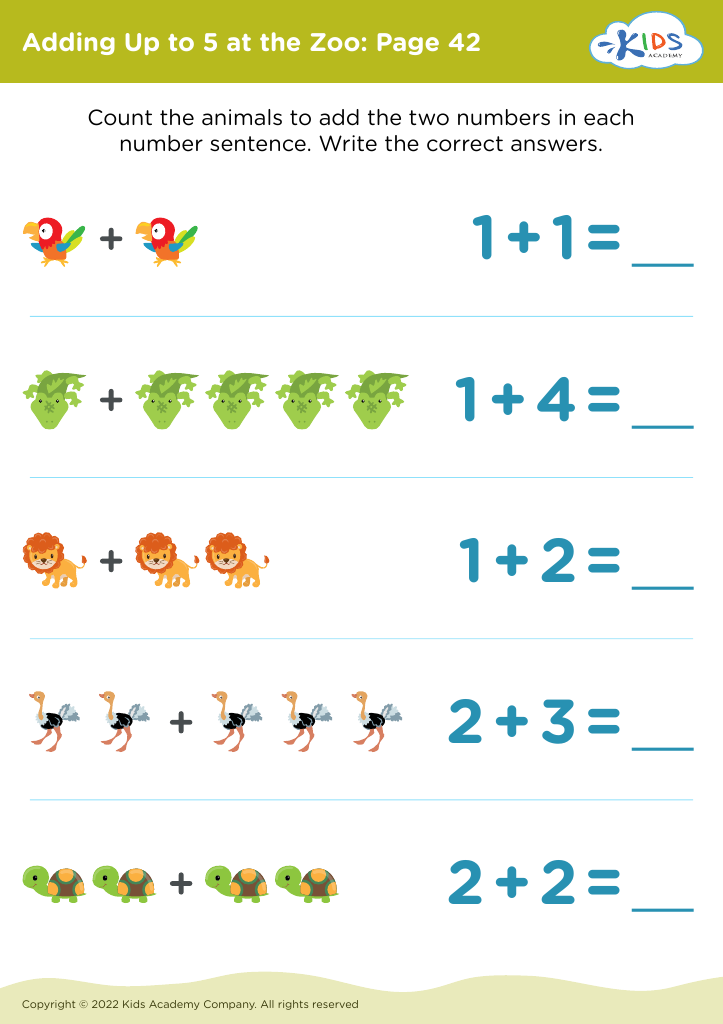Fine motor skills (writing) Math Worksheets for 3-Year-Olds - Page 2
34 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Flowers Worksheet
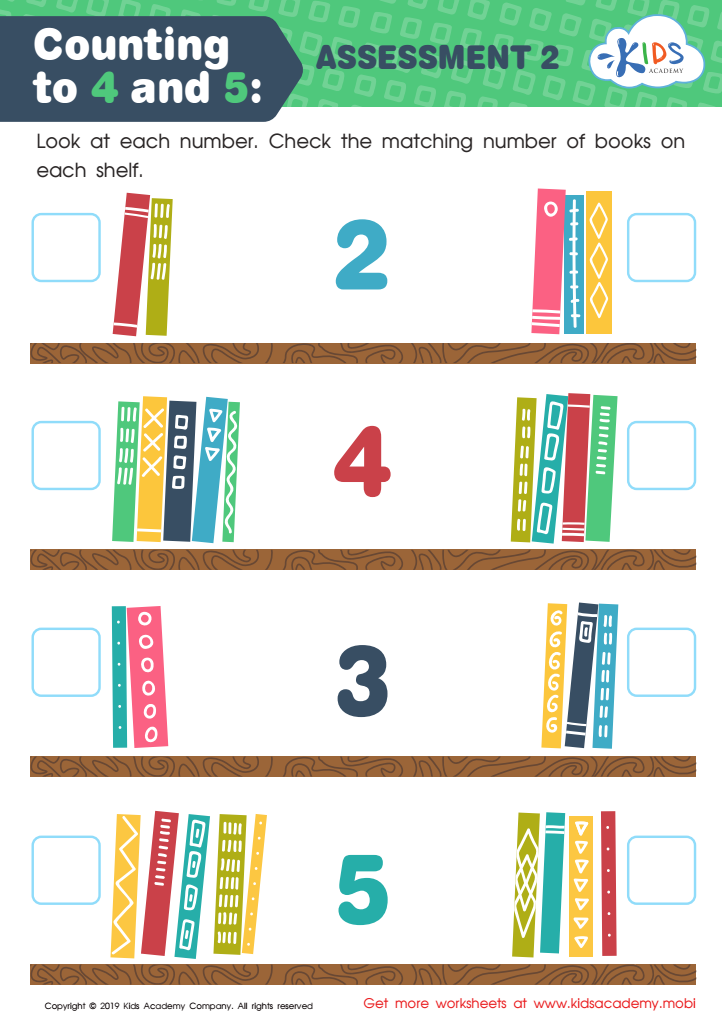

Counting to 4 and 5: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for 3-year-olds as they lay the foundation for writing, mathematics, and overall cognitive development. During this formative age, children’s ability to control small muscles in their hands and fingers directly impacts their capability to grasp writing tools, manipulate objects, and perform tasks requiring precision. Enhancing fine motor skills through writing activities—such as coloring, tracing, and using scissors—promotes hand-eye coordination and strengthens hand muscles, making it easier for children to engage in writing practices down the line.
