Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for 3-Year-Olds - Page 2
37 filtered results
-
From - To
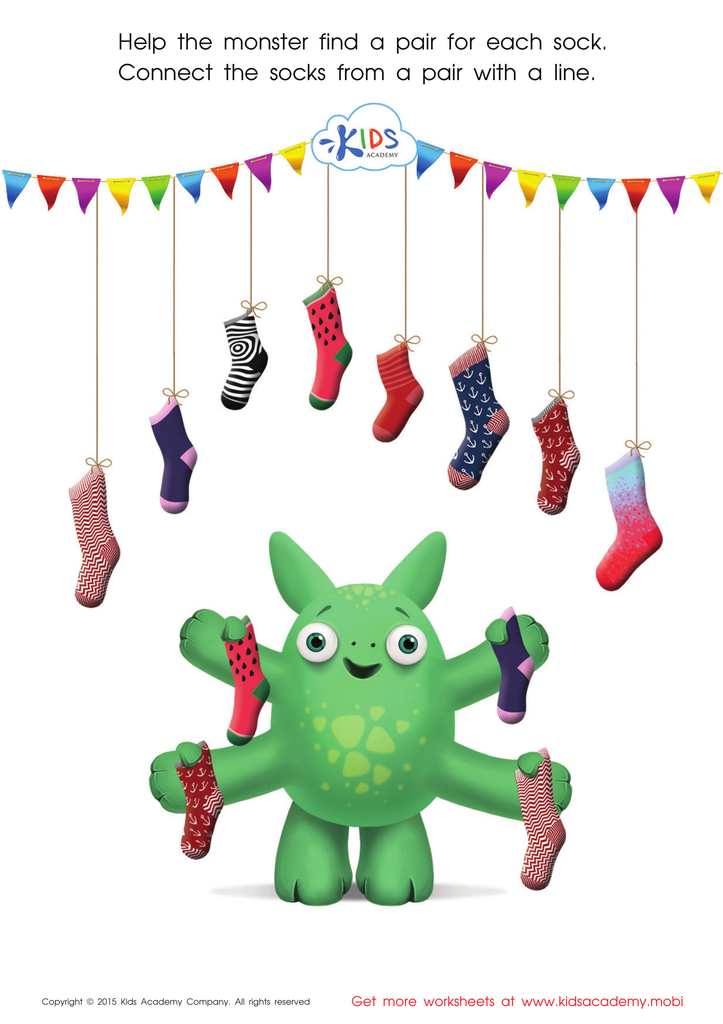


Math Matching Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
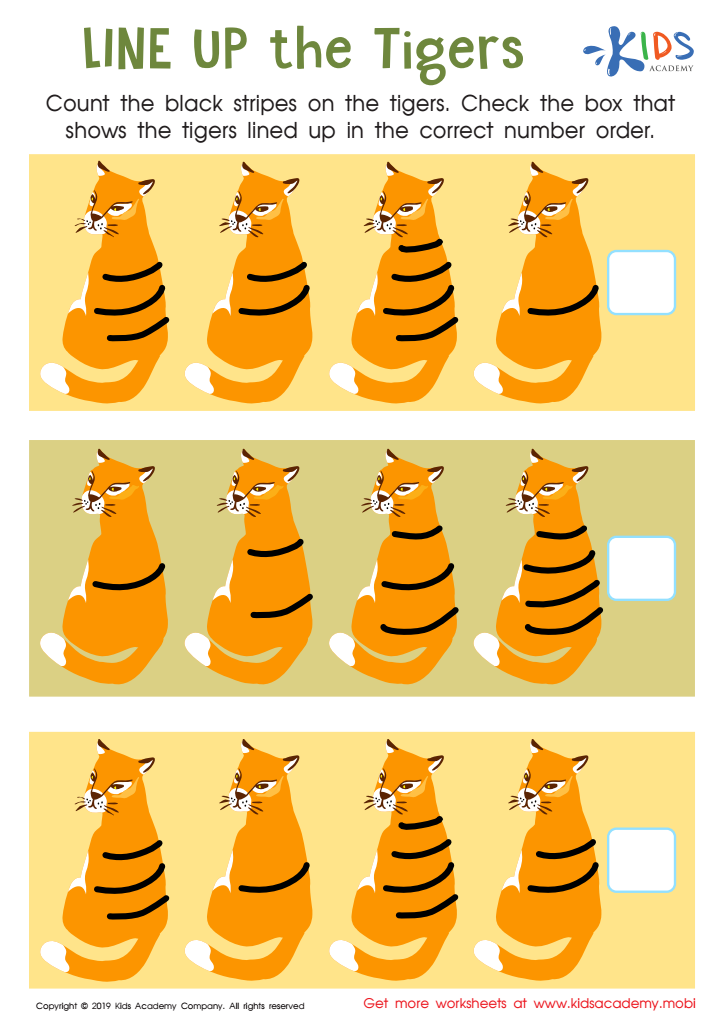

Line up the Tigers Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet


Math Matching Pairs Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for a child's overall development, particularly in early childhood. For 3-year-olds, nurturing these skills while introducing basic math concepts, such as addition and subtraction, lays the groundwork for cognitive and physical growth. Fine motor skills involve precise movements and coordination, helping children master tasks like holding a pencil, cutting with scissors, or manipulating small objects. Engaging in activities that refine these skills can enhance a child's ability to perform mathematical operations.
Incorporating addition and subtraction into fine motor skill activities makes learning interactive and fun. For instance, using manipulatives, such as counting beads or building blocks, not only aids in comprehending these mathematical concepts but also reinforces hand-eye coordination and dexterity. As children practice grasping and moving objects, they develop the necessary skills to write and manipulate tools effectively.
Parents and teachers should recognize that focusing on fine motor skills at this stage prepares children for future academic success. When children gain confidence in their motor abilities, they are more likely to engage in learning, explore creatively, and participate in classroom activities. Supporting this combination of fine motor skills and early arithmetic fosters a holistic approach to education that benefits children's learning trajectories.



 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students