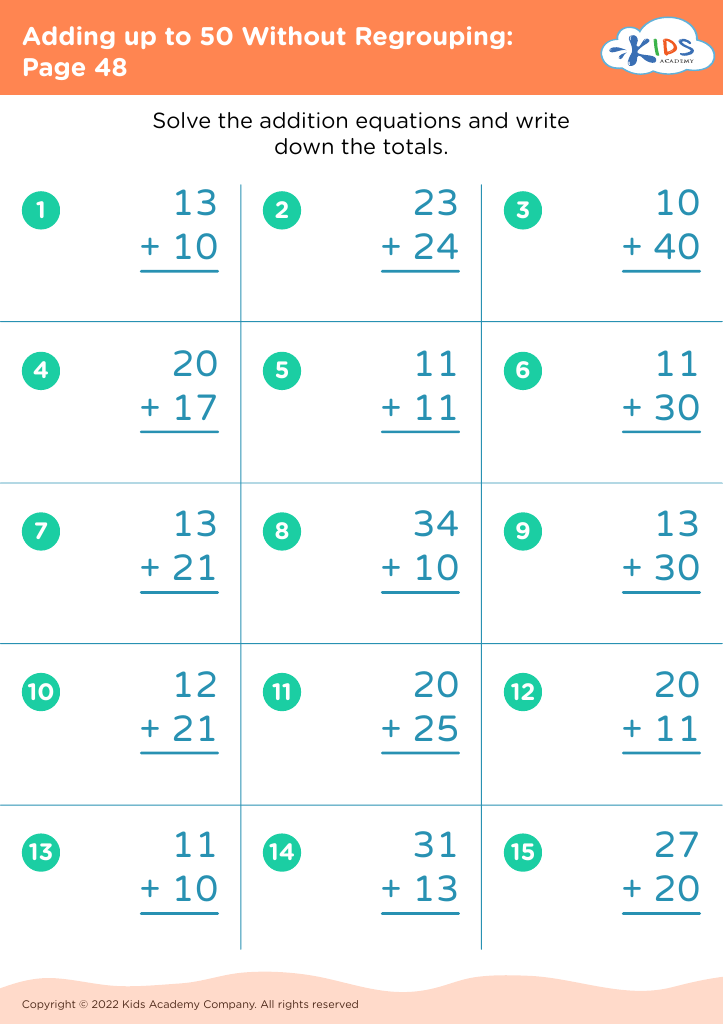
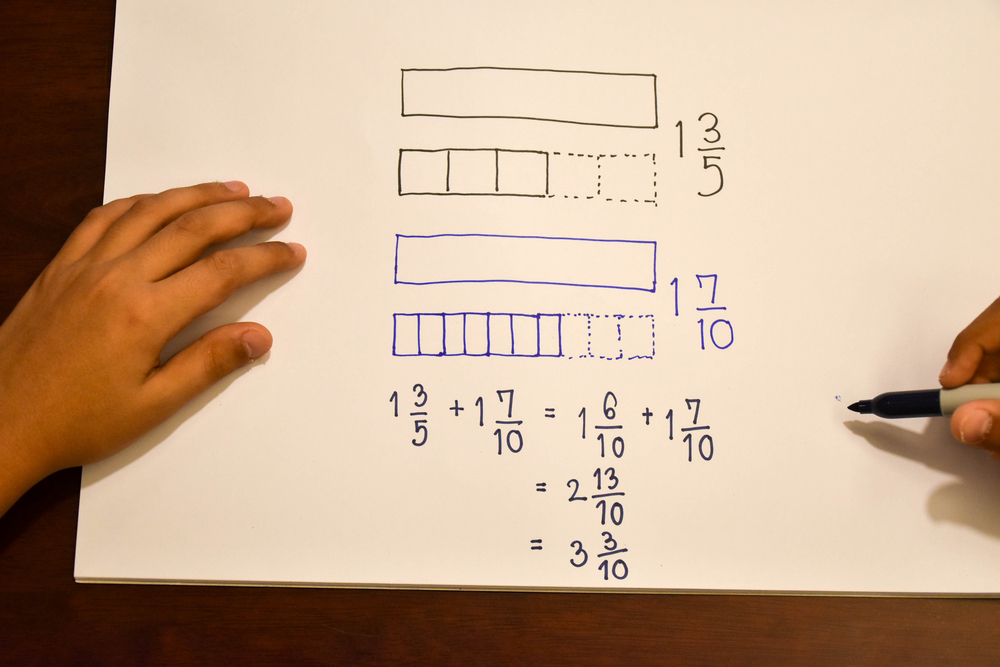
Fine motor skills (writing) Math Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 2
43 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Flowers Worksheet
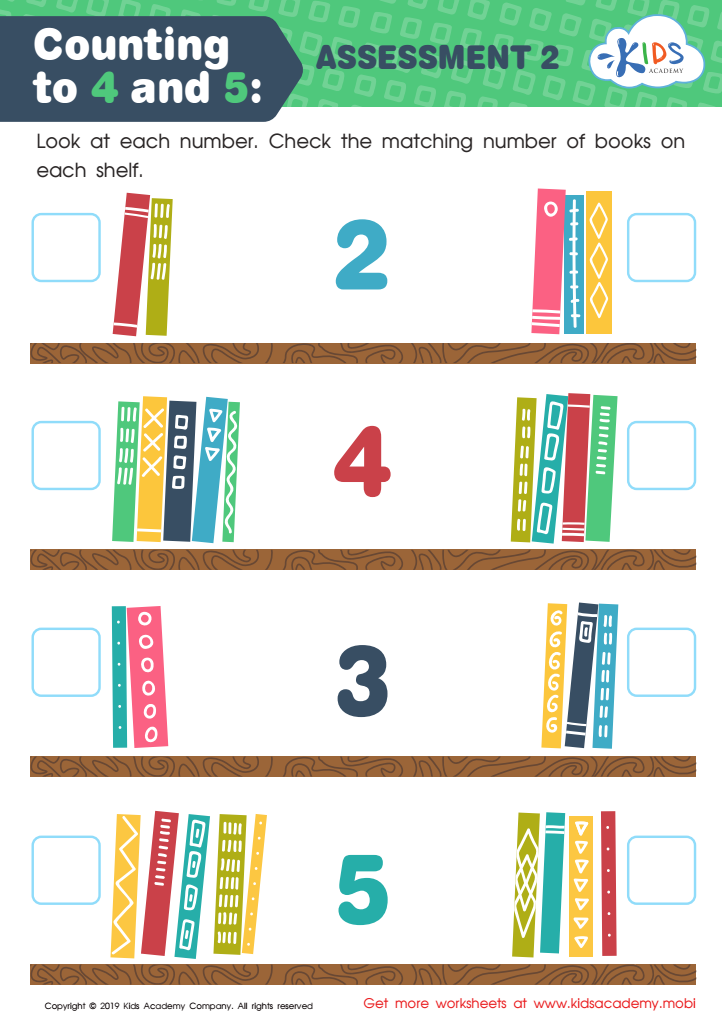

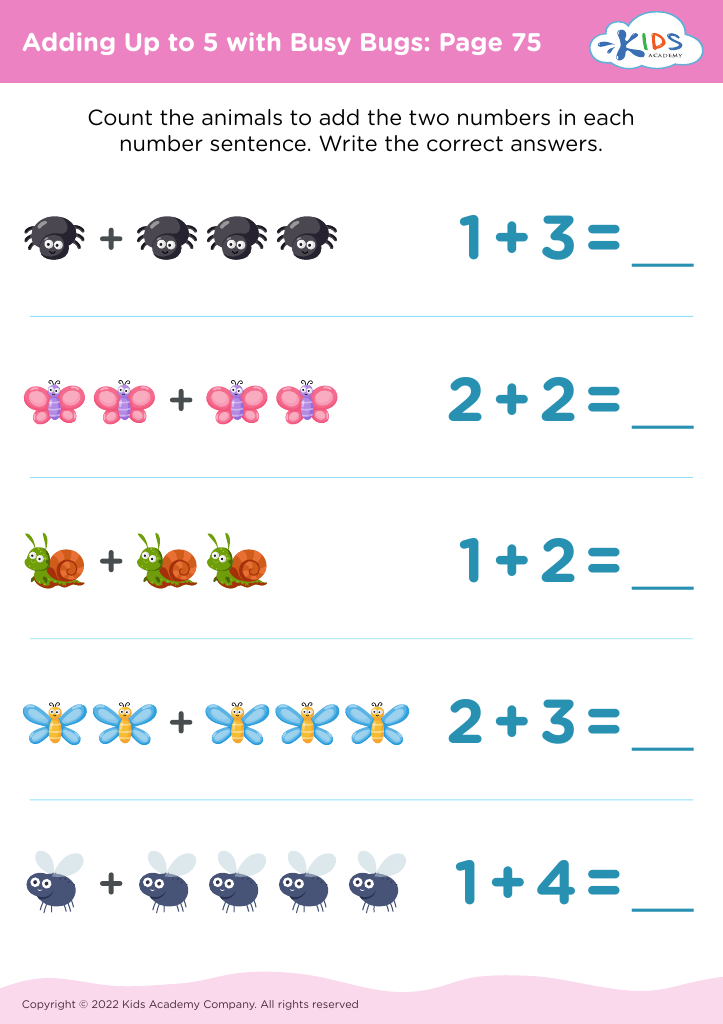
Counting to 4 and 5: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills and early math development are crucial in the formative years of children aged 3-7, as they lay the foundation for both academic success and everyday tasks. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers. These skills are essential for writing, enabling children to hold pencils, manipulate tools, and eventually engage in more complex tasks that require precision. Enhancing these skills not only supports academic pursuits, such as writing and drawing, but also boosts self-confidence as children successfully accomplish tasks independently.
Mathematics, on the other hand, is vital for logical thinking and problem-solving. During early childhood, exposure to basic math concepts—such as counting, shapes, and patterns—helps children develop cognitive skills and understand the world around them. Engaging in math through play—like sorting toys or counting objects—creates a positive attitude towards learning.
Together, fine motor skills and early math skills promote overall cognitive development. When parents and teachers focus on these areas, they not only prepare children for academic settings but also enrich their everyday experiences, fostering curiosity, creativity, and critical thinking—a trifecta essential for lifelong learning.





 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students