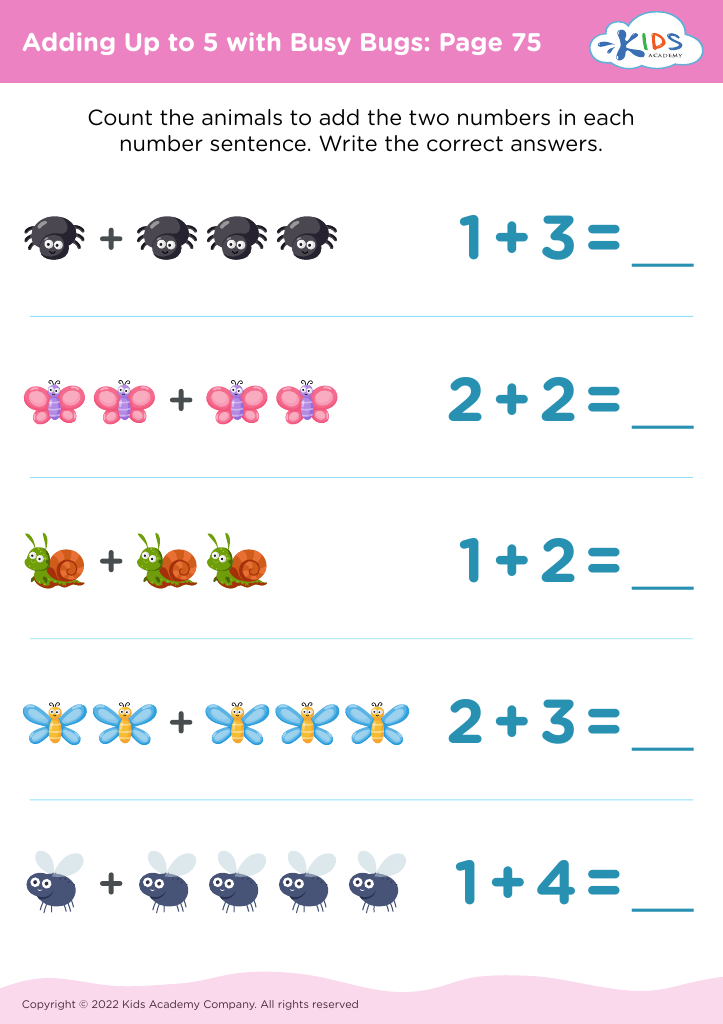
In addition to writing, fine motor skills play a pivotal role in mathematical development. Activities like threading beads, sorting shapes, and using building blocks not only foster mathematical reasoning and spatial awareness but also help children learn to count and recognize patterns. Teachers and parents should care about these skills as proficiency in them encourages confidence and independence, ultimately setting the stage for later academic success.
Moreover, acquiring fine motor skills at a young age contributes to emotional and social development, as children often engage in cooperative play during these activities. Investing time in fostering fine motor skills through interactive and playful strategies aids in holistic development, preparing children for future learning experiences.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students