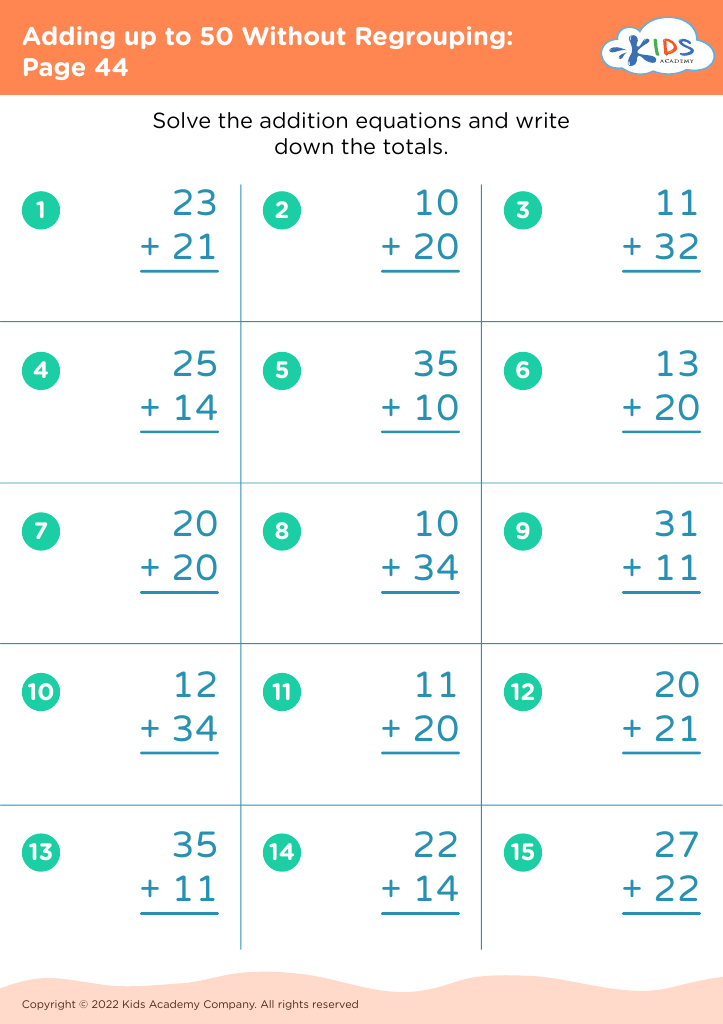
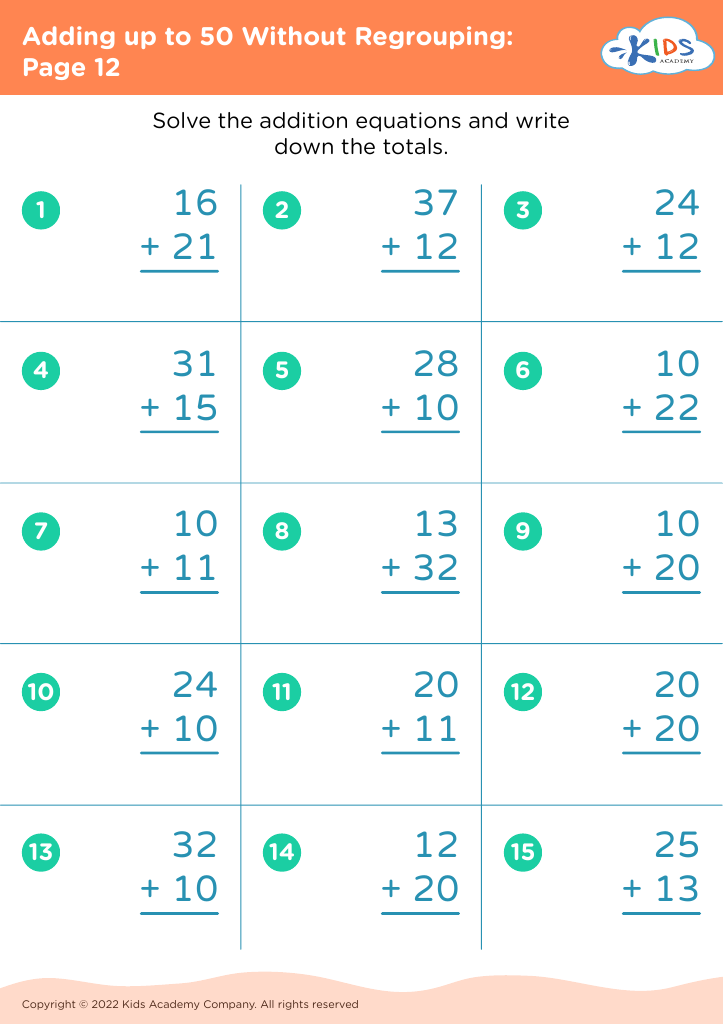
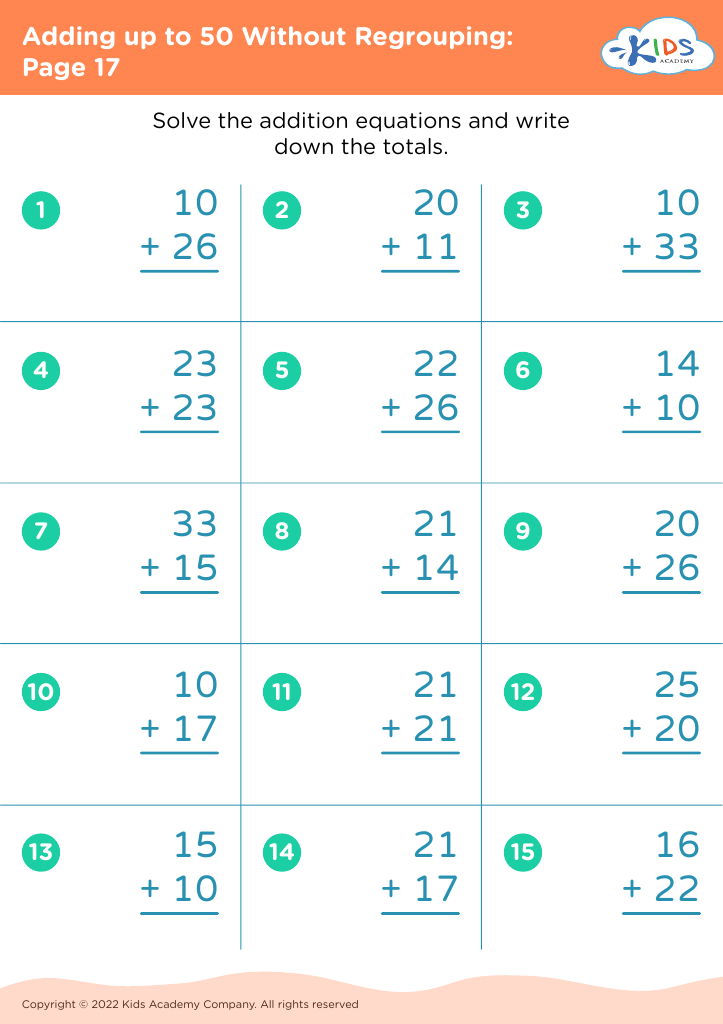
Enhance number recognition Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 5-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Enhance Number Recognition: Adding Up to 50 Without Regrouping Worksheets" are designed specifically for children aged 5-7. These educational resources focus on improving your child's number recognition skills while practicing addition up to 50 without regrouping. With engaging and intuitive exercises, young learners are guided through simple math problems, promoting confidence and proficiency in early arithmetic. Perfect for both classroom and home settings, these worksheets support foundational math education through fun and effective practice. Set your child on the path to a strong understanding of numbers and arithmetic with our expertly crafted worksheets.
Developing number recognition and addition skills up to 50 without regrouping by ages 5-7 is crucial for children's early math proficiency. At this formative age, children are building foundational skills that underpin their future learning. Understanding and recognizing numbers up to 50 ensures that children can confidently grasp larger concepts and engage in everyday activities involving numeracy, like counting money or measuring ingredients for a recipe.
Educators and parents should pay attention to these early skills to foster continuous cognitive development. Fluent number recognition promotes better memory retention, concentration, and logical thinking. Additionally, the ability to add numbers together without regrouping facilitates smoother transitions to more complex arithmetic tasks. It also enhances problem-solving capabilities in a stress-free way, ensuring that learning is an enjoyable experience.
Moreover, proficiency in basic addition fosters a sense of achievement and boosts self-confidence, which is essential for engaging children in further educational pursuits. Early mastery of these skills can reduce future math anxiety by creating a robust mathematical foundation. Overall, nurturing these abilities at an early age sets the stage for academic success and cultivates a positive attitude towards learning mathematics.