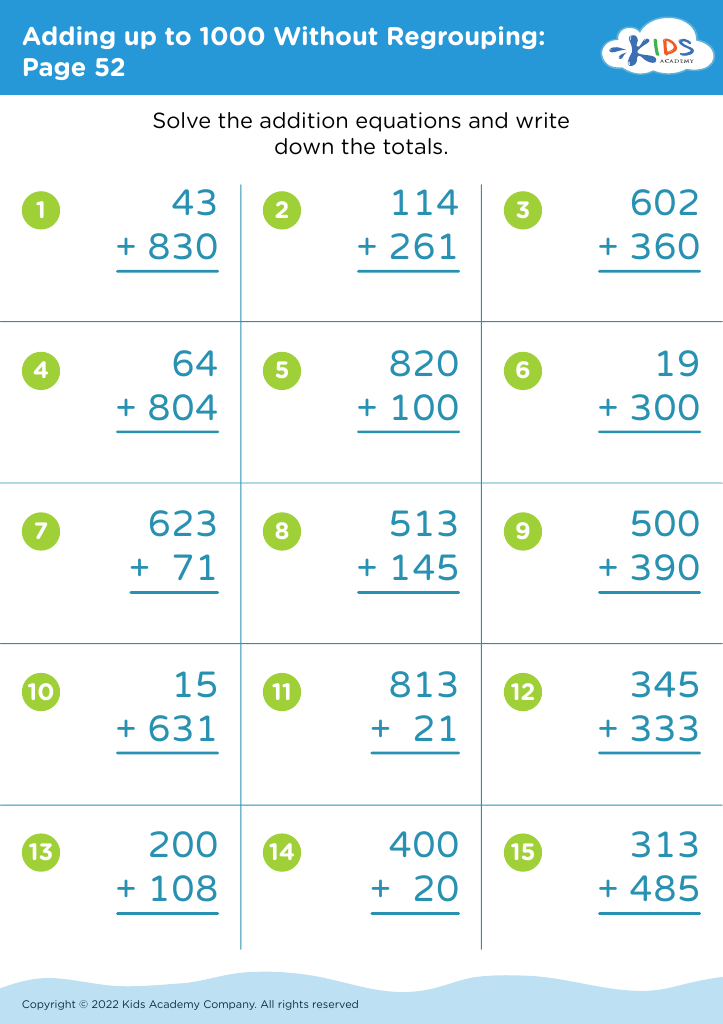
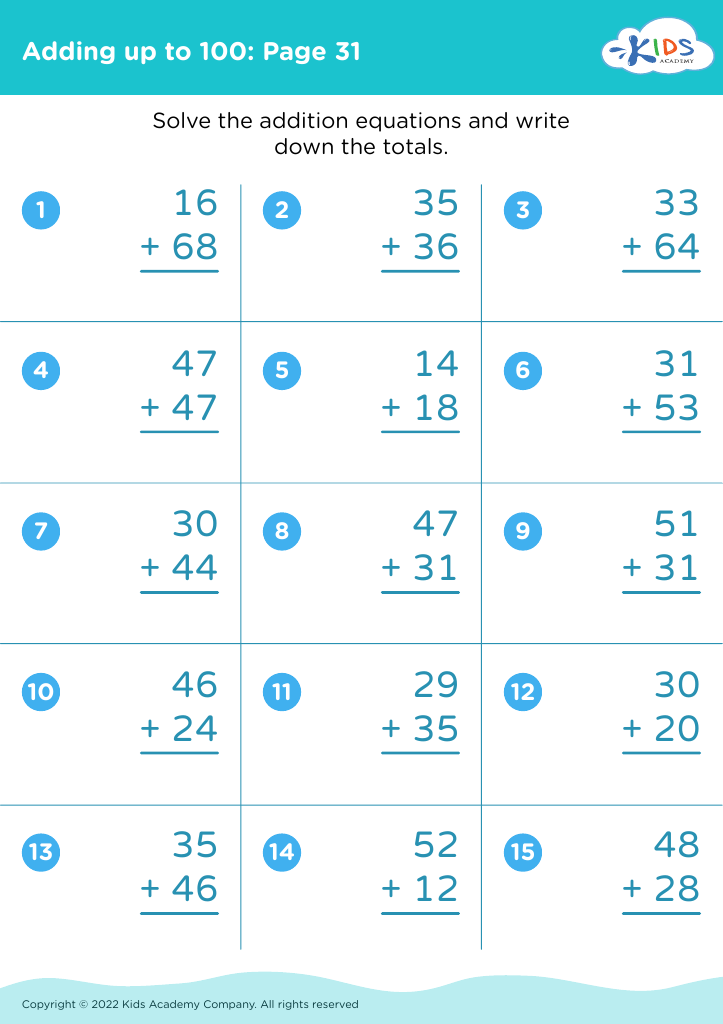
Improve fine motor skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Improve Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-7" combine essential math practice with activities designed to enhance your child's dexterity and hand-eye coordination. These engaging worksheets feature colorful illustrations and age-appropriate addition problems that transform learning into a fun adventure. Perfectly suited for young learners, each page encourages children to solve sums while also incorporating tasks that require careful motion control. Ideal for preschool to early elementary students, our worksheets are an excellent tool to build both math proficiency and fine motor abilities, empowering children with the foundational skills they need for future academic success.
Parents and teachers should care significantly about improving fine motor skills in children aged 4-7 because these skills form a critical foundation for various essential activities that support overall development and academic success. Fine motor skills enable young children to perform precise movements with their hands and fingers, essential for daily tasks such as buttoning clothes, tying shoelaces, and using utensils.
In an educational context, well-developed fine motor skills are crucial for handwriting, drawing, coloring, and cutting with scissors. These activities directly influence a child's ability to express and communicate ideas, thus affecting their performance across subjects. For instance, mastering pencil control contributes to more legible handwriting, which is vital for completing schoolwork effectively and reinforcing literacy development.
Additionally, enhancing fine motor skills bolsters cognitive development. Tasks that require careful hand-eye coordination and precise finger movements also engage areas of the brain responsible for problem-solving, attention, and spatial awareness. This dual engagement aids in advancing both physical and mental dexterity.
Furthermore, successfully developing these skills can boost a child's confidence and independence, inspiring them to tackle new challenges both inside and outside the classroom. By investing in the improvement of fine motor skills, parents and teachers set children up for a successful transition into more advanced academic and everyday tasks.