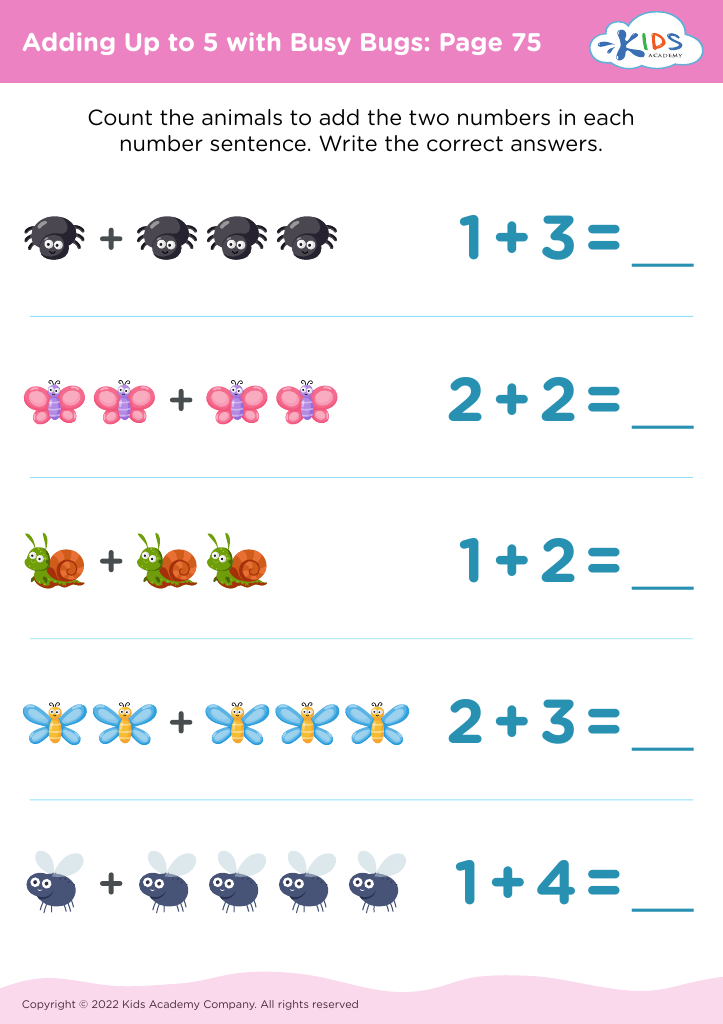
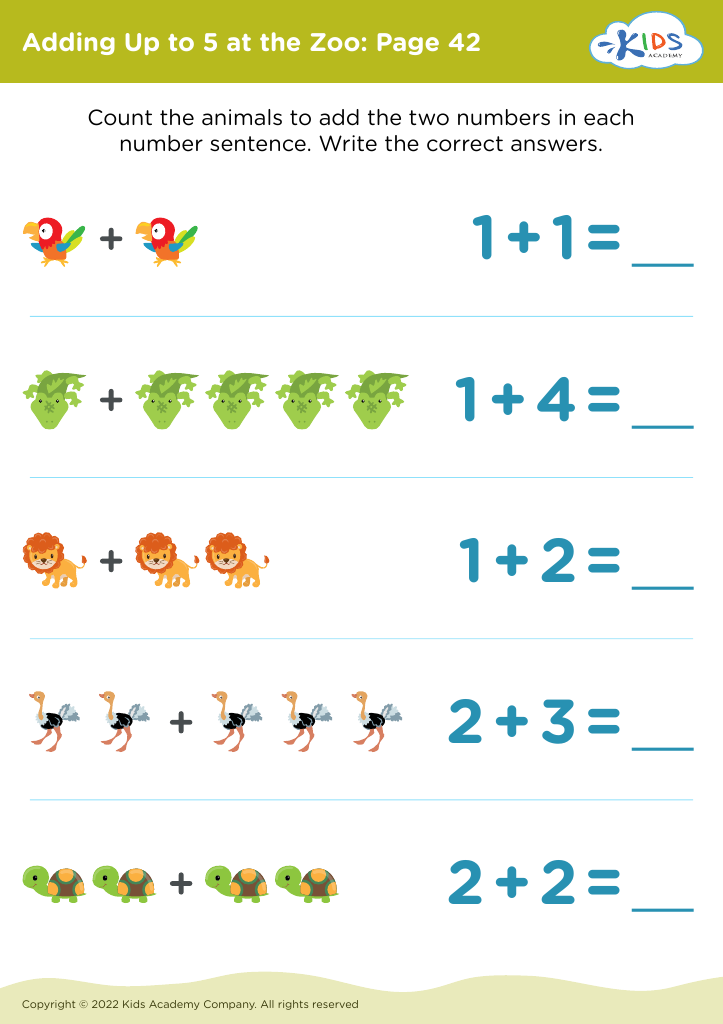Fine motor skills (writing) Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for 4-Year-Olds - Page 2
33 filtered results
-
From - To
Parents and teachers play a crucial role in the early development of a child's fine motor skills as well as their basic mathematical abilities, specifically in writing, addition, and subtraction. For 4-year-olds, these skills lay the foundation for future academic success and everyday function. Fine motor skills, such as writing, help in developing hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Early improvement in these areas ensures that children can efficiently perform tasks like buttoning a shirt or tying shoelaces, thereby fostering independence and self-esteem.
Learning addition and subtraction at this age is equally important because it introduces children to the basics of numeracy, enabling them to understand and apply mathematical concepts as they grow. During early childhood, the brain is highly adaptable and receptive to new information. By nurturing these skills early on, both parents and teachers set the stage for a child's later achievements in more complex math subjects.
Fostering an interactive and supportive environment reinforces these skills in a fun and engaging manner, making learning enjoyable. This, in turn, can encourage a lifelong love of learning, higher cognitive skills, and mathematical acumen. Ignoring these core skills in early development could lead to struggles in academic and everyday tasks down the line.