Basic Math Skills Adding up to 50 Worksheets for Ages 3-7
16 filtered results
-
From - To
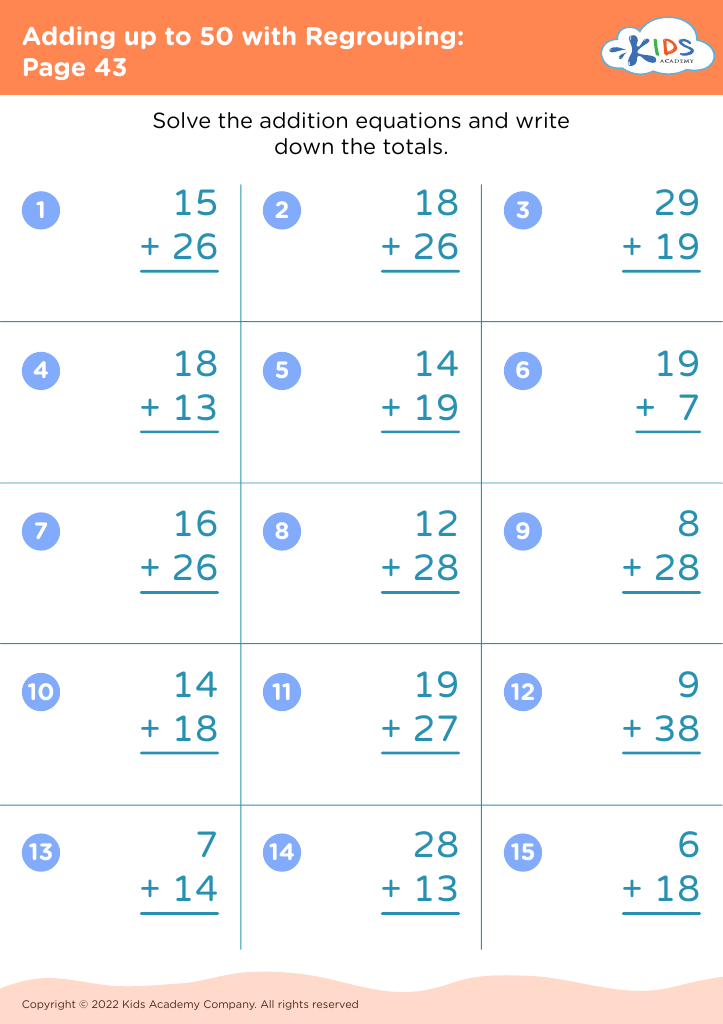
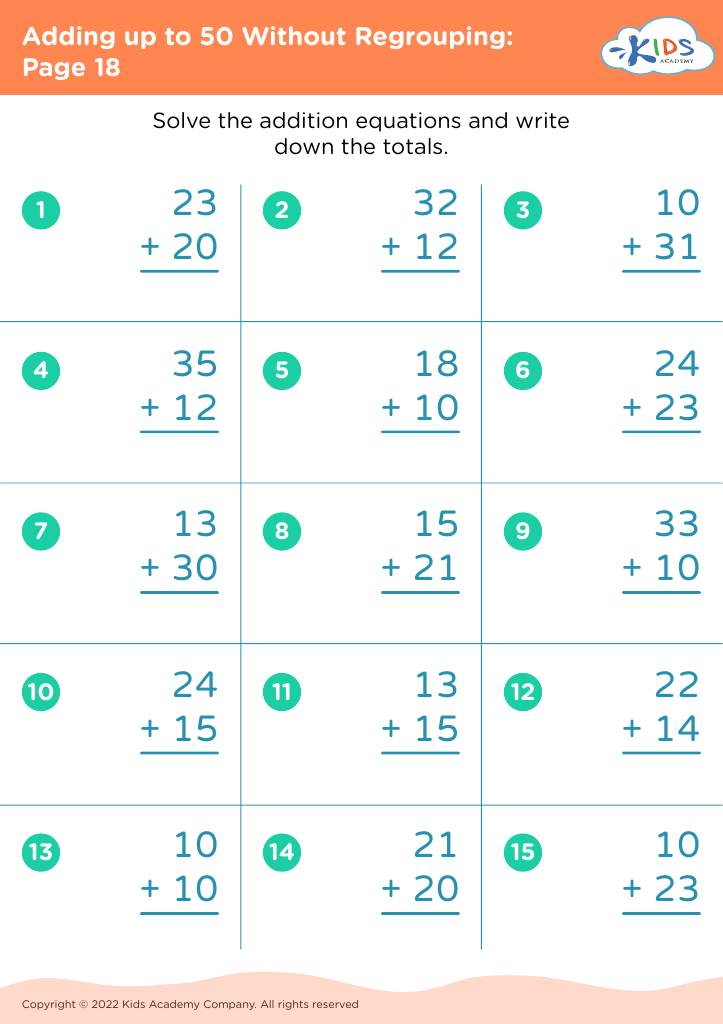
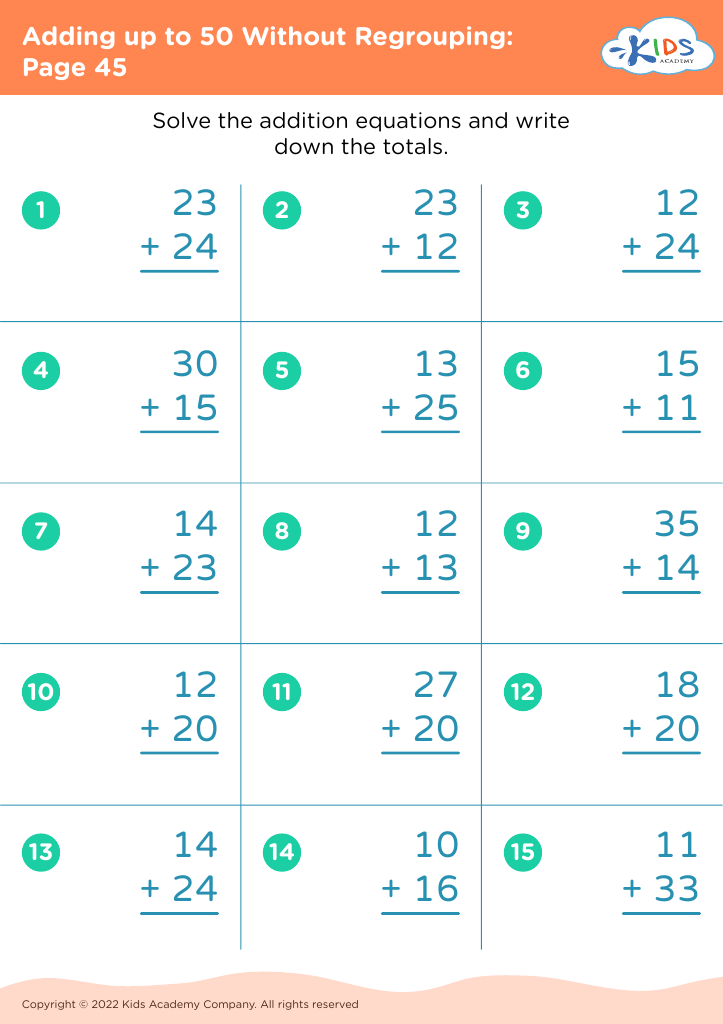
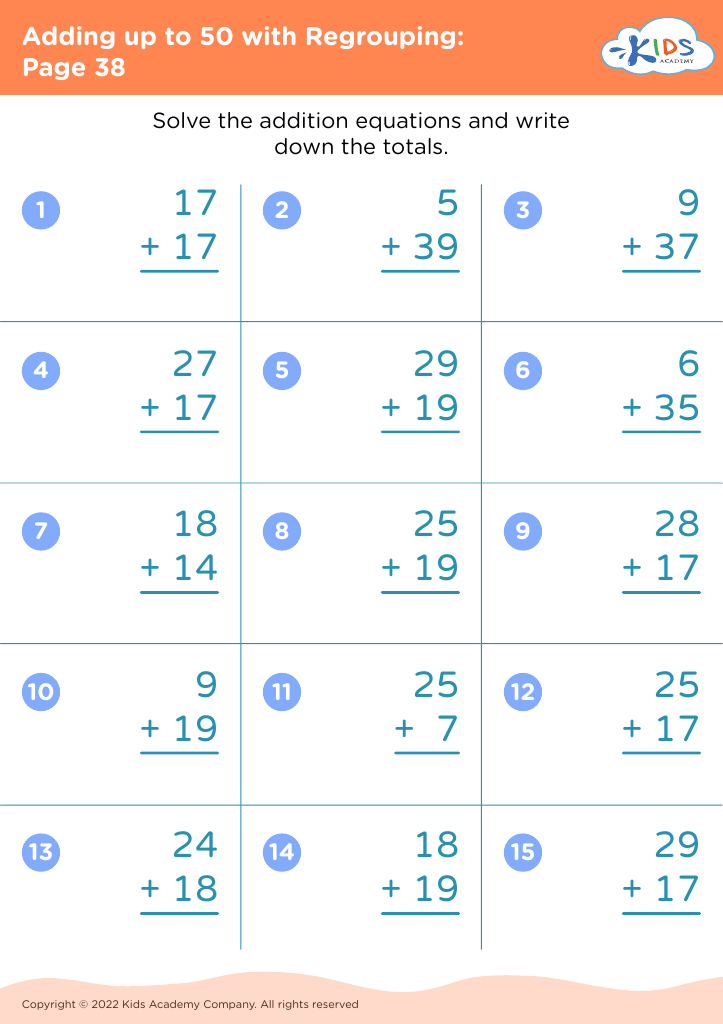
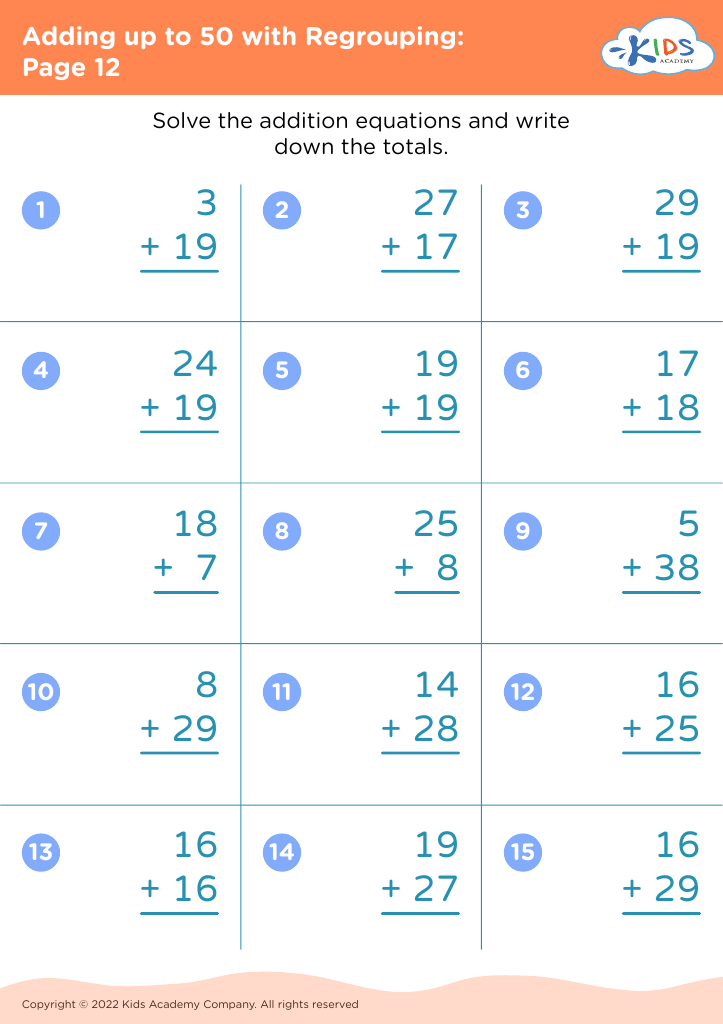
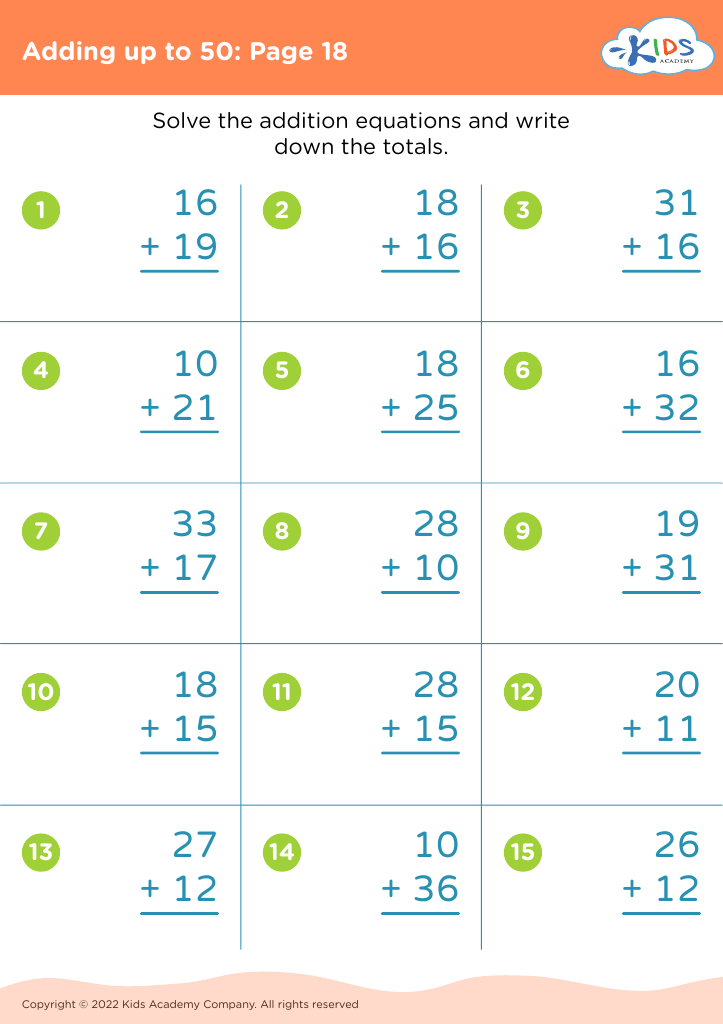
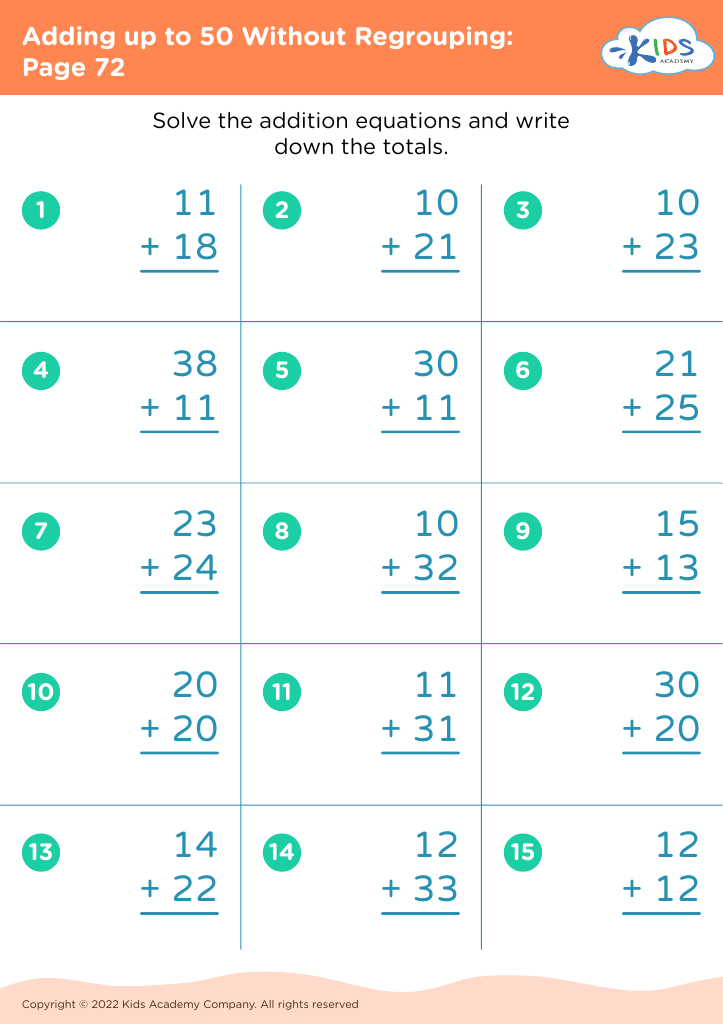
