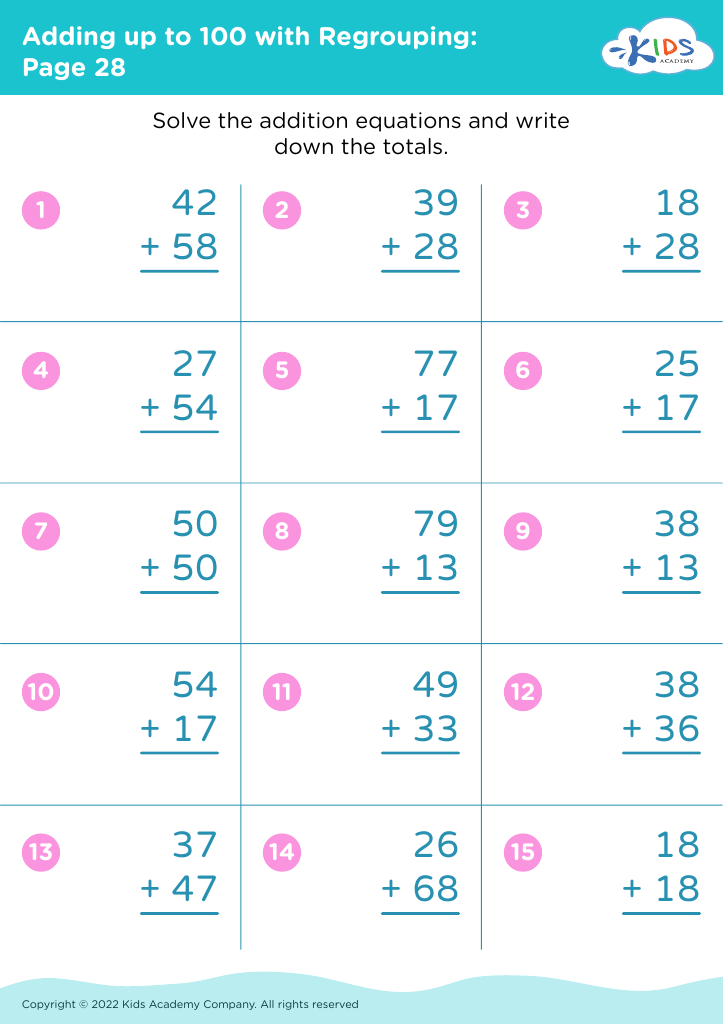
Developing basic arithmetic skills in children ages 3-7 is foundational for their overall cognitive development and future academic success. During these early years, children are incredibly receptive to learning and their brains are at a critical stage of growth. Basic arithmetic skills, such as counting, adding, subtracting, and recognizing numbers, form the groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts that they will encounter later in their education.
Moreover, acquiring these skills at a young age helps to build confidence and positive attitudes towards mathematics. When children feel comfortable and proficient in basic arithmetic, they are more likely to approach new challenges with enthusiasm rather than fear or frustration.
Early arithmetic skills also cultivate critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. As children learn to manipulate numbers and understand the relationships between them, they develop analytical skills that are not only vital for mathematics but are also transferable to other subjects and real-life situations.
Additionally, basic arithmetic plays a crucial role in everyday tasks, such as telling time, measuring ingredients in recipes, and handling money. By ensuring that children grasp these essential skills early on, parents and teachers are equipping them with practical tools that will aid in their independence and daily life.
Investing time and resources in teaching basic arithmetic to young children sets a strong foundation for their future learning, reduces anxiety related to math, and supports their overall development as competent, confident individuals.