Basic geometry concepts Worksheets for Ages 4-8
3 filtered results
Difficulty Level
Grade
Age
-
From - To
Subject
Activity
Standards
Favorites
With answer key
Interactive
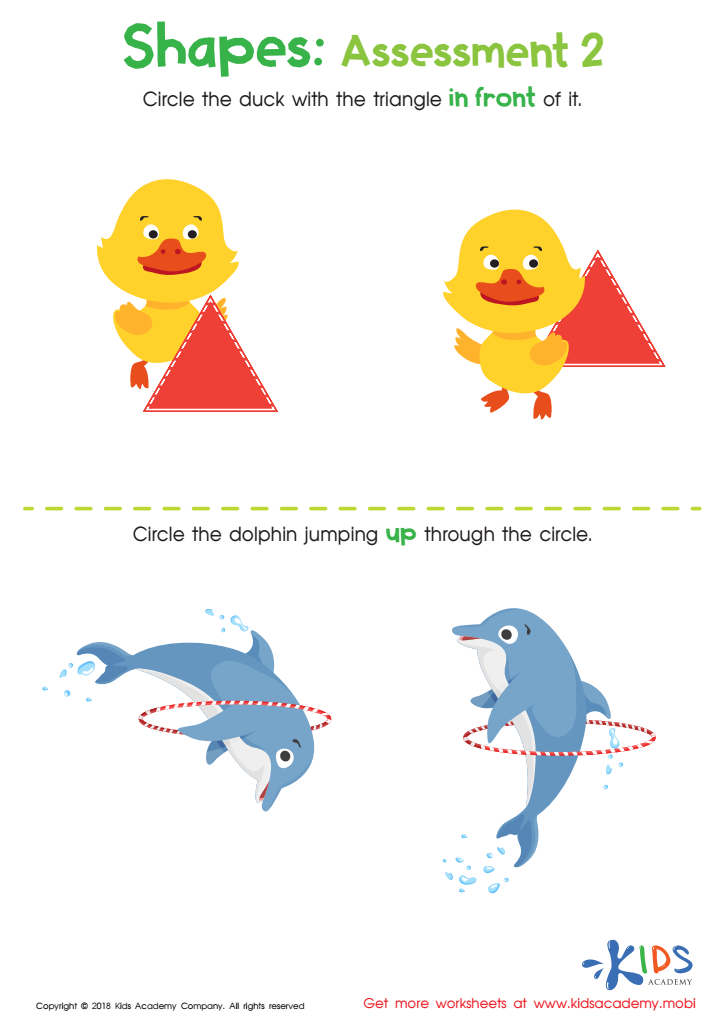

Geometry – Assessment 2 Worksheet
Preschoolers will learn to identify circles and triangles and practice using terms like "in front of" to place objects. This skill is key to further learning and is an important part of development.
Geometry – Assessment 2 Worksheet
Worksheet
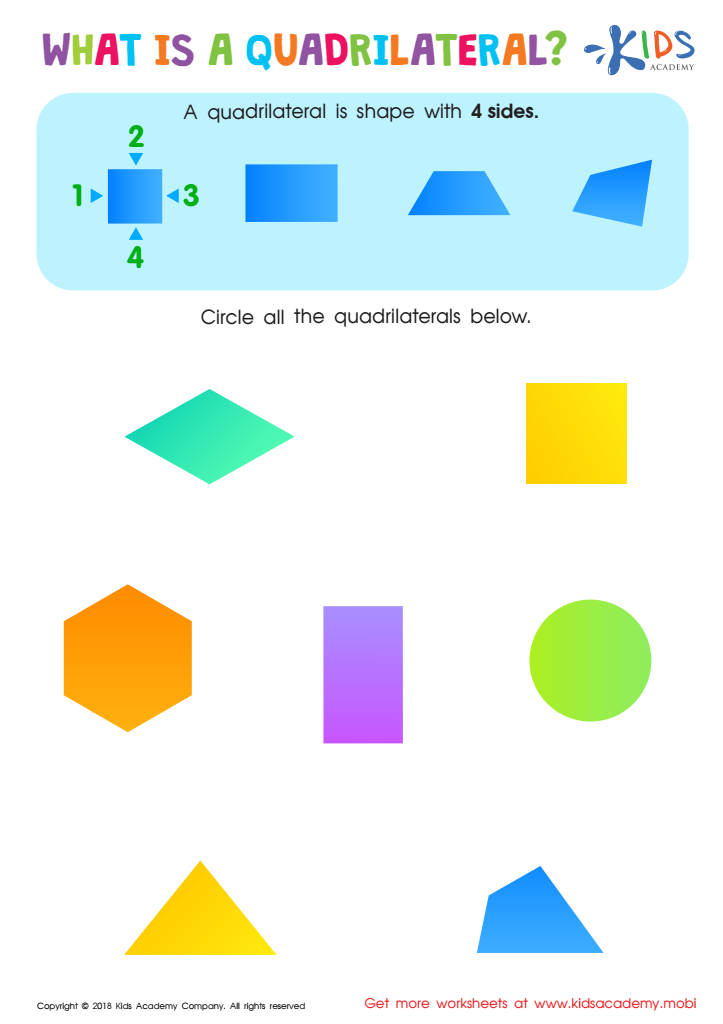

