Observation skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Observation Skills Addition Worksheets" for ages 4-9 help young learners enhance their math capabilities while boosting their attention to detail. These engaging worksheets combine fun addition exercises with observation challenges to sharpen essential skills. Children practice addition within engaging contexts, identifying patterns, and spotting differences to solve problems. Tailored to suit varying difficulty levels, these worksheets support cognitive development and foster a love for learning. Ideal for classroom or home use, they ensure foundational math skills are strengthened through enjoyable, hands-on activities. Watch your child’s skills grow with every completed worksheet!
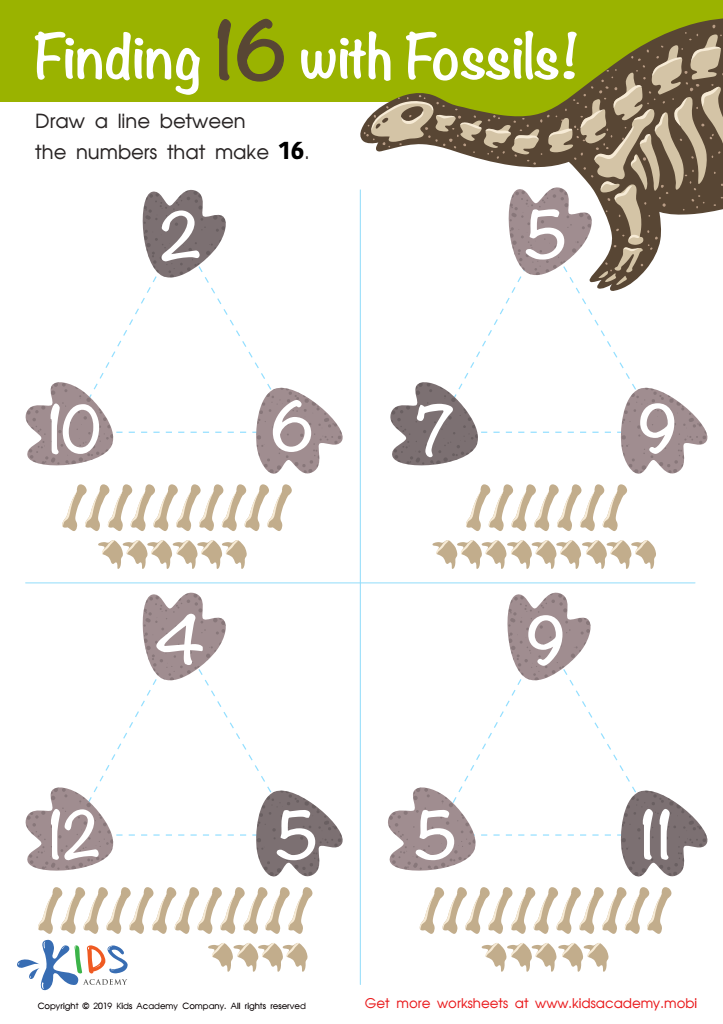

Finding 16 With Fossils Worksheet
Observation skills are fundamental building blocks for a child's cognitive and intellectual development, particularly for those aged 4-9. These skills aid children in accurately making sense of the world around them. For parents and teachers, fostering observation skills can have multiple beneficial impacts on a child's learning journey.
First, enhanced observation skills improve critical thinking and analytical abilities. Children become better at differentiating shapes, colors, sizes, and patterns, which directly supports their ability to solve problems more effectively. For example, recognizing the difference between similar letters and numbers can improve reading and math skills.
Second, good observation promotes curiosity and engagement. Children who are encouraged to observe their surroundings are naturally more inquisitive, asking questions and forming connections, which leads to a deeper understanding of new concepts.
Furthermore, observation skills directly support social development by helping children understand non-verbal cues and social contexts, key for forming healthy relationships with peers and adults.
Lastly, strong observation skills enhance learning retention. When kids observe keenly, they tend to remember details better, aiding in academic success and lifelong learning aptitude.
For these reasons, integrating activities that promote observation—such as nature walks, mindfulness practices, or visual puzzles—should be a priority both at home and in educational settings. By sharpening these skills early, we lay a strong foundation for advanced learning and personal growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students