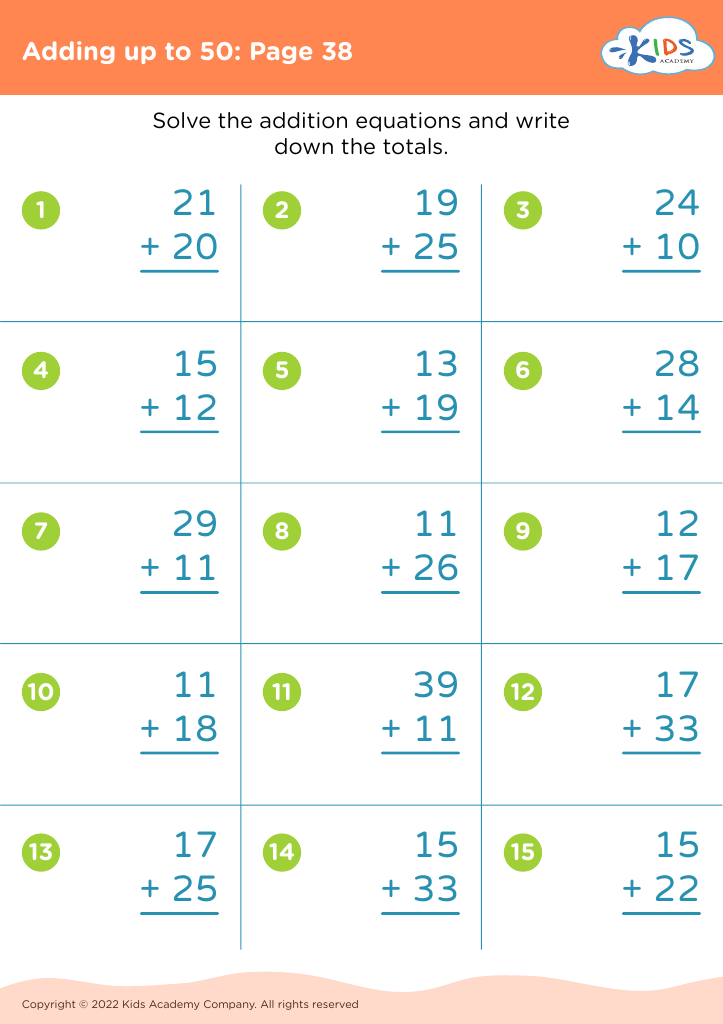
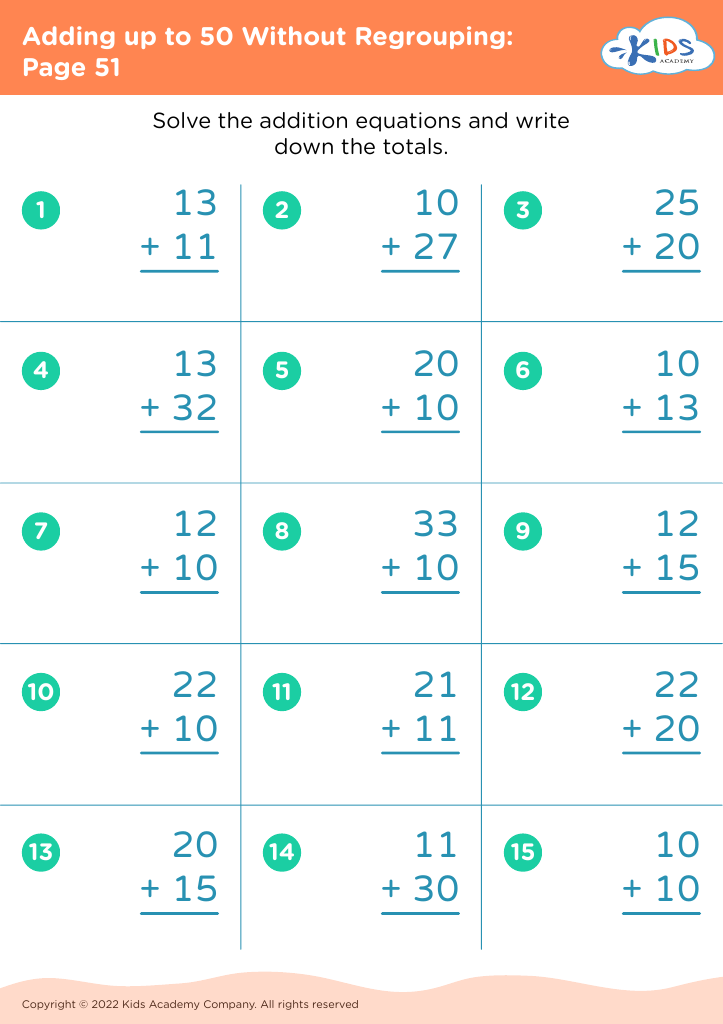
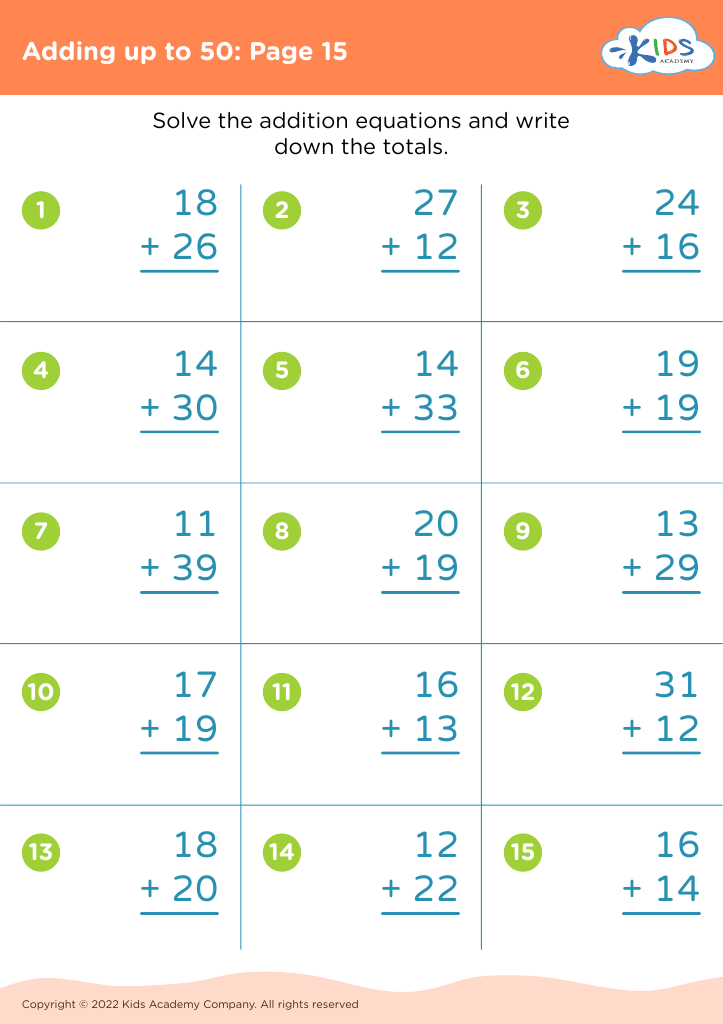
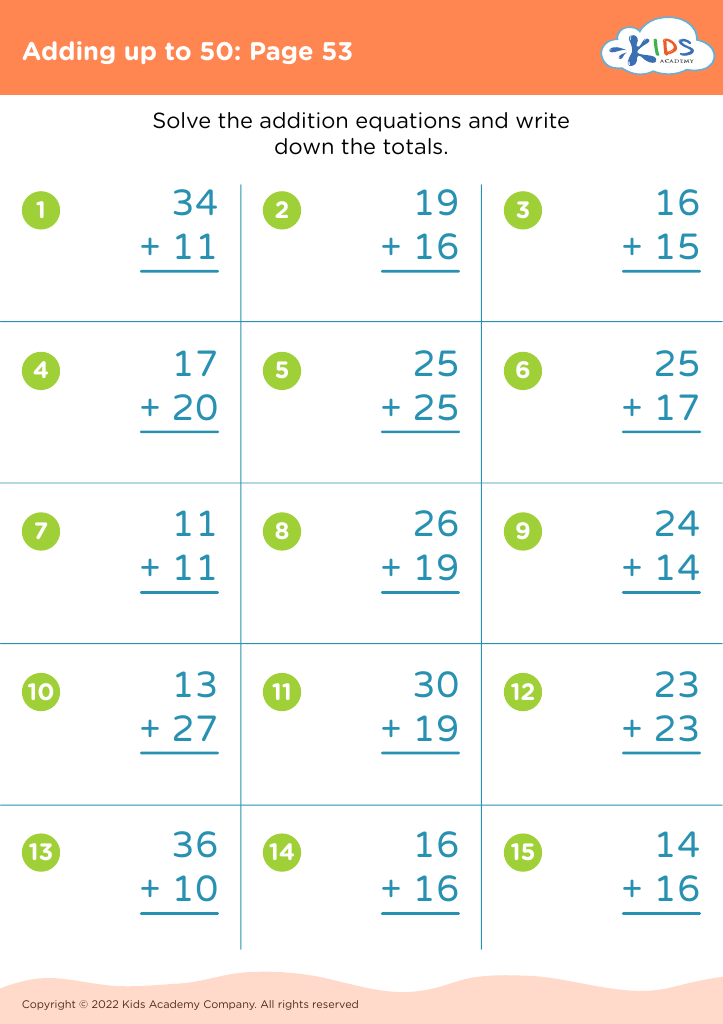
Our "Basic Math Skills Adding up to 50 Worksheets" are designed for children ages 3-7 to develop a strong foundation in math. These engaging and age-appropriate printables make learning