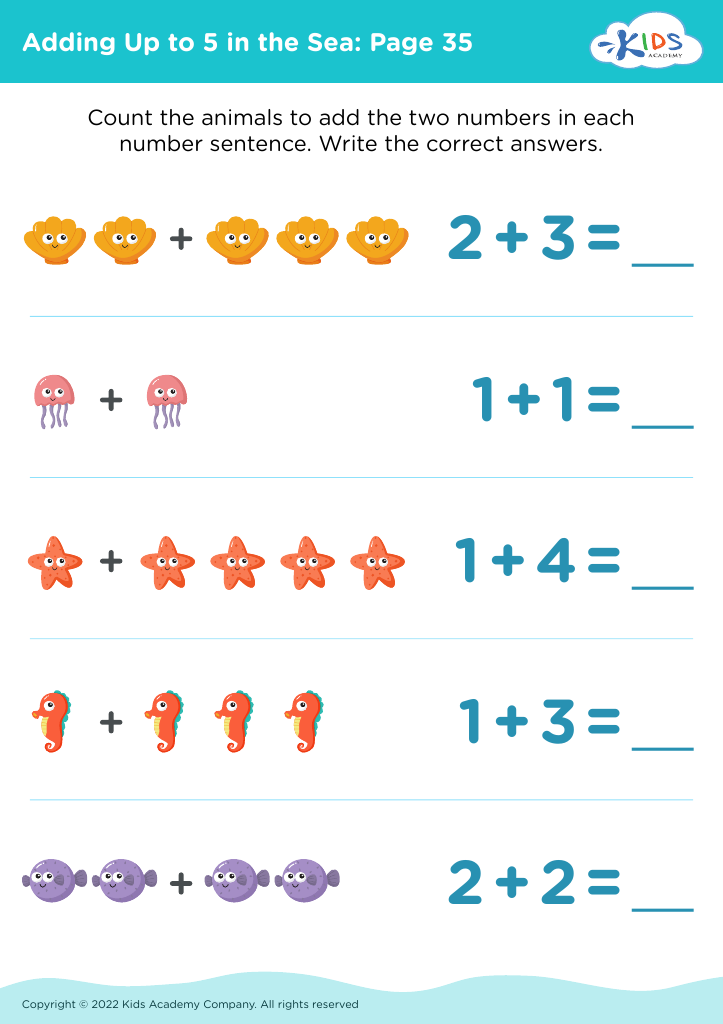
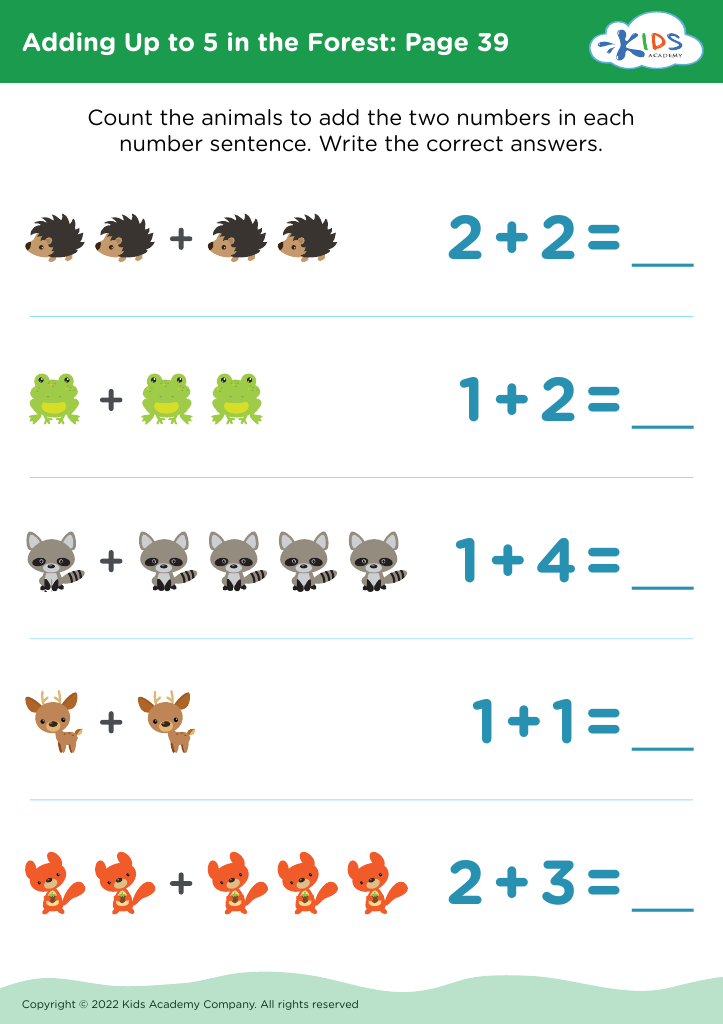Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 2
47 filtered results
-
From - To
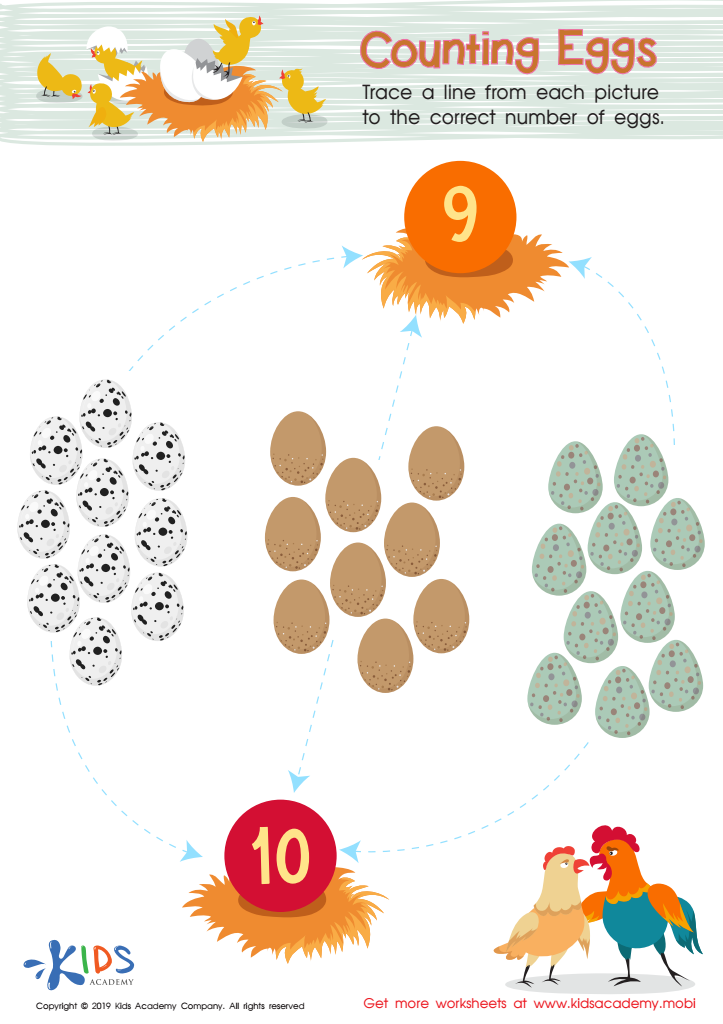

Counting Eggs Worksheet

6 Parrots Worksheet

Rapunzel Addition Maze Worksheet


Math Matching Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet

Line up the Tigers Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet


Math Matching Pairs Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for young children as they lay the groundwork for various developmental areas, particularly in learning addition and subtraction. For children aged 5-6, fine motor skills involve the ability to use small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for manipulating tools, writing, and engaging in mathematical activities.
When children develop fine motor skills, they enhance their ability to connect mathematical concepts to physical objects, such as counting with blocks or beads. This hands-on interaction makes abstract ideas like addition and subtraction more concrete, facilitating deeper understanding. Moreover, children who are adept in fine motor tasks can perform mathematical operations with greater ease and confidence, allowing them to focus on problem-solving rather than struggling with physical manipulation.
Fine motor skills also play a pivotal role in building concentration and cognitive readiness. As children practice tasks that refine these skills, their ability to concentrate, follow instructions, and engage in critical thinking improves. Teachers and parents should prioritize these skills in educational activities and home practices, as nurturing them creates a solid foundation for a child's academic success and lifelong learning. Ultimately, investing time and resources in developing fine motor skills is a vital step toward enhancing children's overall learning experience.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students