as number recognition, sequencing, and problem-solving. Manipulating small objects while counting reinforces numerical understanding through tactile and visual experiences. These multisensory learning experiences can make abstract concepts more concrete and understandable for young children.
Teachers and parents should prioritize fine motor skills counting because it lays a strong foundation for academic success and everyday function. Improved fine motor abilities lead to greater independence and confidence in a child's academic and personal activities. Ignoring this developmental aspect might result in difficulties with more complex tasks in later years, making early intervention essential for nurturing well-rounded development in young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
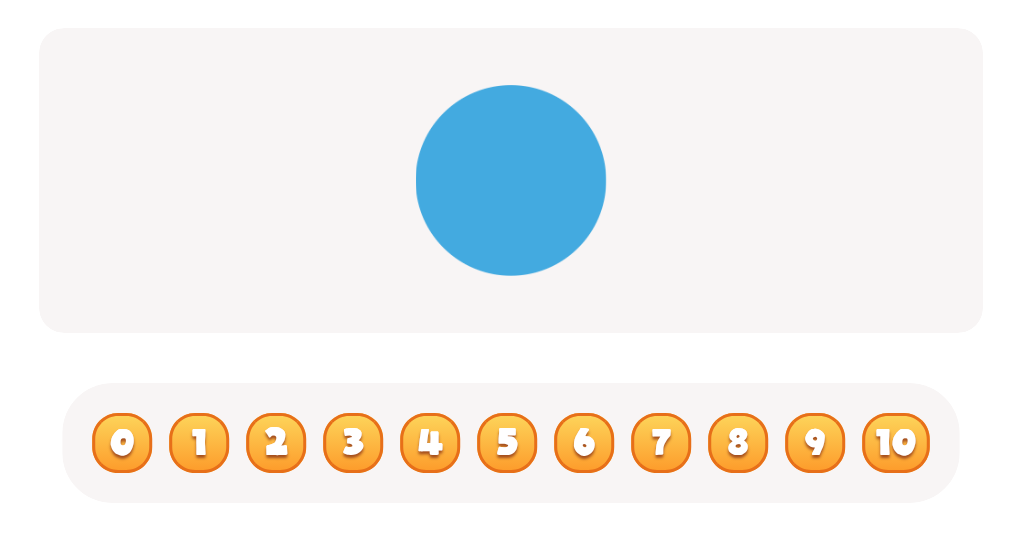
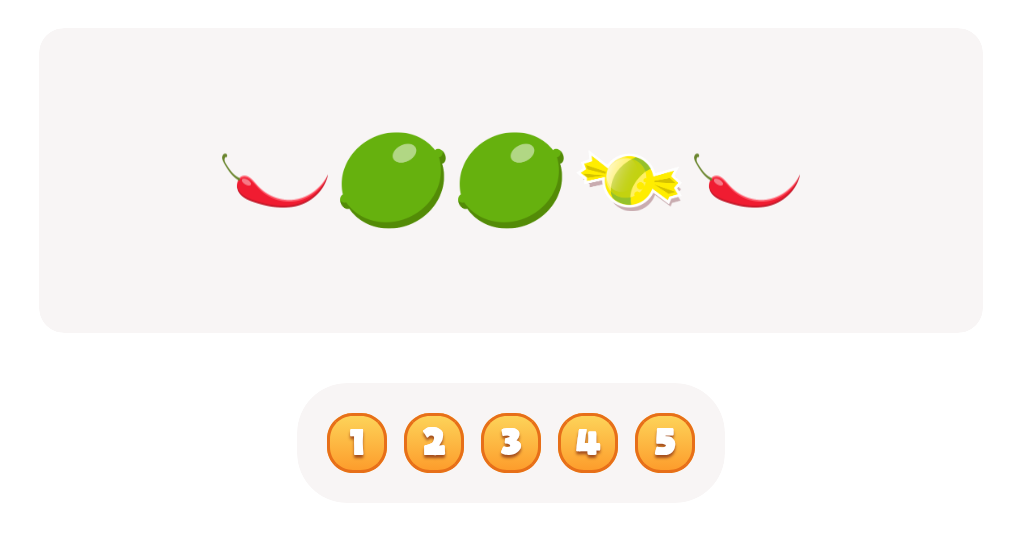








%20(1).jpg)