What Is a Quadrilateral? Worksheet
Does your kid know what a quadrilateral is? If not, this worksheet can help teach them. Explain that a quadrilateral is a shape with four sides and give examples, like a square or a rectangle. Then ask them to circle the quadrilaterals in the pictures. If they already know what a quadrilateral is, this task might be too easy.
What Is a Quadrilateral? Worksheet
Worksheet
 Assign to the classroom
Assign to the classroom

.jpg)
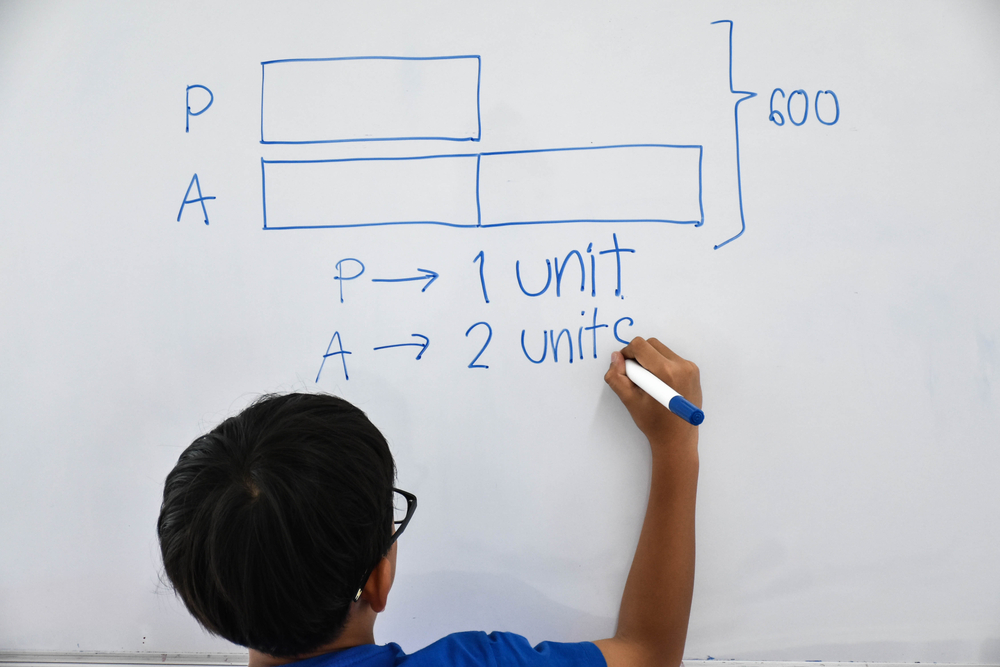
.jpg)