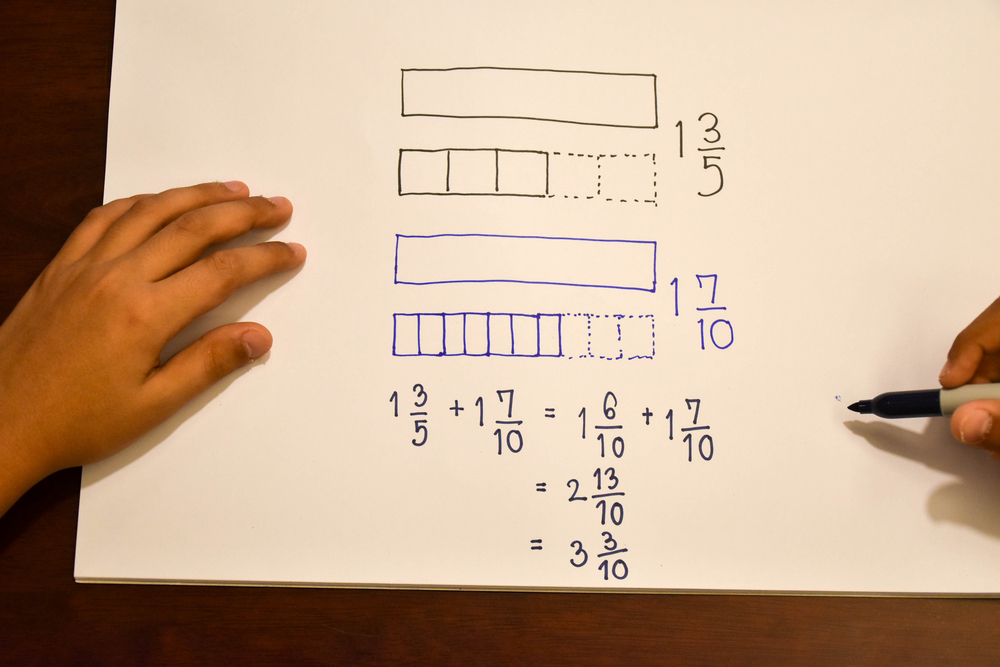
Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
82 filtered results
-
From - To

18 Candles Worksheet

Piecing Together 18 Worksheet

Counting Eggs Worksheet

6 Parrots Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children's overall development, particularly in the early years of 3 to 8. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills in the context of addition and subtraction for several important reasons.
Firstly, fine motor skills are foundational for learning mathematical concepts. When children practice addition and subtraction through hands-on activities, such as using counters or manipulatives, they not only grasp these concepts better but also develop their dexterity and hand-eye coordination. This connection between physical manipulation and cognitive understanding reinforces their ability to perform math tasks accurately.
Moreover, fine motor skill development during these formative years builds confidence. Mastery of small tasks like writing numbers or counting objects creates a sense of achievement that can inspire children to tackle more complex academic challenges as they progress.
Additionally, focusing on fine motor skills helps lay the groundwork for lifelong learning habits and self-regulation. By engaging children in activities that require precision and control, we nurture their ability to concentrate and persevere, critical skills for future success in both academics and everyday life.



 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students