Fine Motor Skills Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 4
83 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter F Tracing Page


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet

Letter F Coloring Sheet
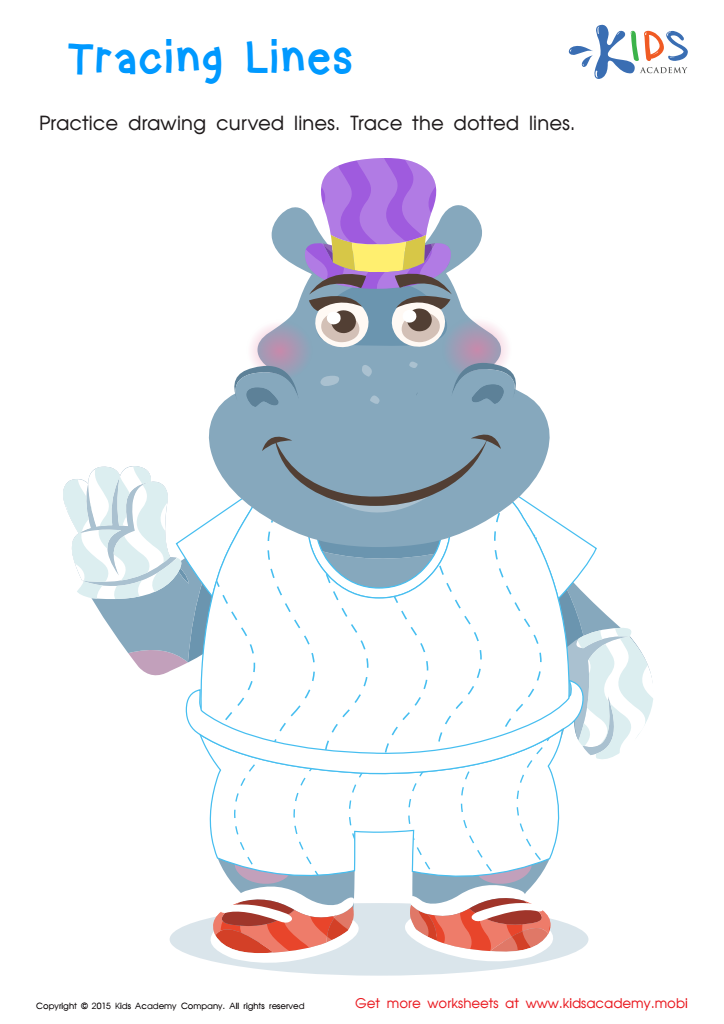


Tracing Lines Worksheet


Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet

Letter T Tracing Page


Letter N Coloring Sheet

1, 2 or 3? Worksheet


Letter D Tracing Page


Uppercase Letters V, W, and X Worksheet


Pen Rhyming Words Worksheet
Fine motor skills are vital for children aged 5-6 as they lay the groundwork for essential daily tasks and learning activities, particularly in grasping the Alphabet. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for writing, drawing, buttoning clothes, and tying shoelaces. At this age, mastering the alphabet is a cornerstone of literacy development, influencing the child’s ability to read and write effectively.
When children engage in activities that target fine motor skills, such as tracing letters or manipulating small objects to form letters, they enhance their hand-eye coordination and control, making future tasks less cumbersome and more natural. This foundation supports cognitive development by improving concentration and proprioceptive skills, or the body's ability to sense movement within joints and joint position.
Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills development tied to alphabet learning as early intervention helps identify any potential difficulties. Supportive, engaging practice can prevent frustration and foster a positive learning environment. Furthermore, as children succeed in manipulating and writing letters, their confidence blooms, positively affecting their overall motivation and academic performance.
In unexplored ways, these early experiences with the alphabet integrate tactile and visual learning, making letter recognition and memory more robust. Essentially, children's success with fine motor skills and alphabet familiarity sets a domino effect of academic benefits that will resonate throughout their educational journey.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students













