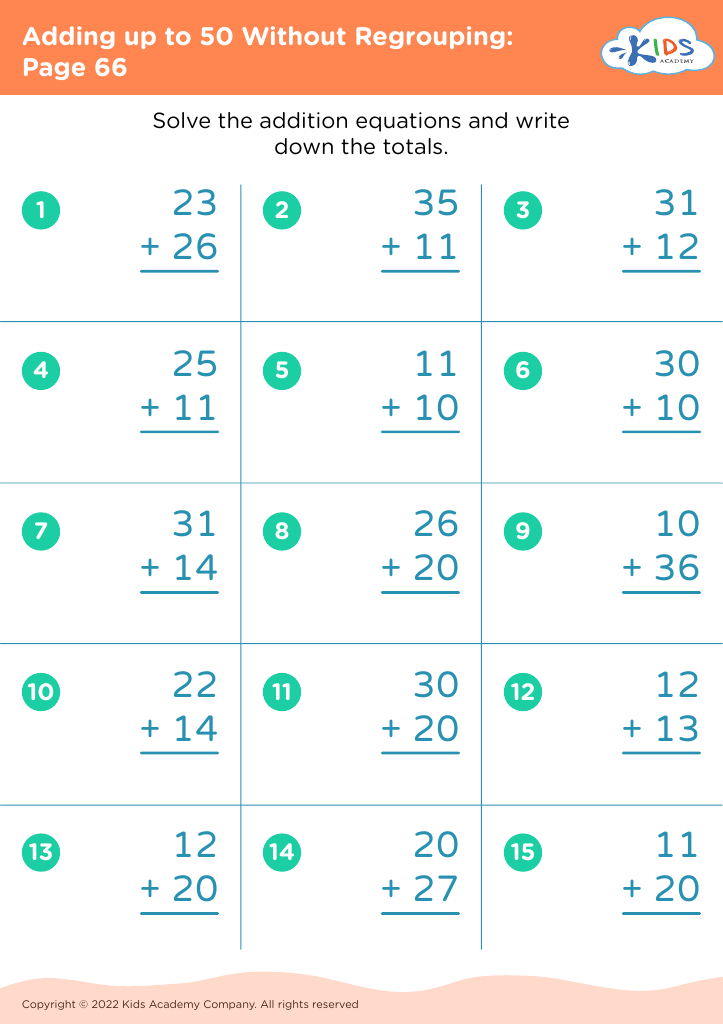
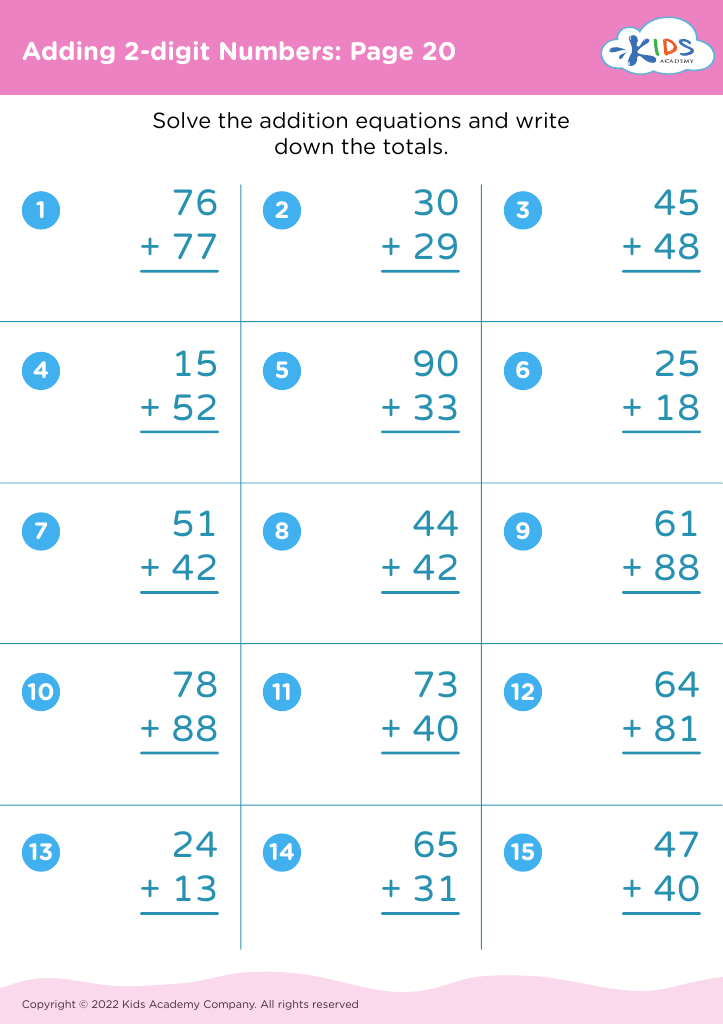
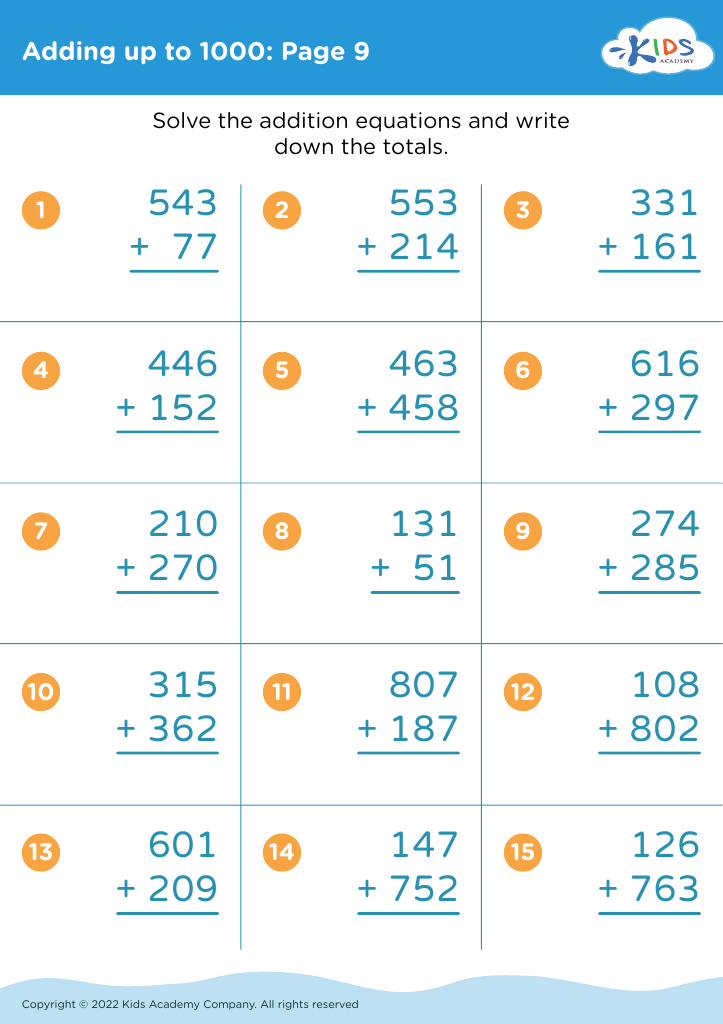
Practice division Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Practice Division, Addition, and Subtraction Worksheets tailored for children ages 3-7! Designed to foster fundamental math skills, these colorful and interactive worksheets make learning fun and effective. Our activities introduce basic division concepts while reinforcing addition and subtraction, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of early math principles. Parents and educators will find a variety of worksheets that appeal to young learners, encouraging independent practice and building confidence. With easy-to-follow instructions and vibrant illustrations, these resources are perfect for at-home learning or classroom use. Start your child's math journey today and watch them thrive as they master essential skills!
Parents and teachers should prioritize practicing division, addition, and subtraction with children ages 3-7 because early mathematical skills serve as a foundation for future learning. At this stage, children are incredibly receptive to new concepts, and mastering basic arithmetic helps build their confidence and foster a positive attitude toward math. These skills not only enhance cognitive development but also improve problem-solving abilities and critical thinking.
Strengthening addition and subtraction skills nurtures a child’s numerical fluency, enabling them to handle more complex operations later in their academic journey. Introducing simple division concepts, like sharing equally, complements these fundamentals, making math relatable and engaging. Furthermore, regular practice of these skills promotes fine motor skills through activities like counting objects or using manipulatives, enhancing overall learning.
Engagement in mathematical activities at home or in the classroom helps create a supportive environment that fosters collaboration and encourages children to ask questions. Moreover, these practices lay the groundwork for understanding everyday situations, such as managing money or telling time. Ultimately, investing time in teaching these skills sets children on a path toward lifelong mathematical success and self-assurance in their abilities.