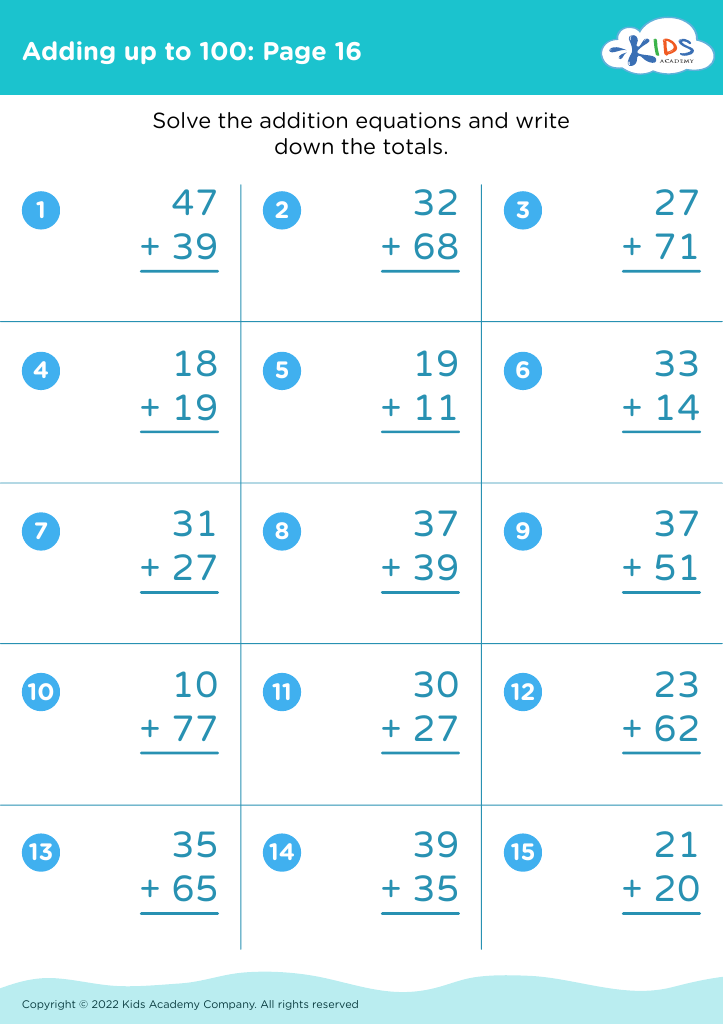
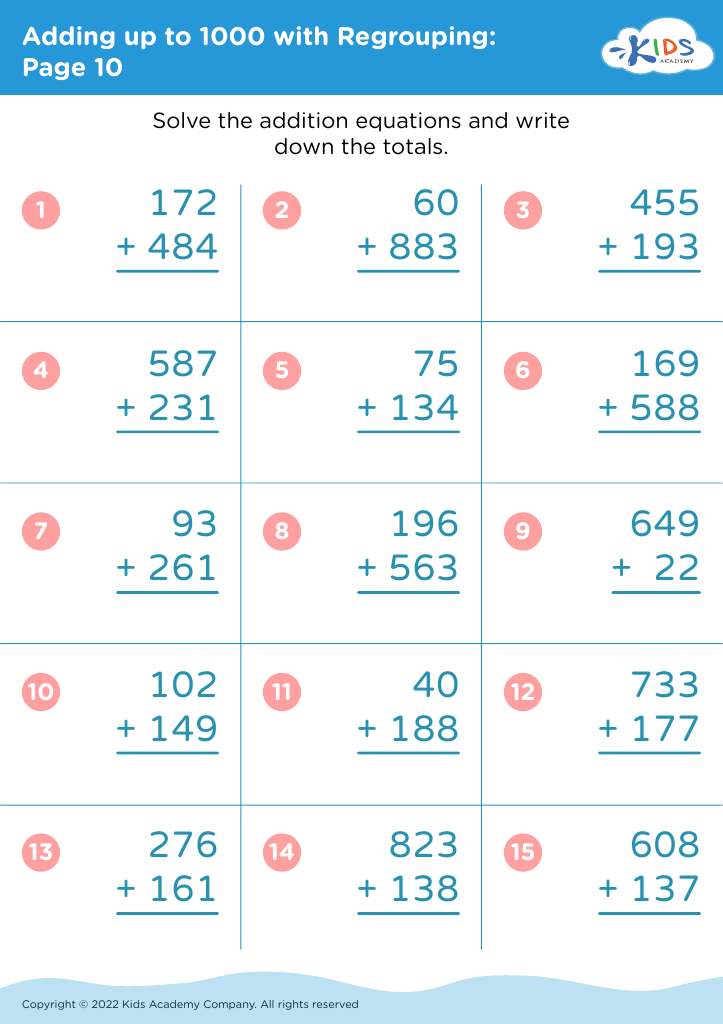
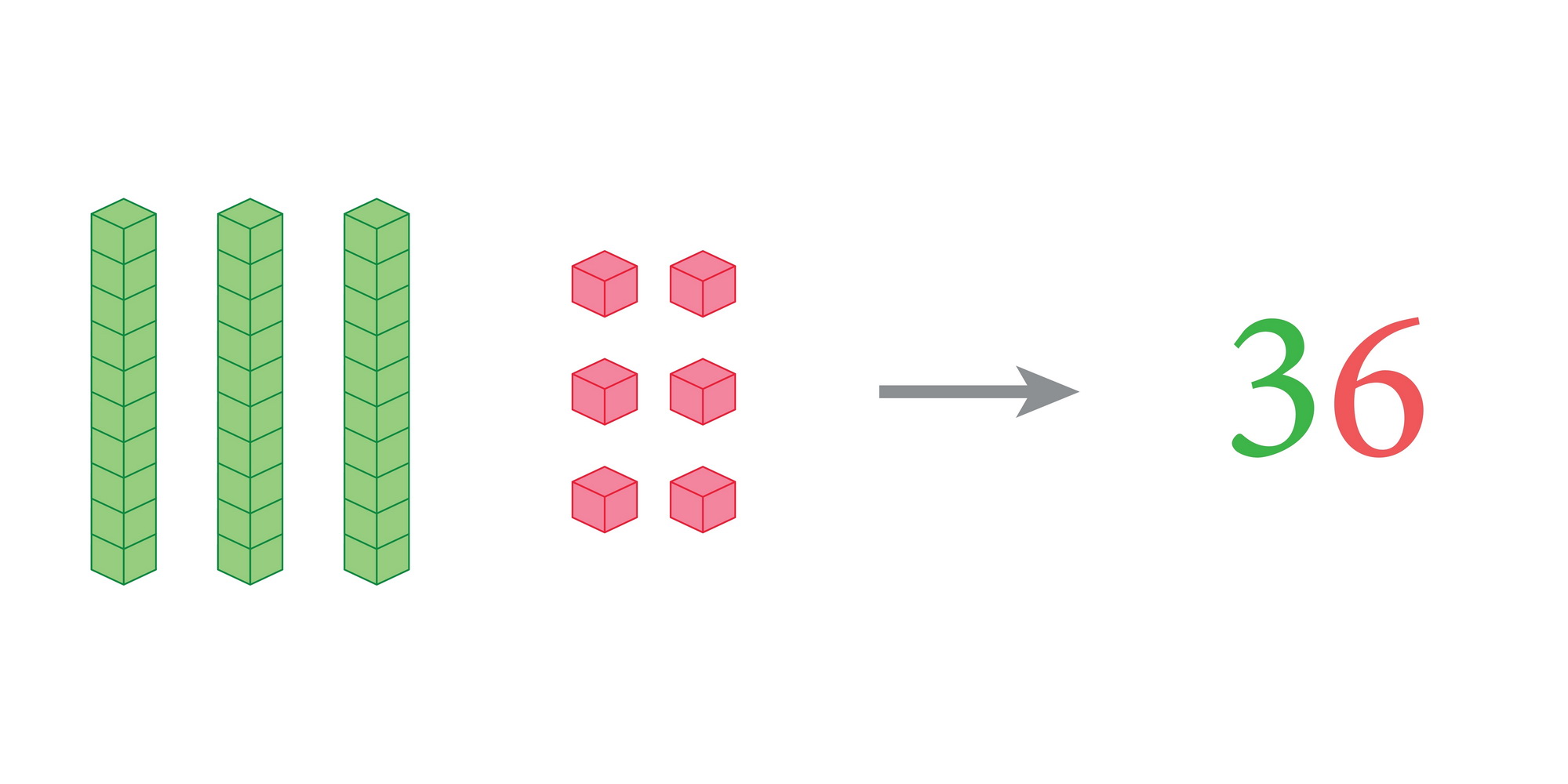
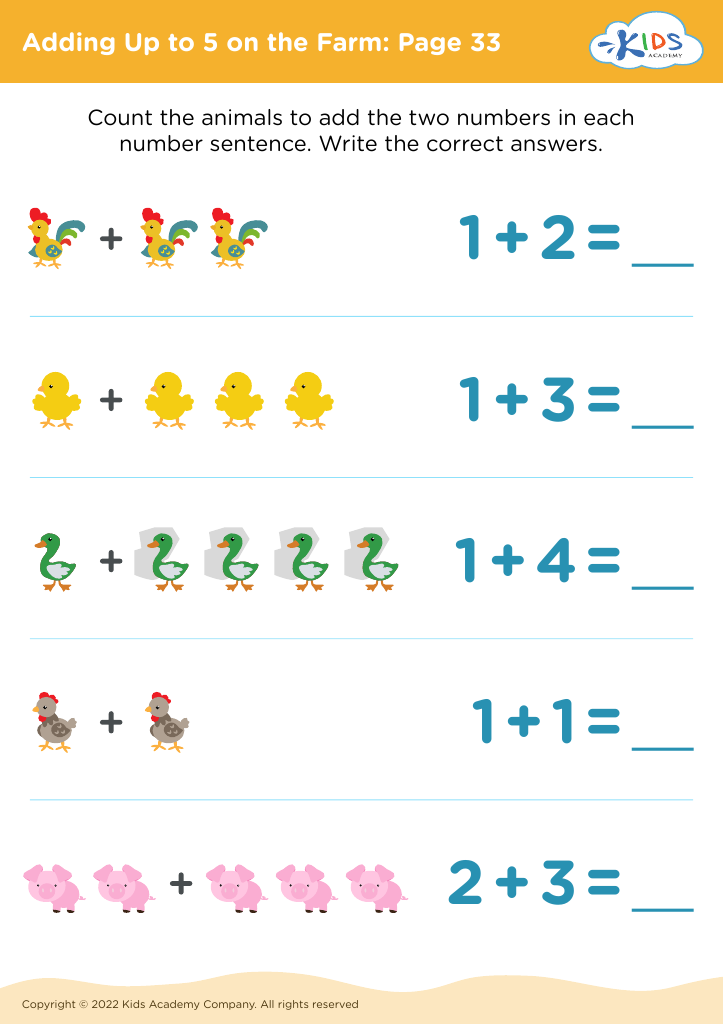Developing fine motor skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 4-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock the potential of your child's learning journey with our specially designed fine motor skills addition and subtraction worksheets for ages 4-8! These engaging worksheets not only help young learners master essential math concepts but also enhance their fine motor skills through fun activities. By incorporating tracing, cutting, and coloring tasks, children can improve their hand-eye coordination and dexterity while reinforcing their understanding of addition and subtraction. Perfect for at-home learning or classroom use, our worksheets provide a well-rounded approach to math education. Give your child the tools they need to succeed and watch their confidence soar!
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of fine motor skills alongside foundational math skills like addition and subtraction for children aged 4-8 because these areas are deeply interconnected and essential for academic success. Fine motor skills—refined movements of hands and fingers—are crucial for various tasks, from writing to manipulating objects, which are foundational for engaging with math materials. Children with well-developed fine motor skills can handle manipulatives, such as counters or blocks, which help them visualize and better understand mathematical concepts.
Furthermore, fostering fine motor skills during this critical age enhances concentration, hand-eye coordination, and problem-solving abilities—traits that spill over into other academic spaces. Children can better control writing instruments, leading to improved handwriting and mathematical notation, which reduces frustration and encourages a positive attitude toward learning.
Moreover, integrating fine motor tasks with math activities, such as using tweezers to pick up counters while practicing addition and subtraction, makes learning engaging and enjoyable. As children build their motor skills and computational understanding together, they cultivate confidence in their abilities, promoting a lifelong love for learning and mathematics. Ultimately, caring about these developmental areas equips children with essential tools for success now and in the future.