fun through colorful graphics and interactive tasks. Children will practice addition with sums up to 50, enhancing their numerical fluency and confidence in basic math. Perfect for classroom use or extra practice at home, our worksheets support cognitive development and early problem-solving skills, ensuring young learners grasp essential mathematical concepts step by step. Fuel your child's passion for math with our expertly crafted, easy-to-understand resources.
Basic math skills are foundational for young children, particularly within the age range of 3-7. Mastering simple addition up to 50 not only builds numeracy skills but also enhances cognitive development, problem-solving abilities, and confidence.
For parents and teachers, fostering these skills means ensuring future academic success. Early exposure to basic addition helps children understand the concept of numbers and how they interact, which is vital for learning more complex mathematical concepts later. It's not just about numbers; it's about teaching children how to analyze, reason, and think critically—a process that applies to various aspects of life and learning.
In this age group, learning should be engaging and interactive. Using tangible objects like toys or blocks can make the abstract concept of addition more relatable and easier to understand. Games and playful activities also make math fun and less intimidating, setting a positive tone for future learning.
Furthermore, proficient math skills are crucial in everyday life. Tasks such as telling time, handling money, and measuring ingredients for recipes are all grounded in primary math concepts. By caring about basic math skills, parents and teachers are equipping children with essential tools for independence and success both inside and outside the classroom.