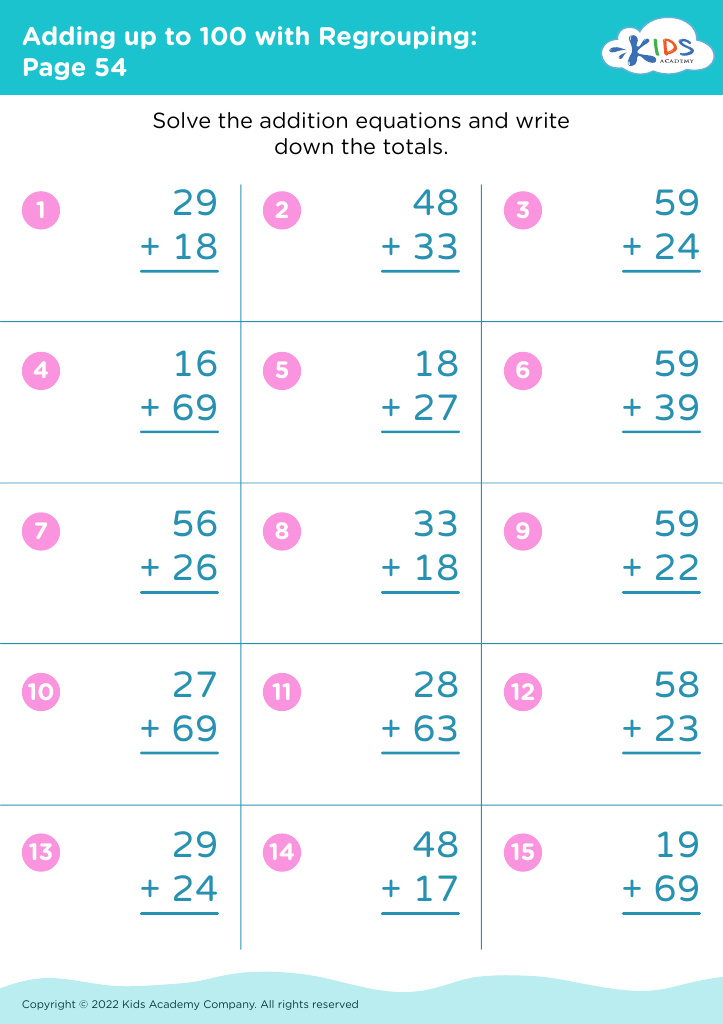
Develops fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 3-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our "Develops Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets" designed for ages 3-7! These fun and engaging activities combine important math concepts with essential fine motor skill development. Through coloring, tracing, and cutting exercises, children enhance their hand-eye coordination and dexterity while mastering numbers, shapes, patterns, and basic math operations. Our expertly crafted worksheets cater to young learners' developmental needs, ensuring that foundational skills are acquired in an enjoyable and effective way. Perfect for parents, teachers, and caregivers, these printable resources make learning math both accessible and exciting for preschoolers and early elementary students.


Counting: Maraca Fun Worksheet
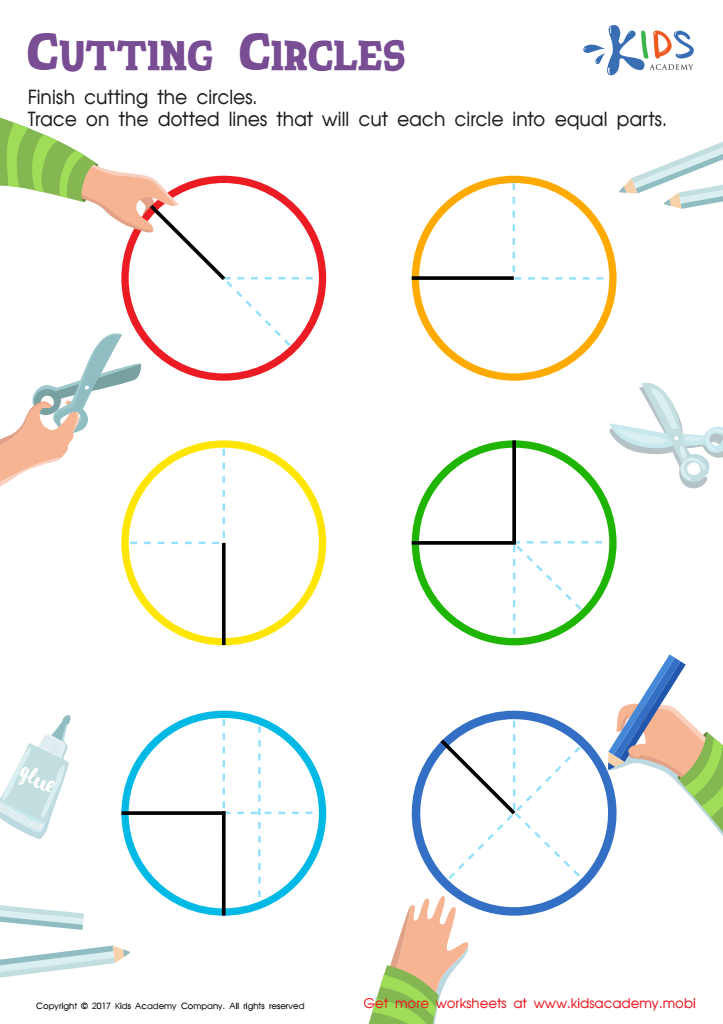

Cutting Circles Worksheet
Parents and teachers should be highly invested in the development of fine motor skills in children ages 3 to 7 because these skills form the foundation for many crucial academic and everyday tasks. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, which are essential for writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating objects. Here is why this is important:
First, having strong fine motor skills allows children to perform essential school activities such as holding a pencil properly, forming letters, and using scissors effective. These abilities are critical for success in early education math tasks which often involve manipulating small objects, drawing shapes, and handling paper.
Second, fine motor skills development is closely linked to cognitive development. Tasks that require precision and dexterity often also demand attention to detail, concentration, and problem-solving skills. When young students learn to sort blocks by size or color, for instance, they are not only improving their fine motor abilities but also enhancing their mathematical thinking and spatial awareness—fundamental components of early math education.
Lastly, these skills boost a child’s confidence and independence. Being able to dress themselves, eat without assistance, and create art projects enables children to feel more self-sufficient and engaged. Therefore, fostering fine motor skills at this critical developmental stage supports both educational growth and personal development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students