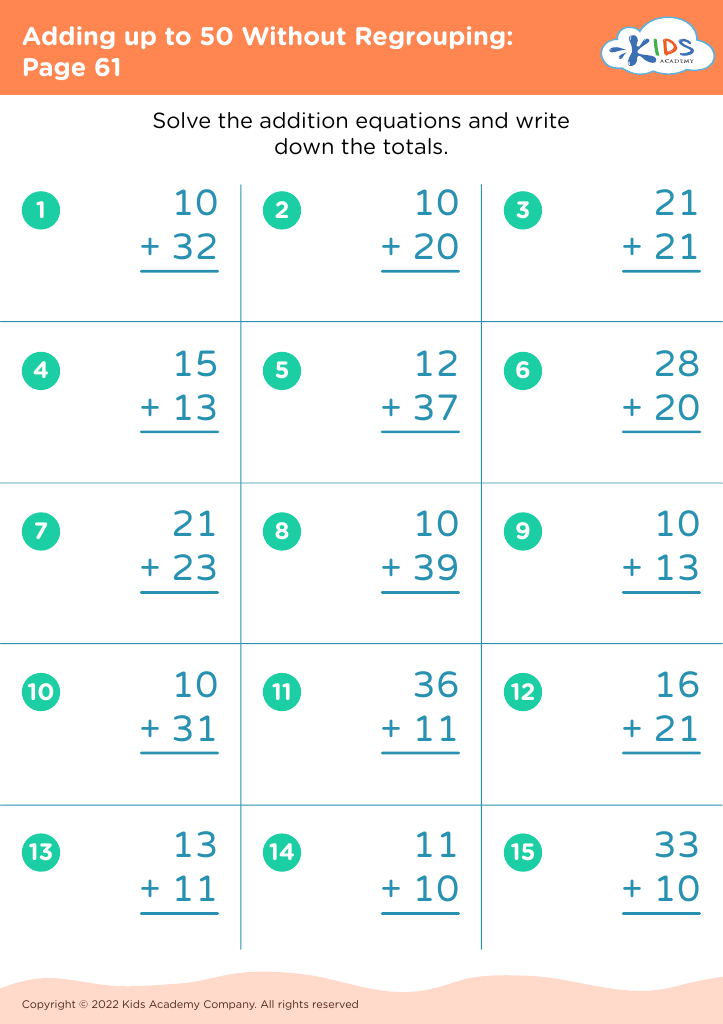
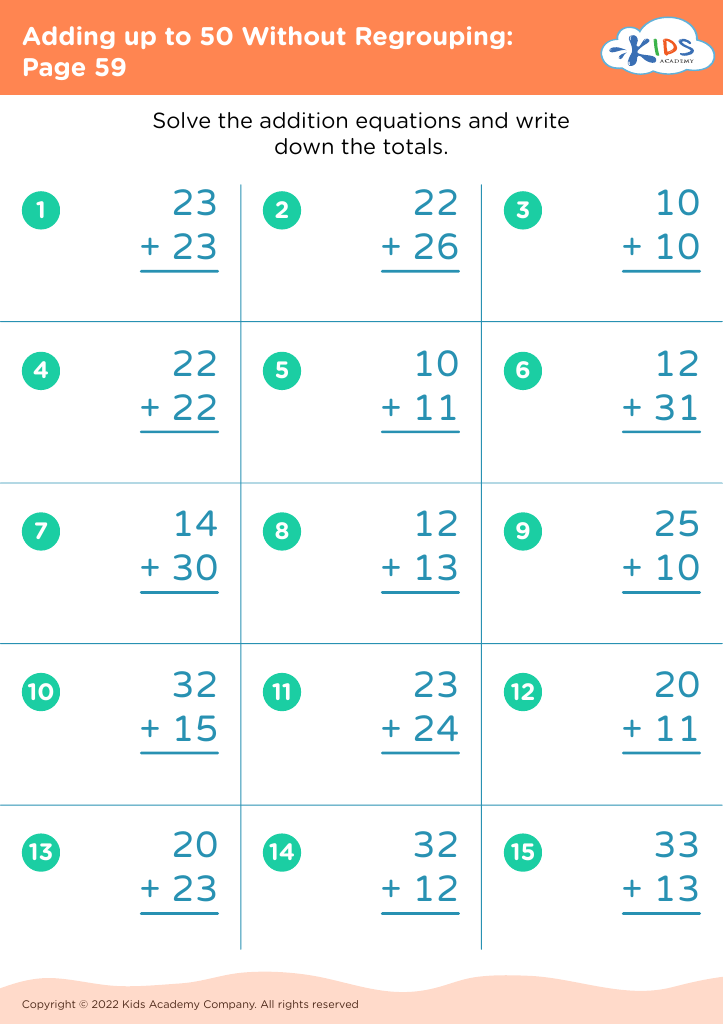
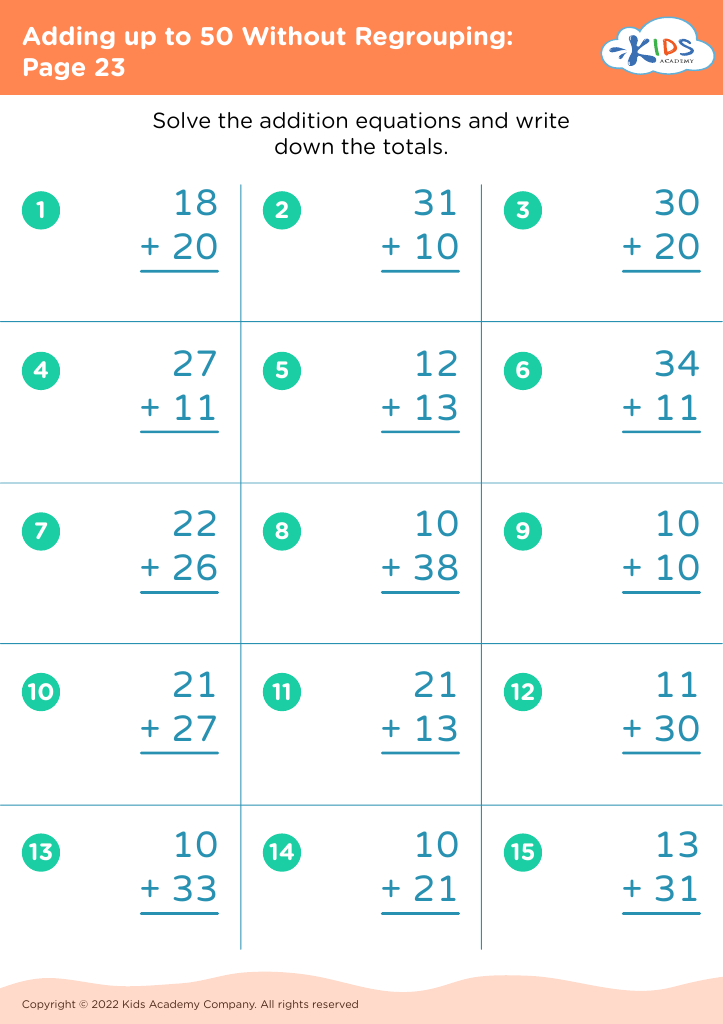
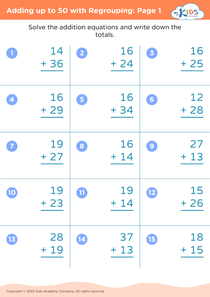
Basic addition practice Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 5-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's math skills with our "Basic Addition Practice: Adding Up to 50 Without Regrouping" worksheets, designed for children ages 5-7. These engaging resources help young learners master essential addition concepts without the complexity of regrouping. Each worksheet features colorful illustrations and easy-to-follow problems that encourage confidence and critical thinking in arithmetic. Perfect for homework, classroom reinforcement, or independent practice, these sheets aim to build a strong foundation in math. Watch your child thrive as they count, add, and enhance their problem-solving abilities while having fun! Start their mathematical journey today!
Basic addition practice for young learners, especially adding up to 50 without regrouping, is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it builds a solid foundation in numeracy skills. At ages 5-7, children are between preschool and early elementary years, which are key stages for developing mathematical understanding. Mastering basic addition not only helps them in future math concepts but also enhances cognitive skills, including problem-solving and critical thinking.
Moreover, reinforcing these skills can significantly boost a child's confidence in math, making them more enthusiastic about learning. Confidence reduces anxiety surrounding math tasks, leading to a more positive attitude towards education in general. Practicing addition in a structured and engaging manner fosters a sense of accomplishment and mastery.
Additionally, understanding basic addition supports essential life skills. Simple math is needed in daily activities like shopping, cooking, or budgeting, thus forming an essential part of a child's education beyond the classroom. Parents and teachers play a vital role in ensuring these skills are developed through practical activities and encouraging environments. Supporting children at this stage equips them with the capabilities they need for academic and real-world success, creating a strong foundation for future learning in mathematics and beyond.