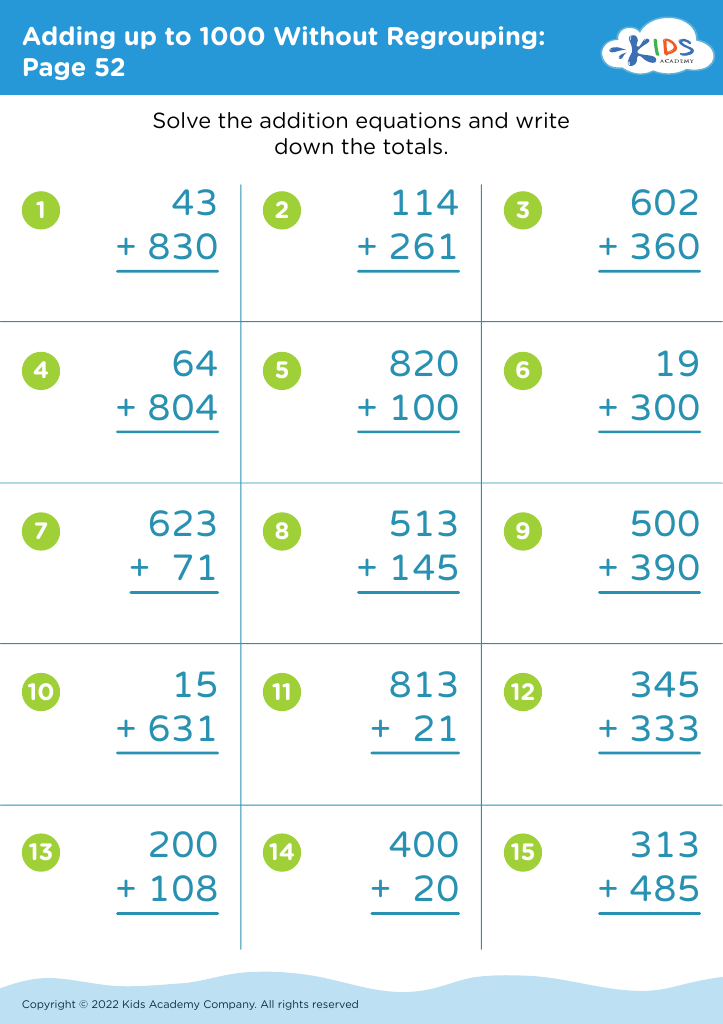
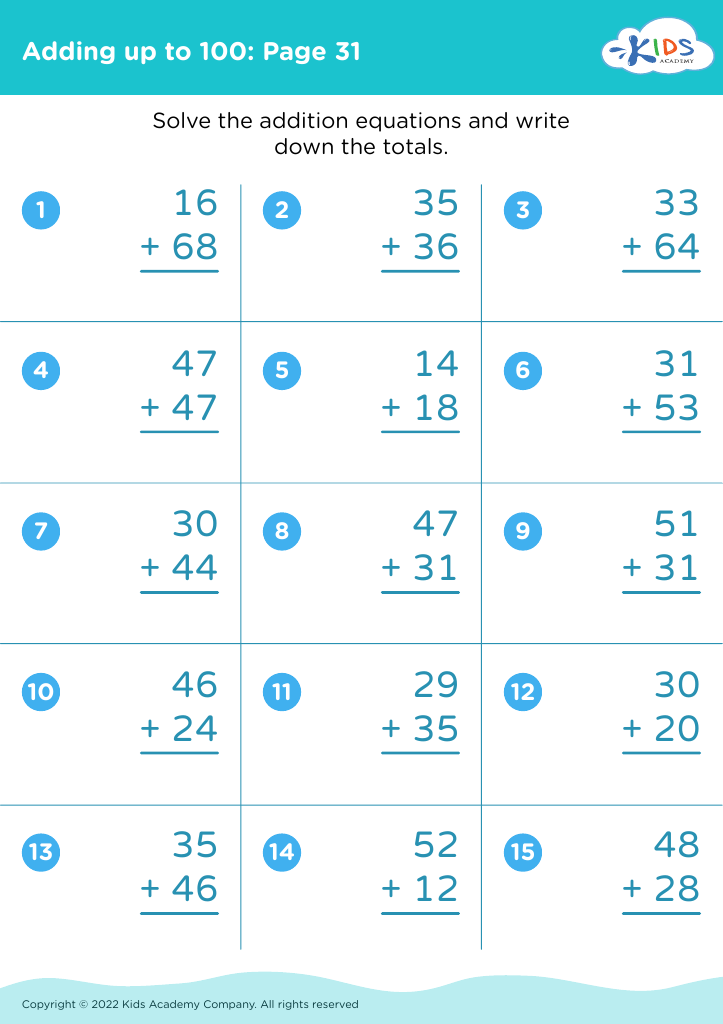
Improve fine motor skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover fun and educational "Improve Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets" designed for kids ages 4-9. These engaging worksheets from Kids Academy expertly combine math practice with activities that enhance fine motor skills. Each sheet supports children as they solve addition problems while working on tracing, cutting, and more, aiding in manual dexterity and pencil grip. Perfect for at-home practice or classroom settings, our worksheets help young learners build foundational math skills and strong fine motor abilities simultaneously. Equip your children with the tools to succeed today with our expertly crafted addition worksheets!
Fine motor skills refer to the coordination of small muscles in movements—usually involving the fingers and hands—in harmony with the eyes. These skills are critical as children ages 4-9 engage in writing, drawing, dressing, and other daily tasks. Teachers and parents have legitimate reasons to focus on improving these skills.
For starters, fine motor skills are foundational for academic success, such as holding pencils, cutting paper, and typing on keyboards. Improving these skills enables children to better engage in classroom activities and complete assignments efficiently and neatly.
Enhanced fine motor abilities also support cognitive development, such as problem-solving and planning activities. They pave the way for a child's brain to process tasks that require focus and coordination, inevitably impacting academic achievement positively.
On a personal development level, honing fine motor skills boosts children’s confidence and independence. When kids can tie their own shoelaces or button their coats, they feel more self-reliant and capable.
Finally, practice in these skills encourages patience and perseverance. Activities like threading beads or assembling puzzles teach children to focus and follow through, qualities valuable throughout life.
In sum, prioritizing the improvement of fine motor skills from a young age lays a crucial groundwork for academic, cognitive, personal, and emotional development.