Fine Motor Skills Reading Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
33 filtered results
-
From - To


The Bingo Song: Coloring The Dog Worksheet


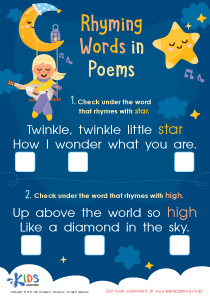
Pen Rhyming Words Worksheet


Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children, particularly those aged 3-4, as they form the foundation for a wide range of essential developmental activities, including reading. Developing fine motor skills enhances a child's ability to hold a book properly, turn pages with ease, and eventually handle a pencil or crayon for writing, drawing, and even annotating text.
These early physical skills support cognitive growth and hand-eye coordination. For instance, manipulating small objects or performing tasks like stringing beads requires precision, concentration, and dexterity, which are all integral to reading readiness and overall academic success.
Moreover, engaging in fine motor skill activities fosters independence and confidence. It encourages children to explore books actively, promoting a love for reading from an early age. This engagement enhances language skills, including vocabulary expansion and comprehension, critical for long-term educational development.
In addition, these skills have profound social benefits. A child adept in fine motor tasks is better equipped to participate in a variety of classroom activities, promoting social interaction and cooperation with peers.
Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skill development through activities like puzzles, arts and crafts, and guided, playful interactions with books. This investment in fine motor skills will pave the way for academic and personal success.